Method and device for writing data and redundant array of inexpensive disk
A redundant disk array and data writing technology, applied in the communication field, can solve problems affecting SSD writing performance, random writing performance, low sequential writing performance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
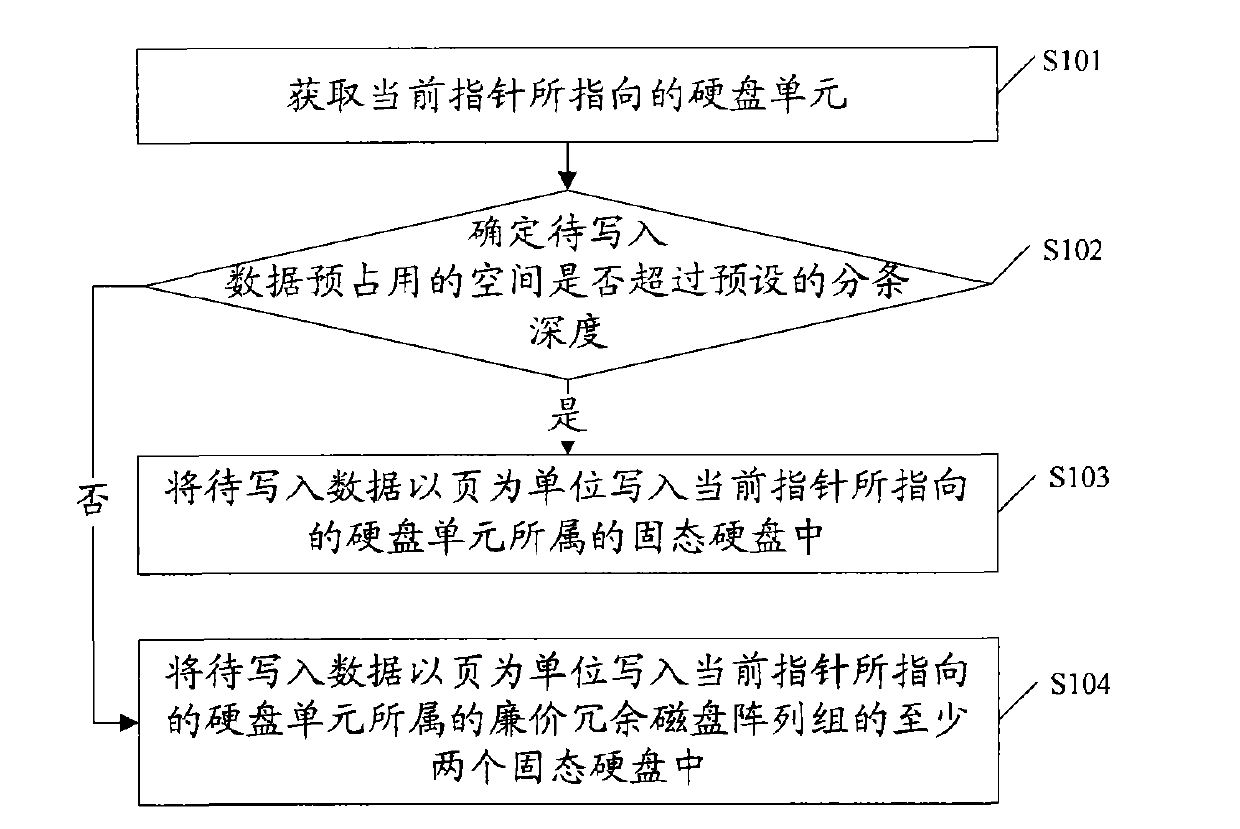
[0034] See figure 1 , Is a flow chart of the method for writing data provided in the first embodiment of the present invention, the method includes:
[0035] S101: Obtain the DU (hard disk unit) pointed to by the current pointer.
[0036] For example, if there is SSD0-SSDX in the system (where X is an integer greater than or equal to 1), the SSDs are equally divided according to the DU of the preset size (such as 4MB), and each SSD in the constructed RAID group (such as RAID0) is maintained An idle DU queue is used to receive the data to be written; at the same time, a current pointer is also maintained to point to which DU to which the data to be written should be sent to at the current moment. If RAID0 includes 4 SSDs, 4 DUs from different SSDs are used to receive data to be written at each moment. For example, 4 DUs from different SSDs include: DU0, DU4, DU8 and DU12, and the current pointer points to DU0, then Get the DU0 pointed to by the current pointer.
[0037] S102: Determ...
Embodiment 2
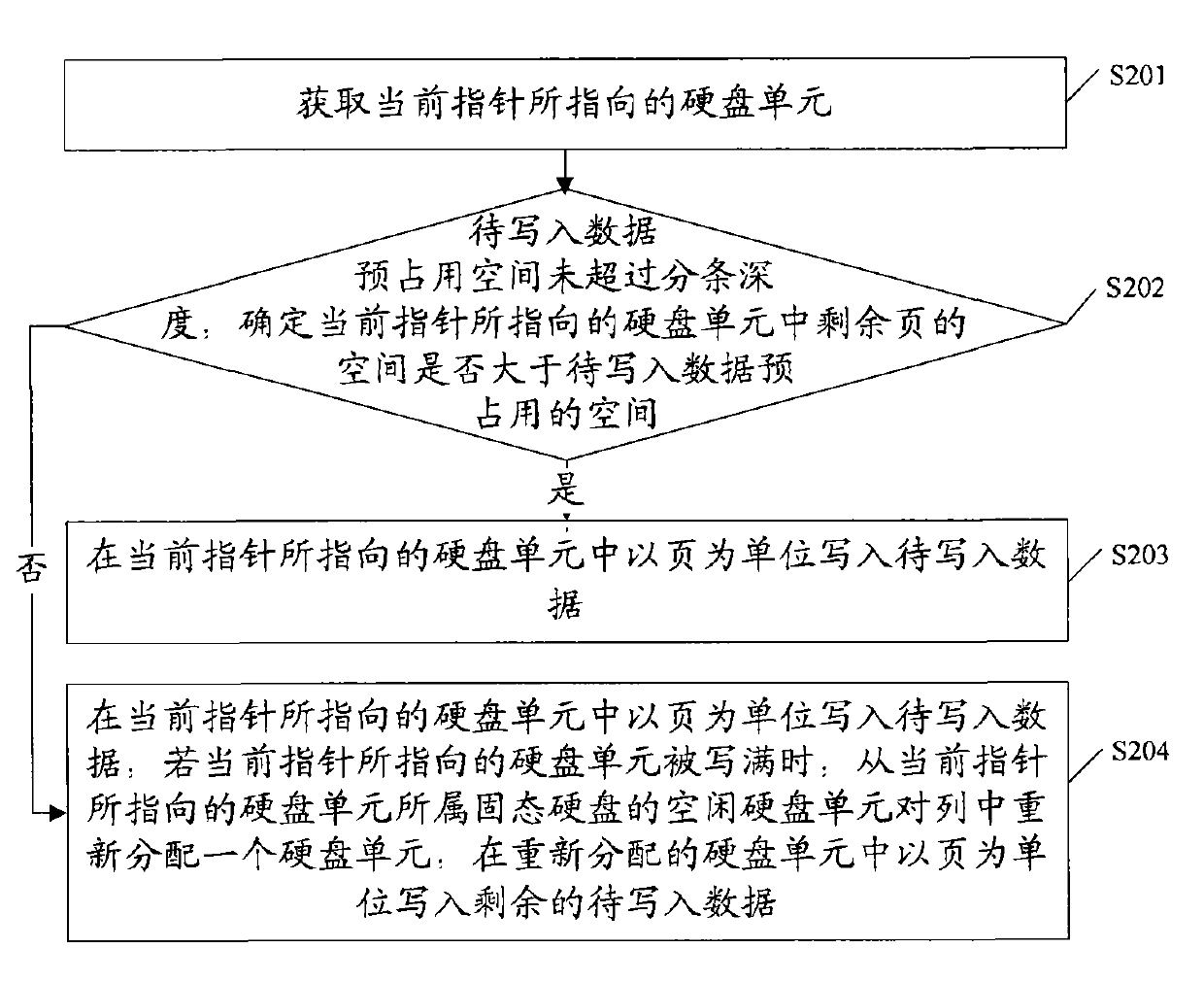
[0049] See figure 2 , Is a flowchart of the method for writing data provided in the second embodiment of the present invention, and the method includes:
[0050] S201: Obtain the DU pointed to by the current pointer.
[0051] For example, the DUs to be received include: DU0, DU4, DU8, and DU12. If the current pointer points to DU0, the DU0 pointed to by the current pointer is obtained.
[0052] S202: If the pre-occupied space of the data to be written does not exceed the preset striping depth (for example, 16K), determine whether the space of the remaining pages in the DU pointed to by the current pointer is greater than the pre-occupied space of the data to be written, and if so, execute S203 ; Otherwise, execute S204.
[0053] S203: Write the data to be written in the DU pointed to by the current pointer in units of pages.
[0054] For example, the DUs to receive data include: DU0, DU4, DU8, and DU12, the current pointer points to DU0, the data to be written does not exceed the pres...
Embodiment 3
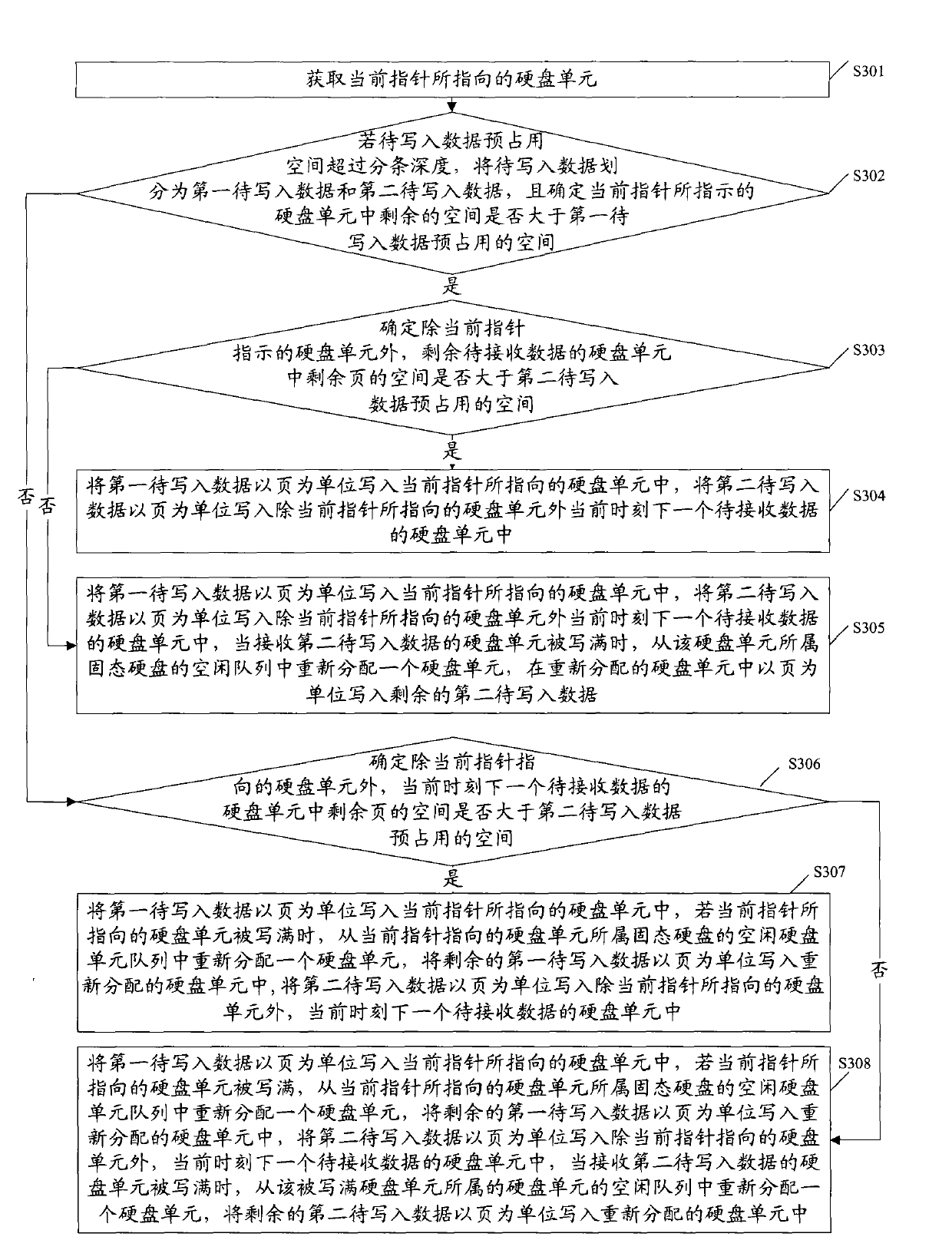
[0064] See image 3 , Is a flowchart of the method for writing data provided in the third embodiment of the present invention, and the method includes:
[0065] S301: Obtain the DU pointed to by the current pointer.
[0066] For example, the DUs to be received include: DU0, DU4, DU8, and DU12. If the current pointer points to DU0, the DU0 pointed to by the current pointer is obtained.
[0067] S302: If the pre-occupied space of the data to be written exceeds the preset striping depth (such as 16K), divide the data to be written into the first data to be written and the second data to be written, and determine what the current pointer points to Whether the space of the remaining pages in the DU is greater than the space pre-occupied by the first data to be written, if yes, execute S303; otherwise, execute S306.
[0068] S303: When the space of the remaining page in the DU pointed to by the current pointer is greater than the space pre-occupied by the first data to be written, it is fur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com