P53 fusion protein and application thereof
A fusion protein and protein technology, applied in the P53 fusion protein and application fields, can solve problems such as not yet produced
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
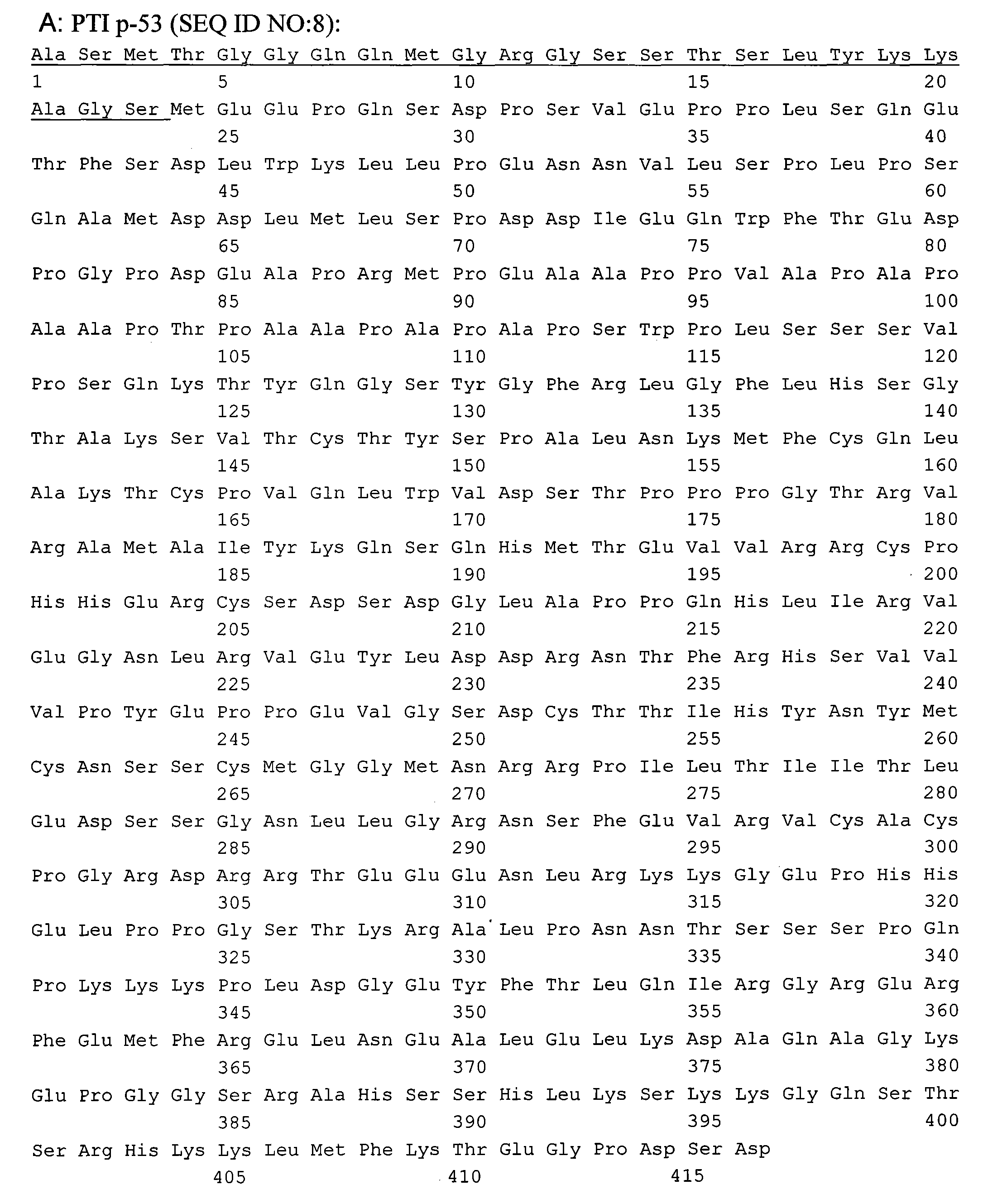
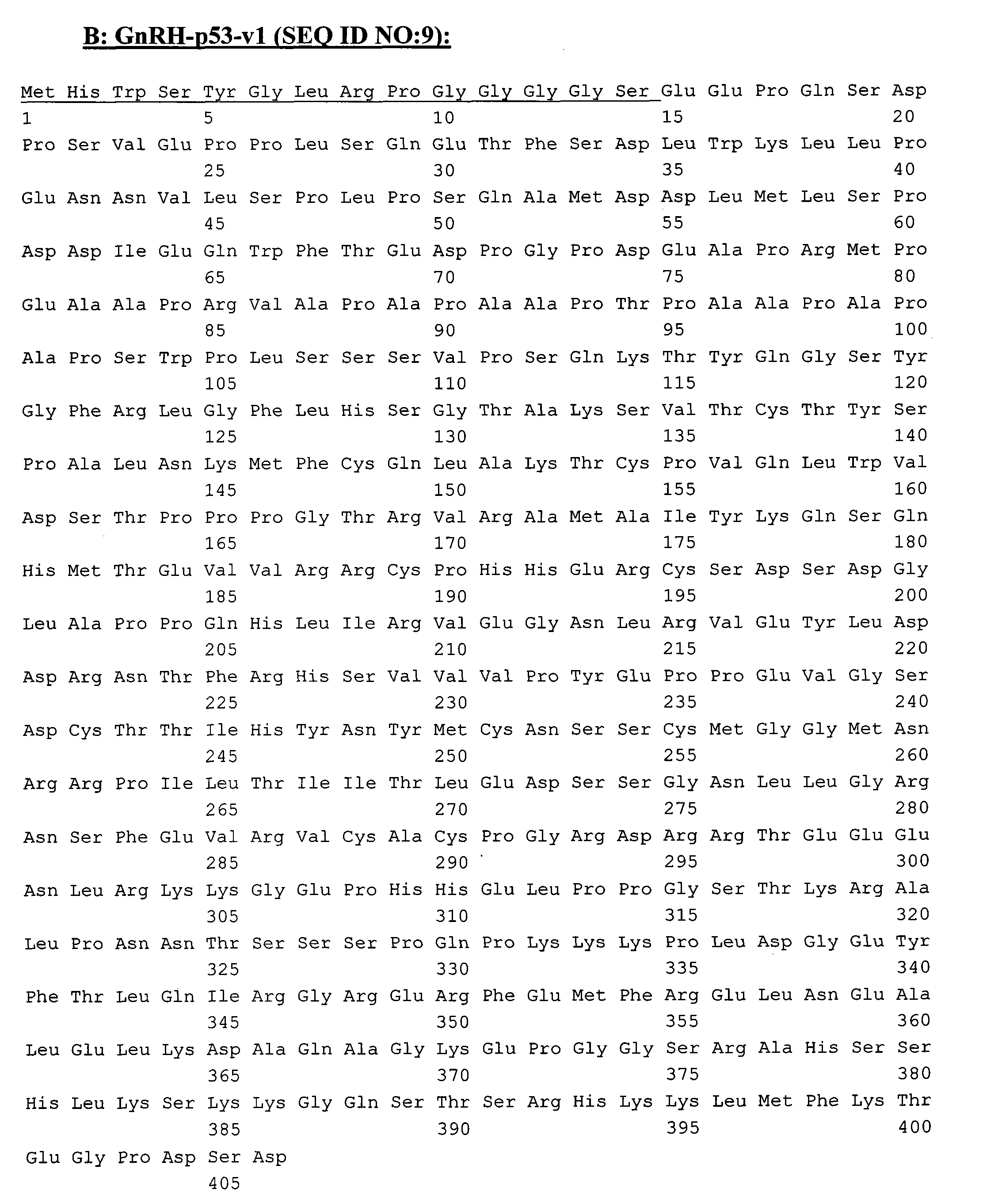
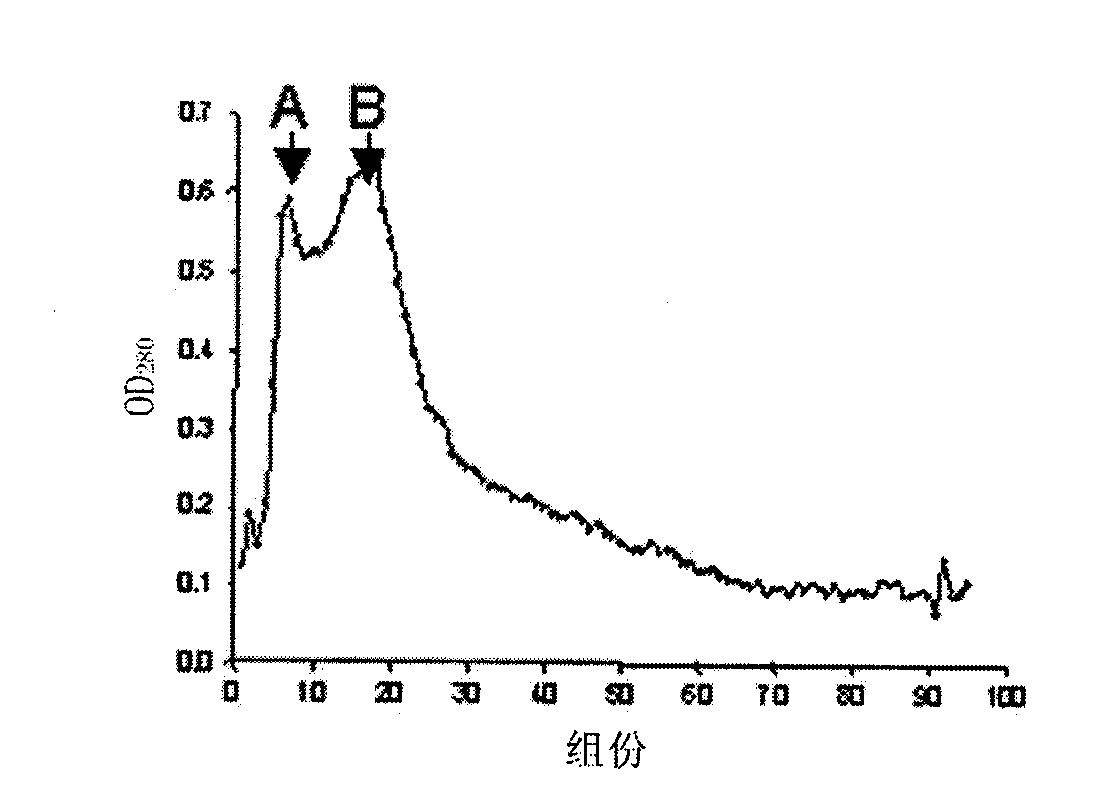
[0119] Example 1: Production of tetrameric p53 fusion proteins in Escherichia coli and identification of the produced p53 fusion proteins Certainly
[0120] Candidate protein drugs based on p53 should be wild-type to reduce immunogenicity, tetramer to improve drug efficacy, and need to be able to enter the targeted cancer cells. Prior to this invention, all attempts to produce wild-type, full-length, tetrameric p53 without chemical cross-modification were unsuccessful. As far as protein therapeutics are concerned, there are several reasons for isolating stable p53 tetramers. First, the active form of p53 is a tetramer. The p53 monomer binds DNA in a cooperative manner, and the binding force of p53 to DNA increases up to 100-fold after forming a tetramer (McLure, KG and Lee, PW 1998 EMBO J 17: 3342-3350). Second, tetramerization is also important for protein-protein interactions, and tetramerization regulates the binding of some proteins to p53. The tetramer structure al...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com