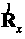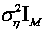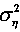Covariance matching-based multi-antenna spectrum sensing method
A spectrum sensing and covariance technology, applied in the field of cognitive radio, can solve problems such as performance degradation, and achieve the effect of convenient threshold determination, good detection performance, and overcoming noise uncertainty
Inactive Publication Date: 2011-03-16
SOUTHEAST UNIV
View PDF1 Cites 21 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Technical problem: The classic energy detection method only uses the energy information of the received signal to judge the presence or absence of the primary user signal. When there is correlation in signal sampling or noise uncertainty occurs, its performance will drop significantly
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment Construction
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
The invention discloses a covariance matching-based multi-antenna spectrum sensing method, which specifically comprises a semi-blind detection method and a complete-blind detection method. In the semi-blind detection method, a new detection amount is constructed by comparing a received-signal sampling covariance matrix with a known noise covariance matrix (herein, the noise covariance refers to noise variance, M refers to the number of receiving antenna, and I[M] refers to a M*M unit matrix); and in the complete-blind detection method, another new detection amount is constructed by the fact that the normalized sampling covariance matrix of a main signal is approximately equal to a diagonal matrix when the main signal does not appear. In the two methods of the invention, because of using correlation as the basis of decision amount of construction, the statistic characteristics of a master user signal and a transmission channel are not required to be known in advance; and especially fora complete-blind detection algorithm based on covariance matching, the spectrum sensing can effectively be implemented under the condition that the noise variance is unknown.
Description
technical field The invention relates to two implementation methods adapted to idle frequency band perception in cognitive radio, and belongs to cognitive radio technology in wireless communication. Background technique Cognitive radio technology is considered to be a technology that can effectively alleviate the contradiction between the increasing spectrum demand and limited spectrum resources. Cognitive radio requires that the communication between secondary users (unauthorized users) cannot interfere with the normal communication of primary users (authorized users). To avoid such interference, cognitive radio systems usually require secondary users to periodically detect the activities of primary users using spectrum sensing technology. Only when it is detected that the signal of the primary user does not appear, the secondary user can use the spectrum resources vacated by the primary user. Therefore, the effective implementation of spectrum sensing is the premise and ...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): H04B17/00H04B1/707H04B17/382
Inventor 曹秀英杨喜彭盛亮朱鹏程
Owner SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com