Selective mirroring method
A selective and mirroring technology, applied in the field of selective mirroring, can solve problems such as wasting time and cost, and users cannot reconfigure, so as to achieve the effect of improving data stability and user convenience
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] Now, selective mirroring according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
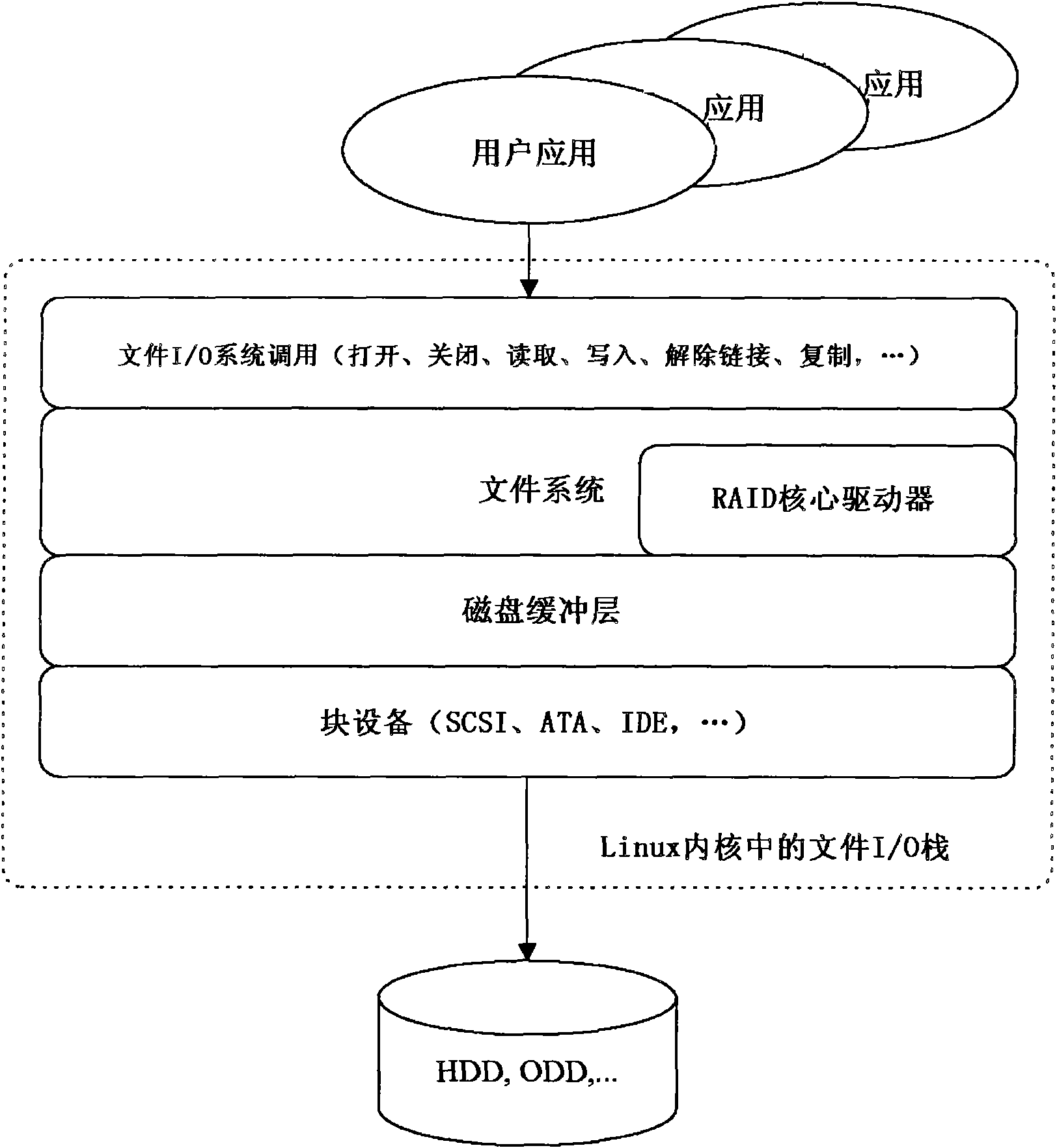
[0036] The selective mirroring method according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention is applied with a directory or a file, including a folder, as a basic unit, can be applied to multiple directories or multiple files, and maintains one or more copies of a single original.
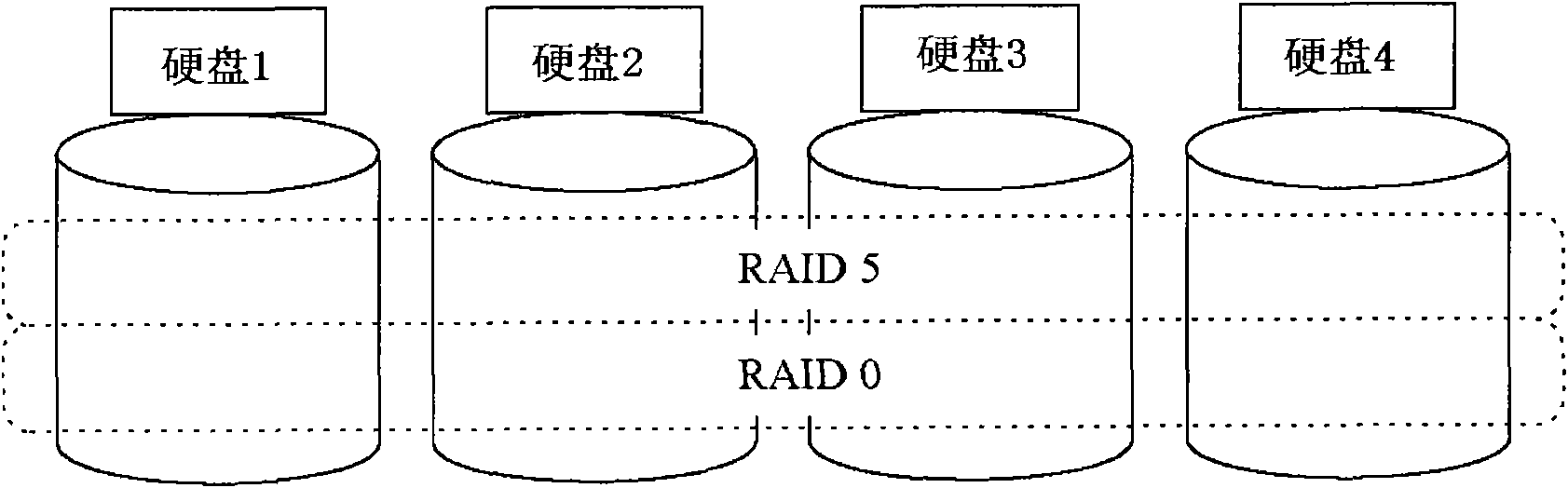
[0037] In an embodiment of the present invention, a read / write function similar to a Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks (RAID) function can be performed, and a mirror function for redundantly storing one or more Prevents data loss when devices such as storage (NAS) systems are damaged.
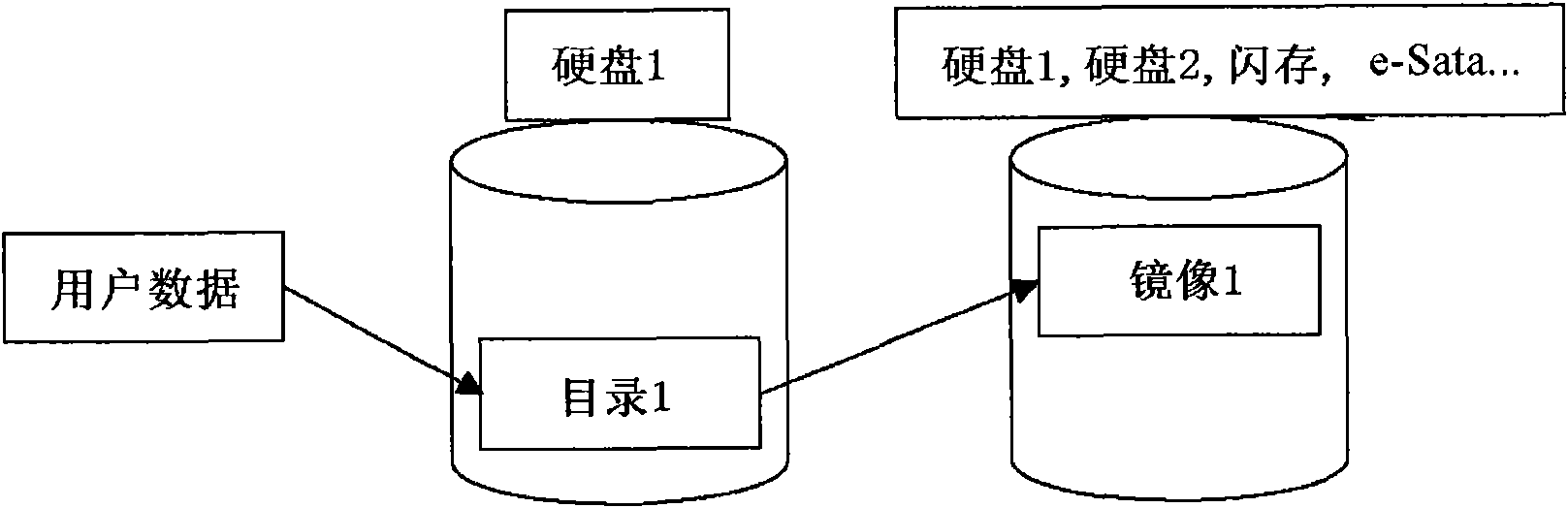
[0038] For example, if figure 2 As shown, when user data is recorded in the first directory 1 (or directory 1) of the first hard disk (or HDD1), in one or more other storage media (such as HDD1, HDD2, flash memory, e-Sata network, etc. e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com