Method for underground in-situ extraction of hydrocarbon compound in oil shale
A technology for extracting oil and compounds, which is applied in the direction of earthwork drilling, wellbore/well components, and production fluids, etc. It can solve the problems of large heat loss, difficult fluid control, and high energy consumption, so as to improve the utilization rate of heat, Save energy and time, shorten the effect of the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
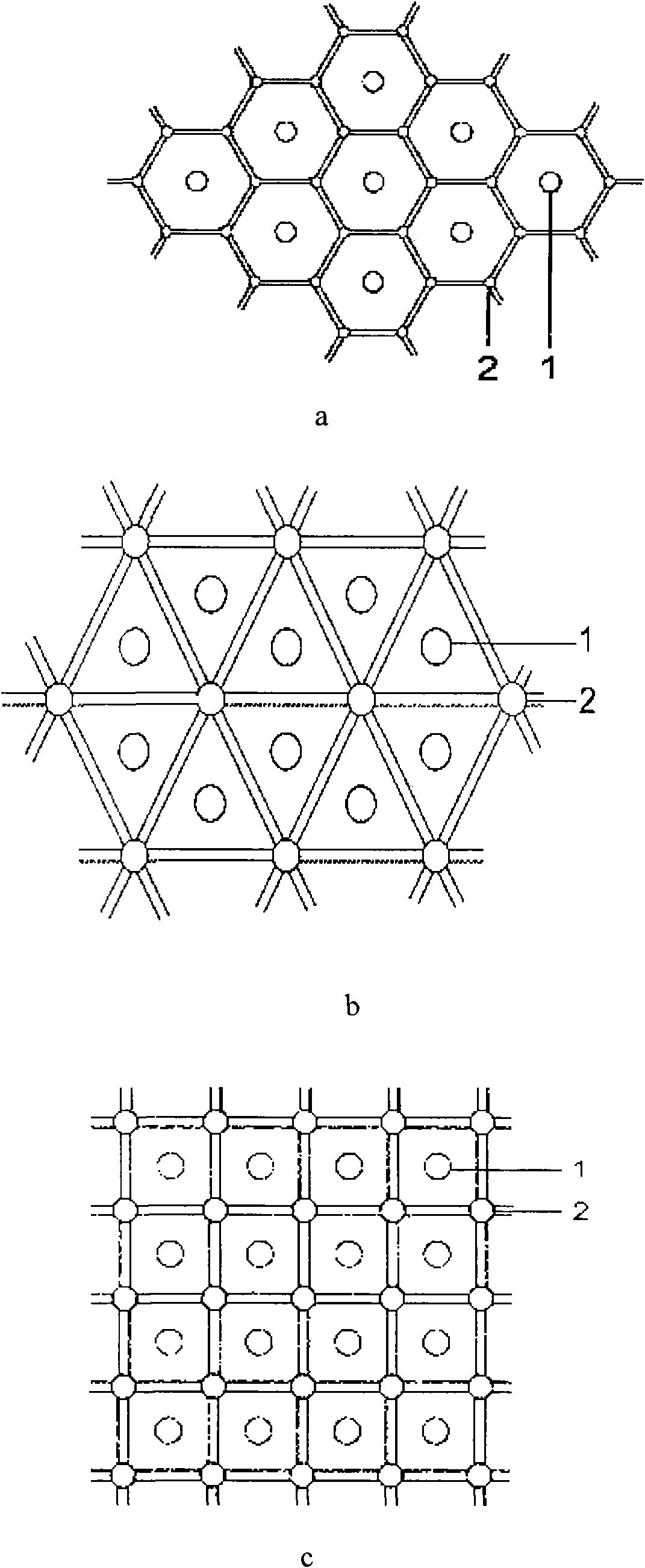
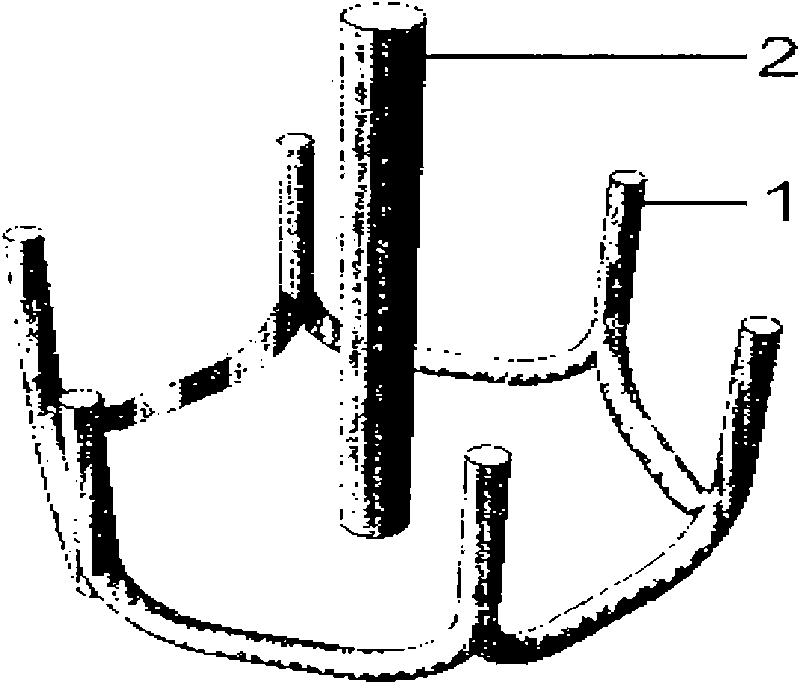
[0045]a. Arrange three working wells 2 and one production well 1 in the delineated working area for extracting hydrocarbons in oil shale. The plane distribution of working wells 2 is triangular. The distance between them is 18m, and the distance between production well 1 and working well 2 is 10.39m;
[0046] b. After the well enters the oil shale deposit, the bottom between the connected working wells is drilled through directional drilling;
[0047] c. The oil shale is deposited downward by directional blasting, producing regular and irregular fissures; the resulting fissures are filled with sand to support the fissures, so as to facilitate the penetration and flow of near-critical water;
[0048] d. Inject water into the working well 2, and stop injecting when the water surface reaches the top plate of the oil shale layer;
[0049] e. Inject nitrogen gas into the working well 2 to make the pressure in the well reach 2MPa, close the working well 2 and the production well 1,...
Embodiment 2
[0054] a. Arrange four working wells 2 and one production well 1 in the delineated working area for extracting hydrocarbons in oil shale. The distance between them is 20m, and the distance between production well 1 and working well 2 is 14.14m;
[0055] b. After the well enters the oil shale deposit, the bottom between the connected working wells is drilled through directional drilling;
[0056] c. The oil shale is deposited downward by directional blasting, producing regular and irregular fissures; the resulting fissures are filled with sand to support the fissures, so as to facilitate the penetration and flow of near-critical water;
[0057] d. Inject water vapor at a temperature of 400°C into the working well 2, and stop the injection when the water surface reaches the roof of the oil shale layer;
[0058] e. Close working well 2 and production well 1, heat to form a microenvironment of 330°C and 9MPa near-critical water in the oil shale layer, and keep the temperature and...
Embodiment 3
[0063] a. Arrange six working wells 2 and one production well 1 in the delineated working area for extracting hydrocarbons in oil shale. The plane distribution of the working wells 2 is hexagonal. The distance from the working well 2 is 19m, and the distance between the production well 1 and the working well 2 is 19m;
[0064] b. After the well enters the oil shale deposit, the bottom between the connected working wells is drilled through directional drilling;
[0065] c. The oil shale is deposited downward by directional blasting, producing regular and irregular fissures; the resulting fissures are filled with sand to support the fissures, so as to facilitate the penetration and flow of near-critical water;
[0066] d. Inject water into the working well 2, and stop injecting when the water surface reaches the top plate of the oil shale layer;
[0067] e. Inject carbon dioxide gas into the working well 2 to make the pressure in the well reach 3MPa, close the working well 2 an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com