Rotor wing helicopter
A technology of rotor helicopters and main rotors, applied in rotorcraft, motor vehicles, jet flaps, etc., can solve the problems of complex main rotor structure, accident-prone, and difficult maintenance, and achieve simple structure, high reliability, and convenient maintenance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
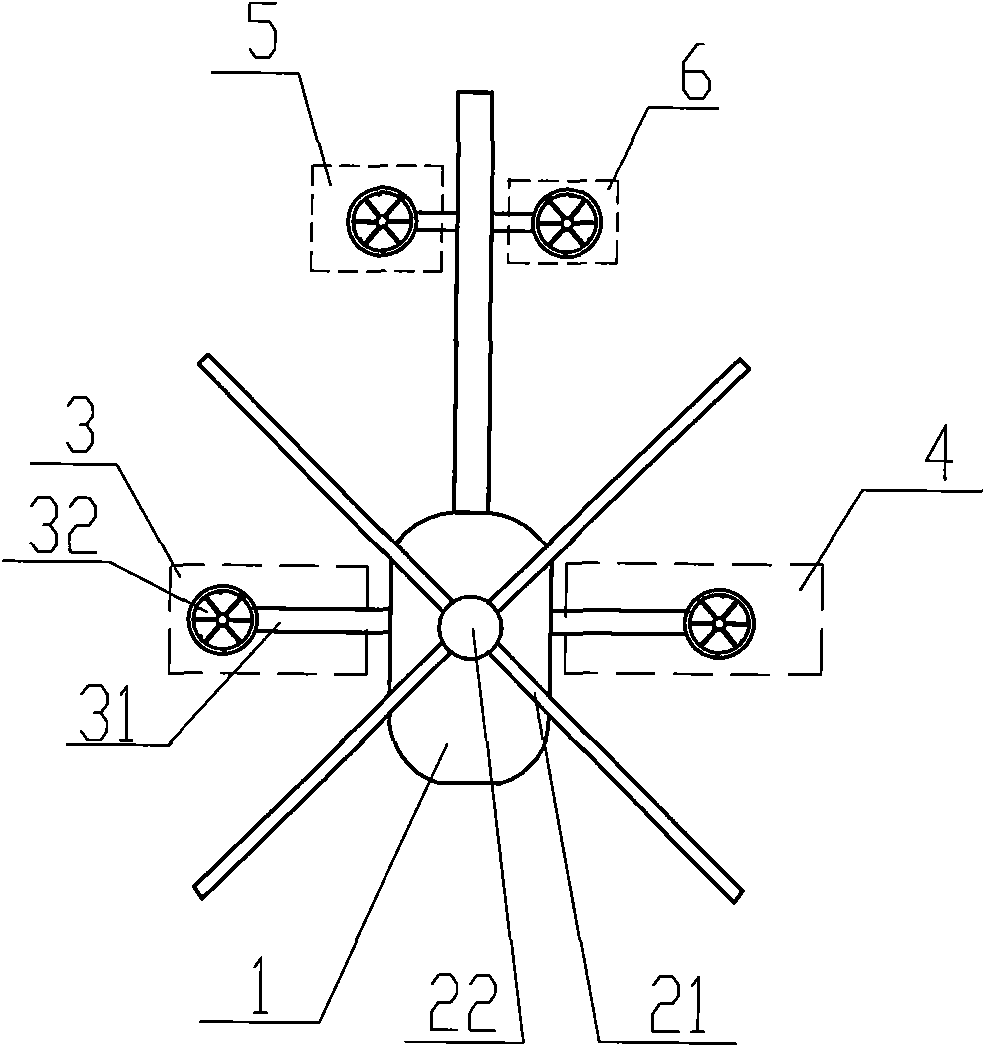
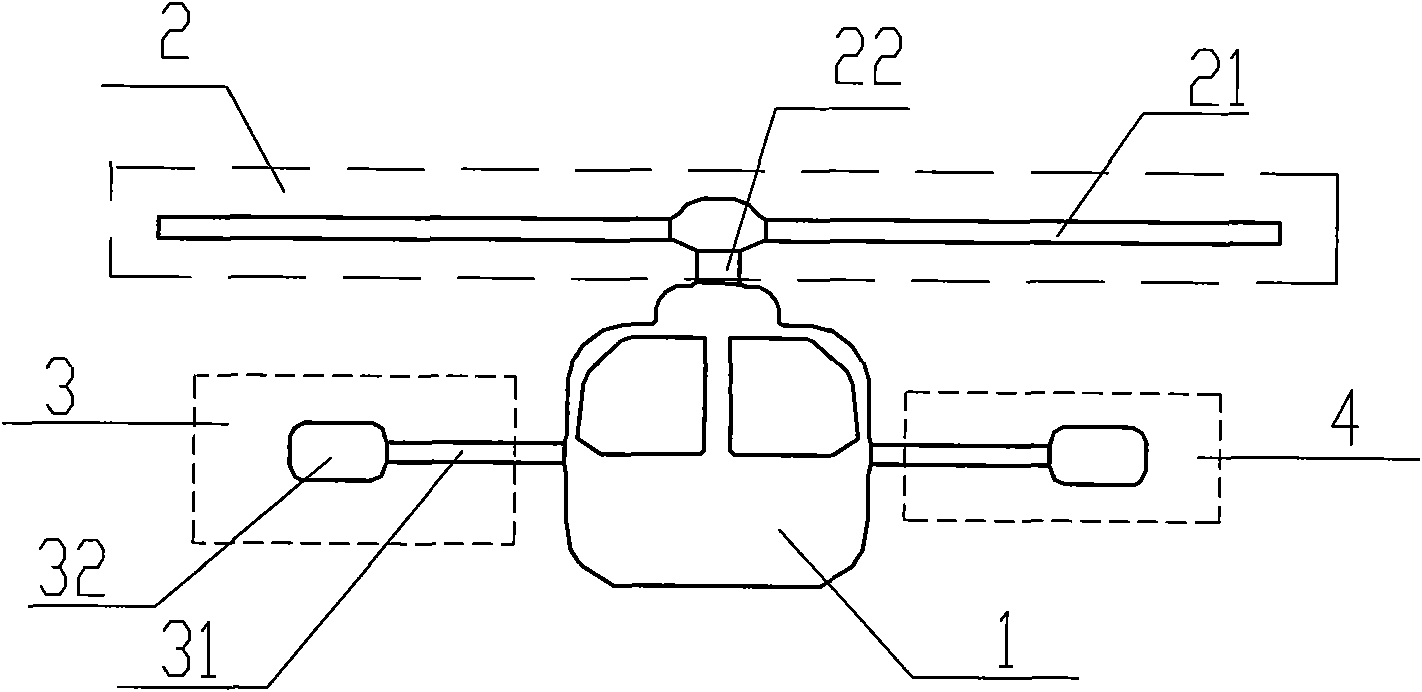
[0014] see figure 1 with figure 2 , a rotor helicopter, including a fuselage 1, a steering control system installed in the fuselage 1, a main engine, a main rotor 2 connected to the main engine through a speed reducer, and a tail rotor. The main rotor 2 provides lift and the power to fly forward. The structure includes a propeller 21 and a transmission shaft 22. The propeller 21 is tilted forward and fixed on the transmission shaft 22. The fixing method can be hinged, seesaw, hingeless or non-hinged. One way in the bearing type is connected, which is the same as the connection way in the prior art. The transmission shaft 22 is connected with the main engine through a speed reducer, the input end of the speed reducer is connected with the main engine to obtain power, and the output end of the speed reducer is connected with the transmission shaft 22 to transmit power to the propeller 21 to make it rotate. The rotor helicopter structure also includes a left-tilt control mecha...
Embodiment 2
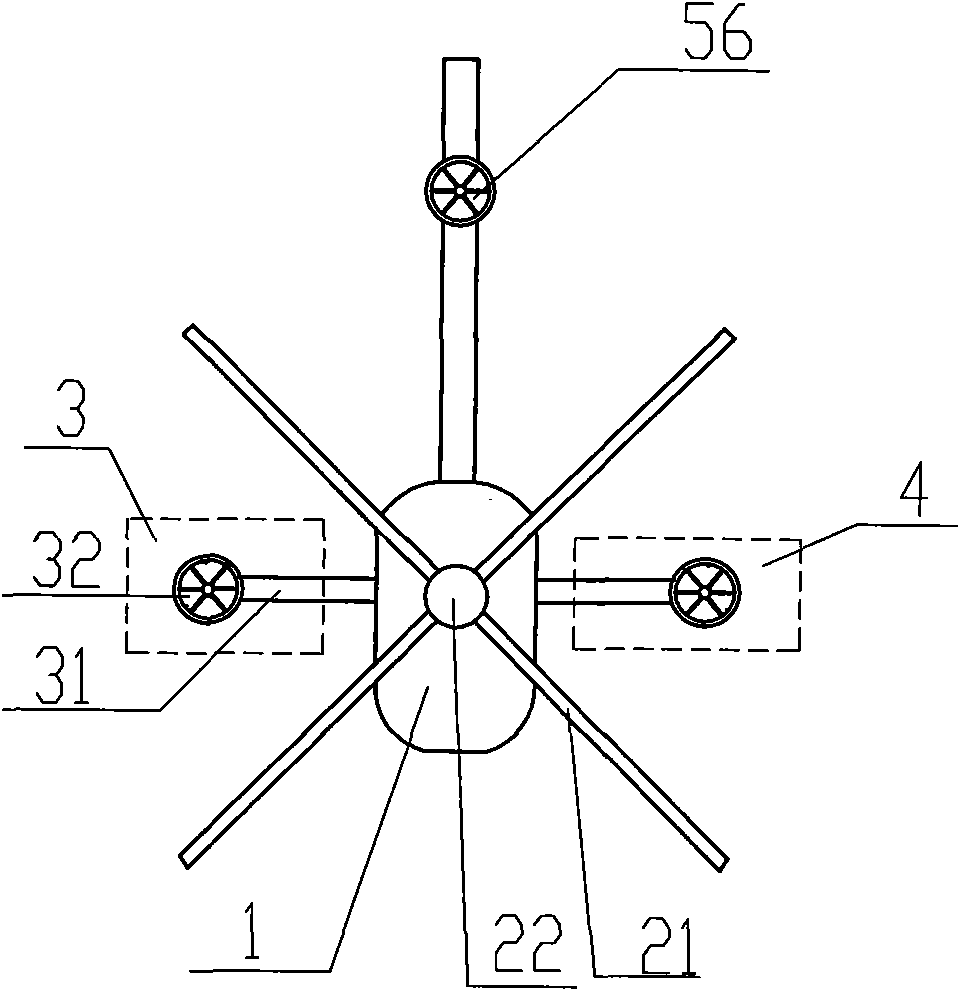
[0018] see image 3 , the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the forward tilt control mechanism and the backward tilt control mechanism are the same forward tilt and backward tilt control mechanism 56, the power unit in which is horizontally arranged at the tail, and the control lines drawn from the steering control system are connected to In the power unit, the power unit adopts a ducted propeller structure. The propeller in this direction control mechanism can rotate forward and also can reverse. Upward thrust is generated during forward rotation, and the aircraft pitches backward; downward thrust is generated during reverse rotation, and the aircraft leans forward.
Embodiment 3
[0020] see Figure 4 with Figure 5 , the difference from Embodiment 2 is that the three direction control mechanisms of the left tilt control mechanism 3, the right tilt control mechanism 4 and the forward and backward tilt control mechanism 56 adopt a high-pressure jet structure, wherein the left tilt control structure 3 includes a structure fixedly connected to the fuselage The support rod 31 on 1, the open end of the support rod 31 is connected with a vertically downward high-pressure gas nozzle 33, the inside of the support rod 31 is provided with a high-pressure gas delivery pipeline, and the high-pressure gas delivery pipeline is connected to the main engine through the high-pressure gas flow controller . The high-pressure gas generated by the operation of the main engine is sent to the high-pressure gas flow direction controller, which includes an air inlet, an exhaust gas discharge port, and several functional outlets. The exhaust outlet is used for normal gas disch...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com