Wireless sensor node alliance generating method based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm
A wireless sensor and improved particle swarm technology, applied in wireless communication, instrumentation, computing, etc., can solve the problems of unsupported parallel multi-task environment alliance generation, uncertainty stability, etc., achieve good convergence, expand the search range, The effect of resolving instability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
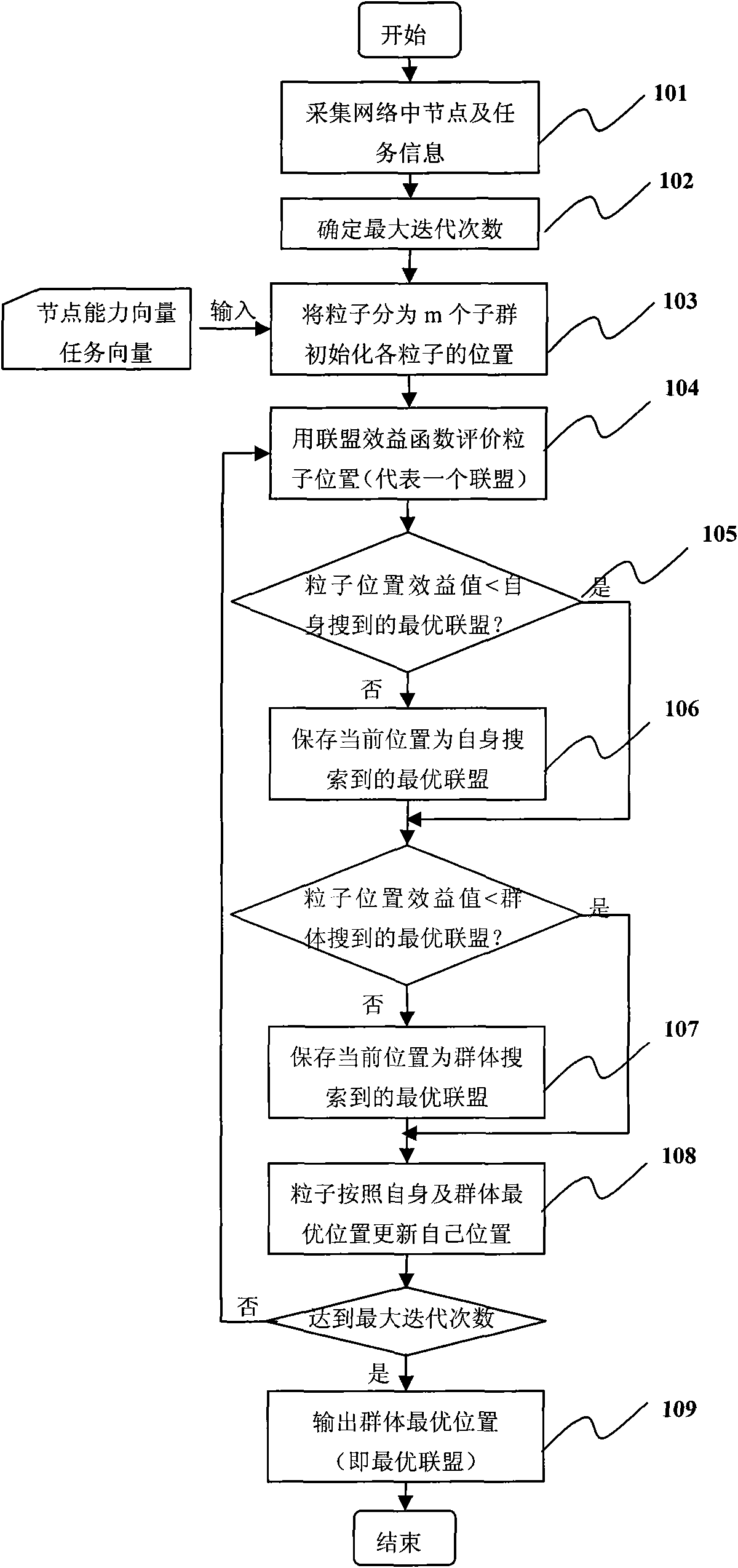
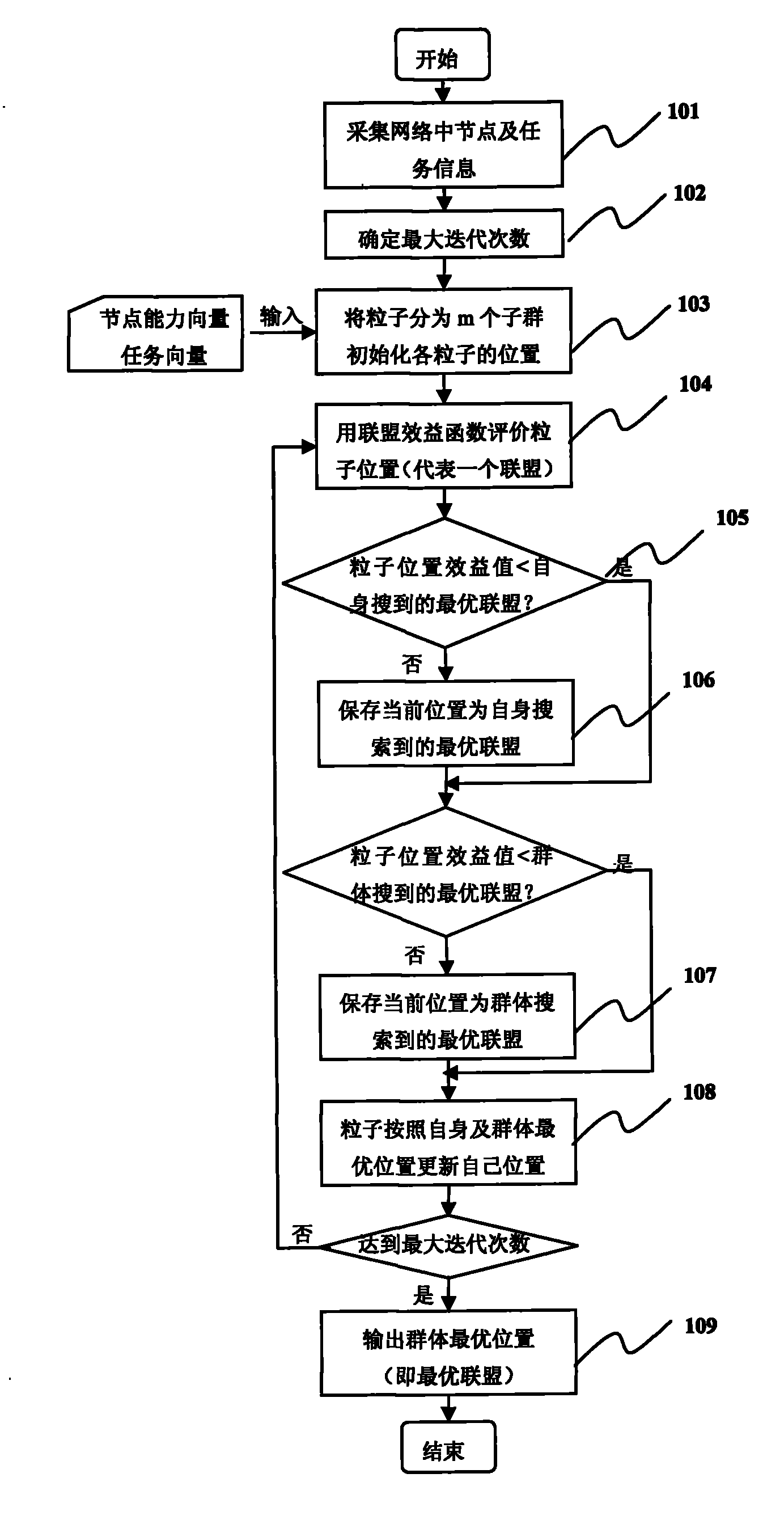
[0072] When the intrusion detection task is performed in WSN, multi-node cooperation is required to complete it. This method is used to generate a node alliance and cooperate to complete the intrusion detection task.
[0073] 101. Collect node and task information in the network, specifically as follows:
[0074] Suppose there are 10 nodes in the system, and the node information database maintains the capability vectors of 10 nodes. Assuming that this task needs to consider six parameters, the system first quantifies the collected node parameters to obtain the node capability vector. Similarly, quantify the specific parameter values of the task's capability requirements to obtain the task's capability requirement vector, and set the capability requirement vector for performing the intrusion detection task as T=[10, 35, 25, 41, 23, 42].
[0075] 102-103, input the capability vector of the nodes in the network and the capability requirement of the task. In the current networ...
example 2
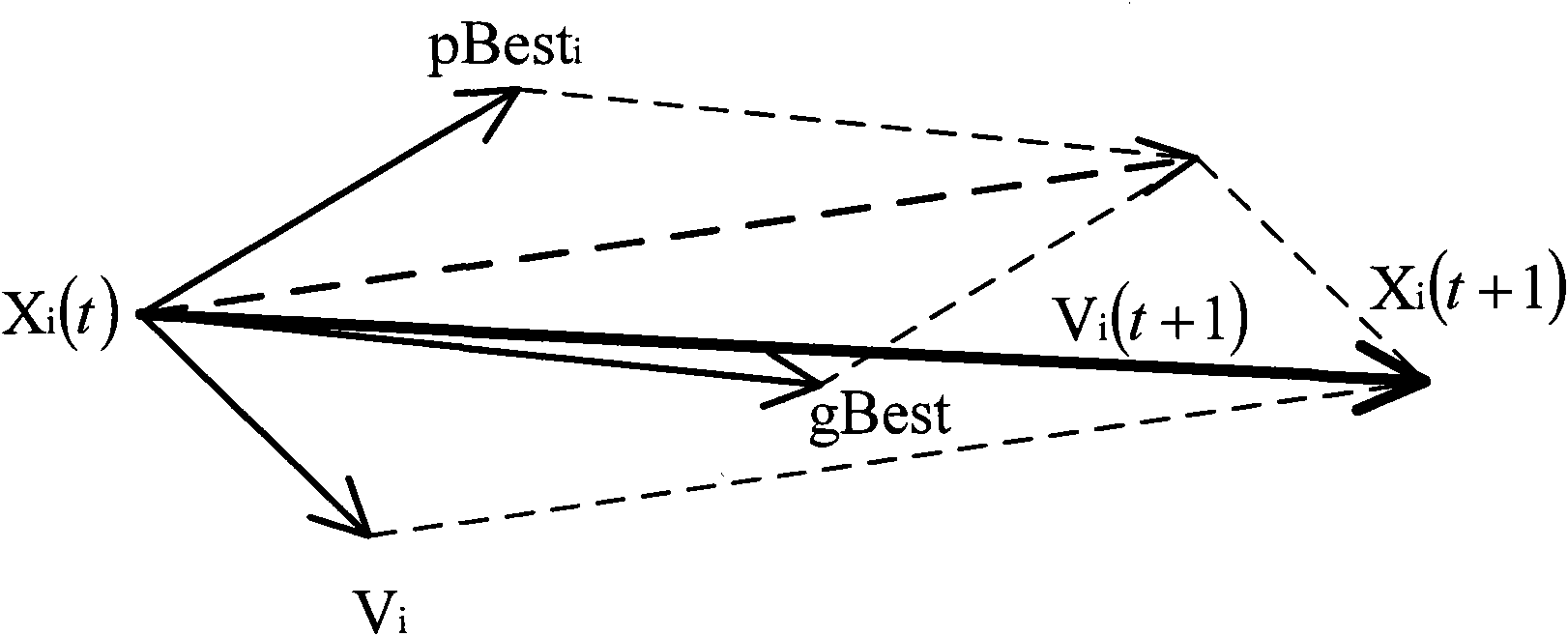
[0082] Prove the parallelism of the algorithm in the present invention. Assuming that there are three parallel intrusion detection tasks in the system, it is known that the capability requirements of these three tasks are respectively, t 1 = [10, 35, 35, 41, 23, 42], t 2 = [20, 30, 38, 40, 27, 45], t 3 = [15, 25, 41, 42, 34, 38]. It is known that there are 10 nodes in the system. According to the number of tasks that need to be executed in parallel at this time, the particle swarm is divided into 3 subgroups, and each subgroup is responsible for generating a coalition. Assuming that the number of particles in each subgroup is 5, which is the same as in Example 1, each subgroup searches independently and generates 3 alliances, and the benefit of each alliance gradually tends to the optimal solution during the iterative process.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com