System for access control of unidirectional light bus network based on priority level dynamic regulation
A network access control and dynamic adjustment technology, applied in transmission systems, electromagnetic wave transmission systems, optical fiber transmission, etc., can solve the problems that cannot meet the real-time requirements of data transmission, can not make good use of optical bus resources, etc., to improve real-time performance Requirements, the effect of improving the utilization rate of the optical bus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] refer to figure 1 and figure 2 , a unidirectional optical bus network access control system based on priority dynamic adjustment, comprising a unidirectional optical bus including M nodes, M≥3, and M is a natural number, the unidirectional optical bus includes a convening node, M-2 intermediate nodes and a termination node; the data flow of each node on the optical bus is a single service type. The unidirectional optical bus network access control system based on dynamic adjustment of priority also includes:
[0044] The node urgency parameter (J) calculation module is used to calculate whether the data at the node is urgent to send. Data streams arriving at each node have a service with a maximum waiting delay T i , where i represents different nodes on the optical bus, and t i Indicates the delay that has been waiting since the arrival of the first packet of the service; the node urgency parameter J = t i ...
Embodiment 2
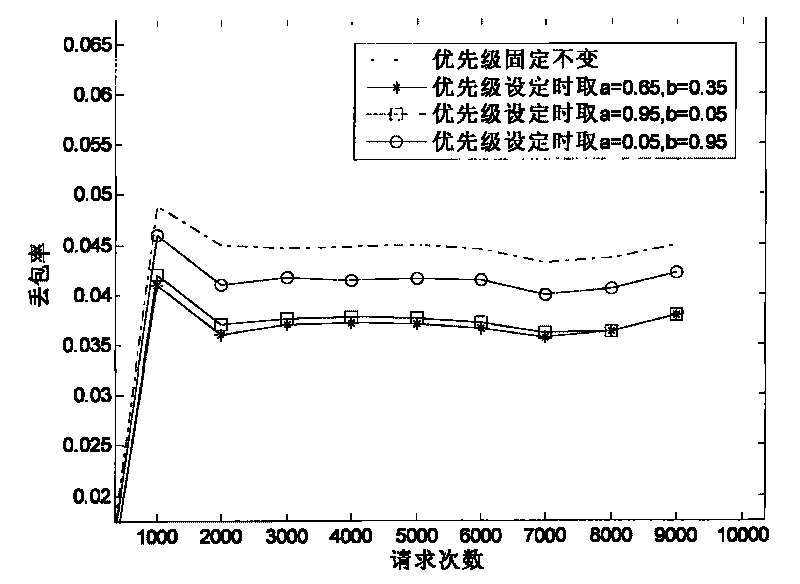
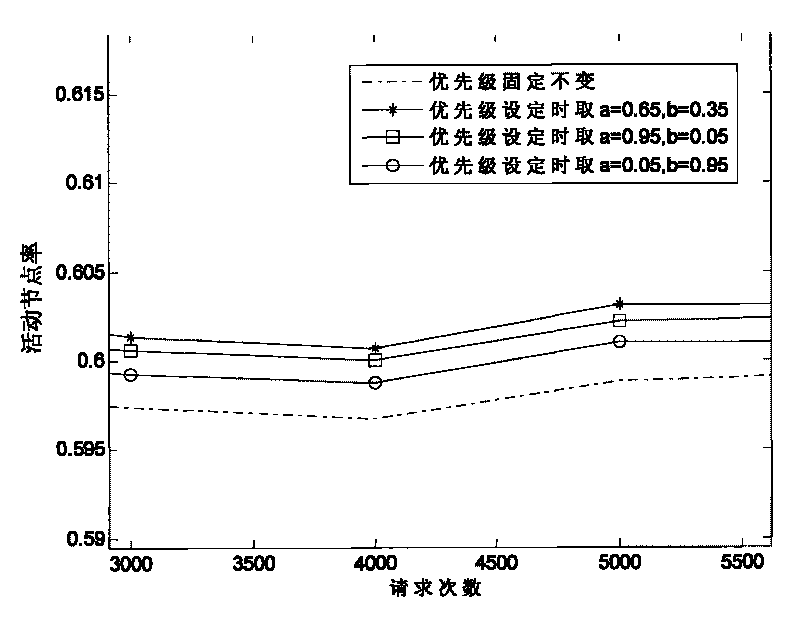
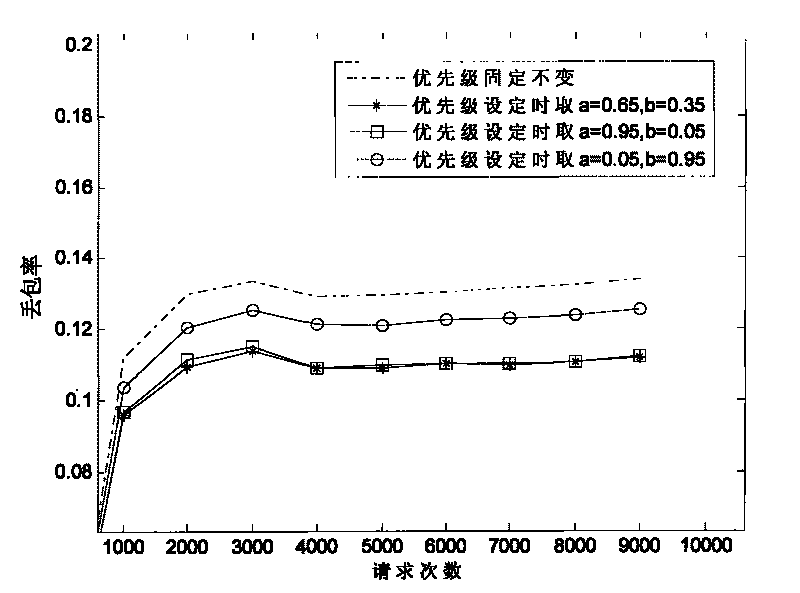
[0084] In the present embodiment, the number of optical bus nodes M=6, other parameters are the same as in embodiment 1, evaluate the packet loss rate of the optical bus under different priority setting methods, and obtain the attached image 3 The results shown, evaluate the optical bus activity under different priority setting methods, and get the attached Figure 4 From the results shown, it can be seen that the packet loss rate is the largest and the active node rate is the smallest when the priority is fixed. When the priority setting emphasizes the delay requirement (that is, a=0.95, b=0.05), the packet loss rate is the smallest, but the active node rate is small. When the priority setting focuses on the rate of active nodes (ie, a=0.05, b=0.95), the packet loss rate is higher, and more requests are lost due to time delay. However, when the priority setting considers the delay and the active node rate at the same time (i.e. a=0.65, b=0.35), the packet loss rate is small...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com