Helicopter rotor wings with commutation net cover
A technology of helicopter rotor and rectifying net, which is applied in the aviation field, can solve the problems of increased body vibration and noise, large force on the hub, and difficult blades, etc., to achieve the goal of improving ride comfort, huge economic benefits, and enhancing national defense strength Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
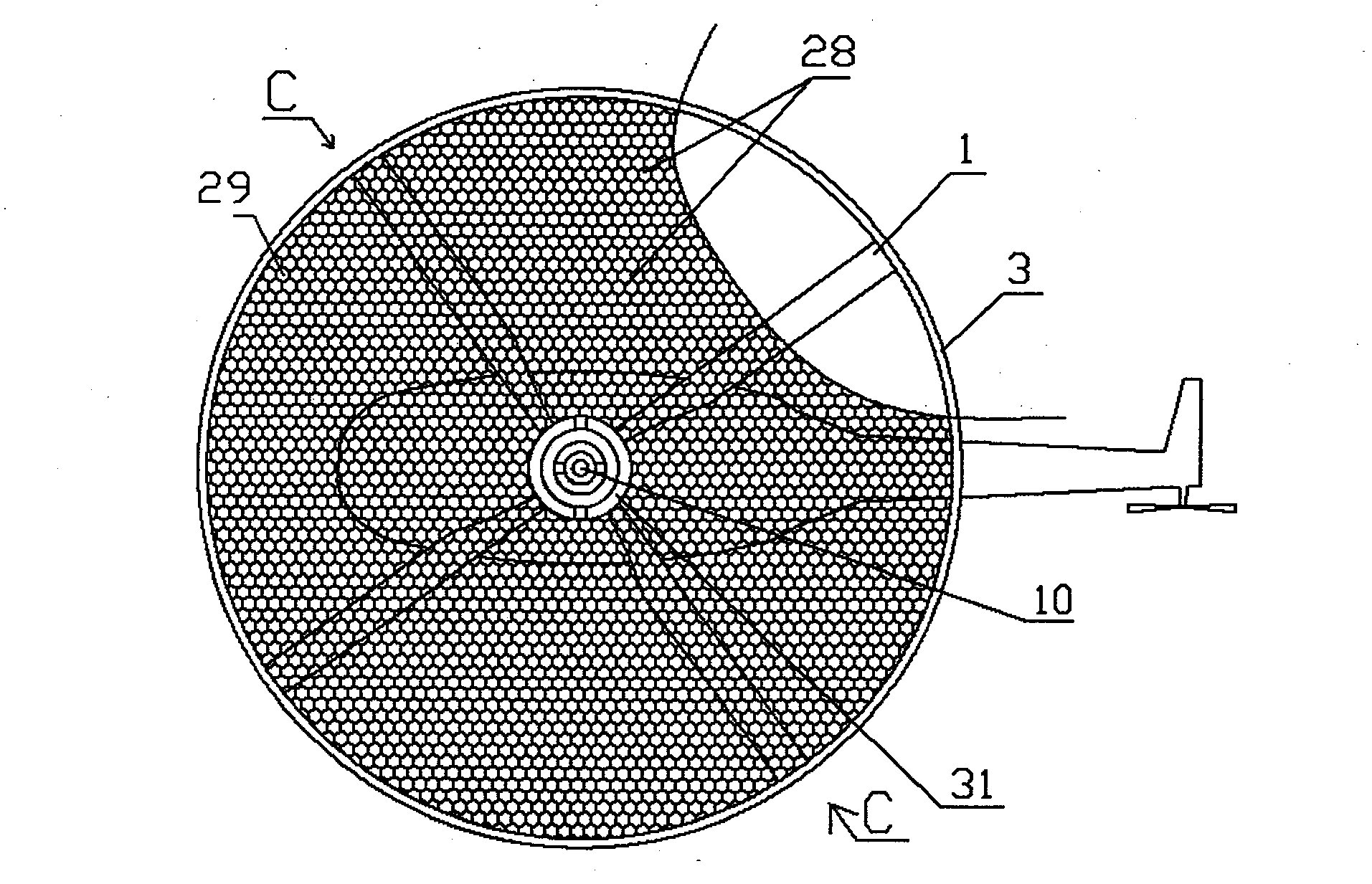
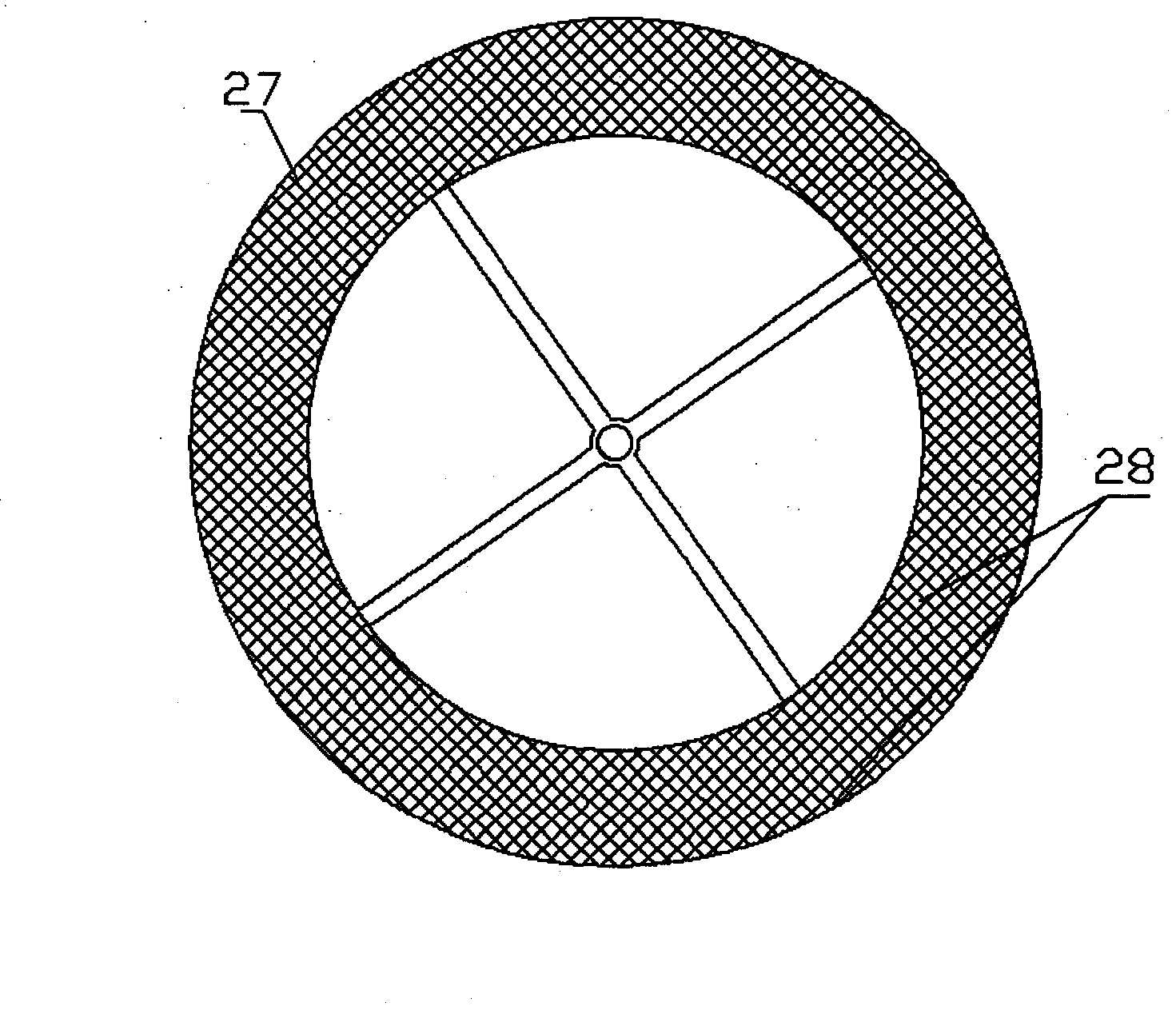
[0017] Embodiment one: in figure 1 ; Figure 9 In the shown embodiment, it is a relatively simple application mode of the present invention on existing helicopters. The connection between the root of the blade 1 and the propeller hub abandons the original swing hinge and pendulum hinge or some elastic elements, and the variable pitch hinge and swash plate etc. are still retained, the rotor has four blades 1, a fairing net cover 28, a circle of annular outer support frame 3, etc., the outer chord of the blade 1 top has an axle, the inner surface of the annular outer support frame 3 Four shaft sleeves are evenly distributed, and are respectively connected with the outer chord of the blade 1 in the form of a shaft and a shaft sleeve, so as to adjust the upward angle of attack of the blade 1; 31 is connected with the bearing at the top of the rotor shaft 10, so that the fairing screen cover 28 can be tilted with the top of the axis line of the rotor shaft 10 as the base point, bu...
Embodiment 2
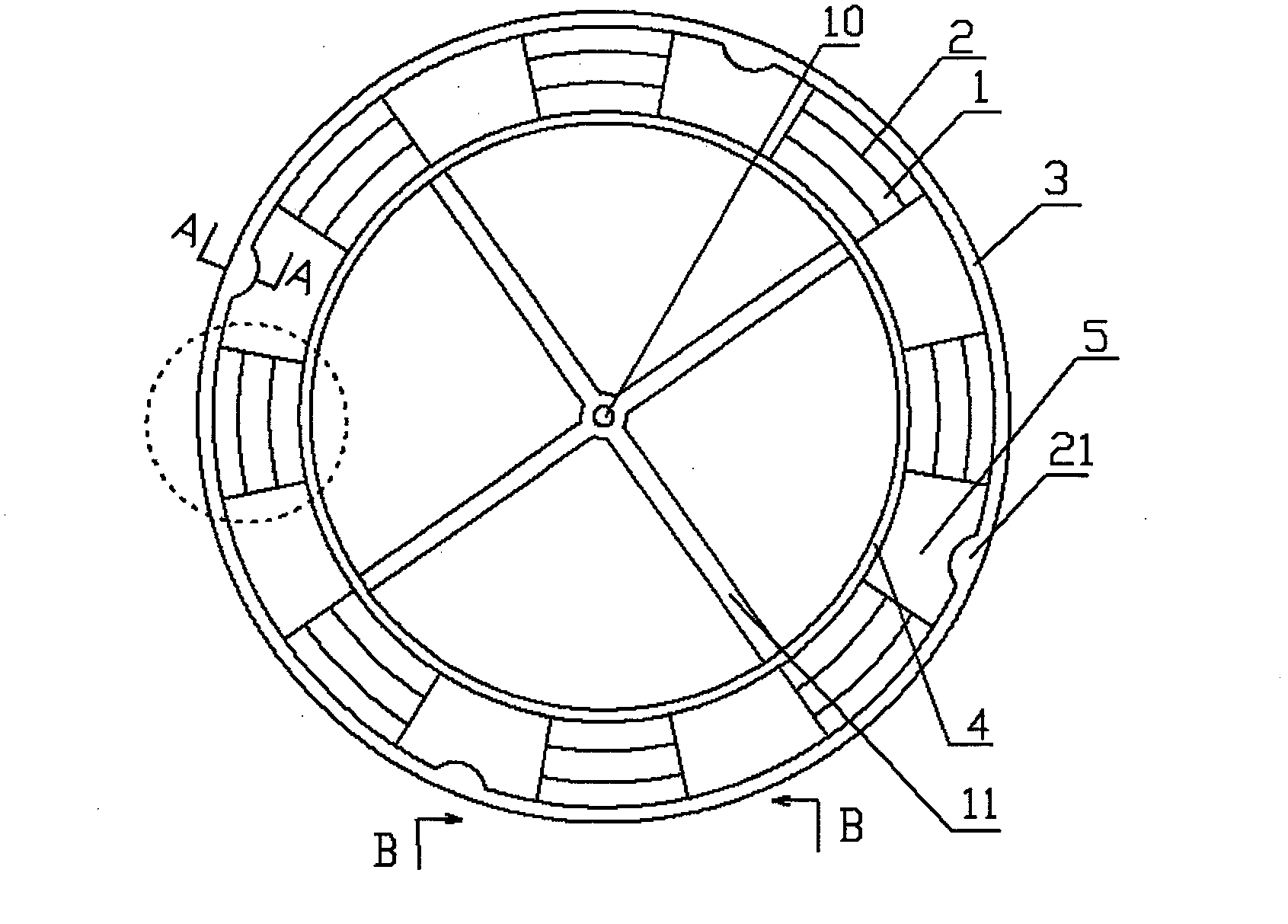
[0019] Embodiment two: if figure 2 ; image 3 ; Figure 4 ; Figure 5 ; Figure 6As shown, this embodiment includes: eight blades 1, four sets of control ring regulators 21, an annular propeller hub 4, an annular outer support frame 3, a rectifying net cover 28, and an inner surface of the annular outer support frame 3. Ring groove 30, there is a blade angle of attack control ring 9 that can move up and down in the ring groove 30, four spoke plates 11, and two wing knives 2 are arranged on each blade 1 to prevent airflow from slipping centrifugally. Four rigid webs 11 are rigidly fixedly connected between the annular propeller hub 4 and the rotor shaft 10 . The paddles 1 are evenly distributed between the annular outer support frame 3 and the annular paddle hub 4, and there are gaps 5 between the paddles 1, and the downwash airflow generated by the paddles 1 in front of the gaps passes through the gaps 5 downward; Figure 4 ; Figure 6 As shown: the blade 1 connected to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com