RF based spatially selective excitation in mri
A selective and spatial technology, applied in magnetic resonance measurement, instruments, measuring devices, etc., can solve problems such as methods that do not teach spatial selective excitation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
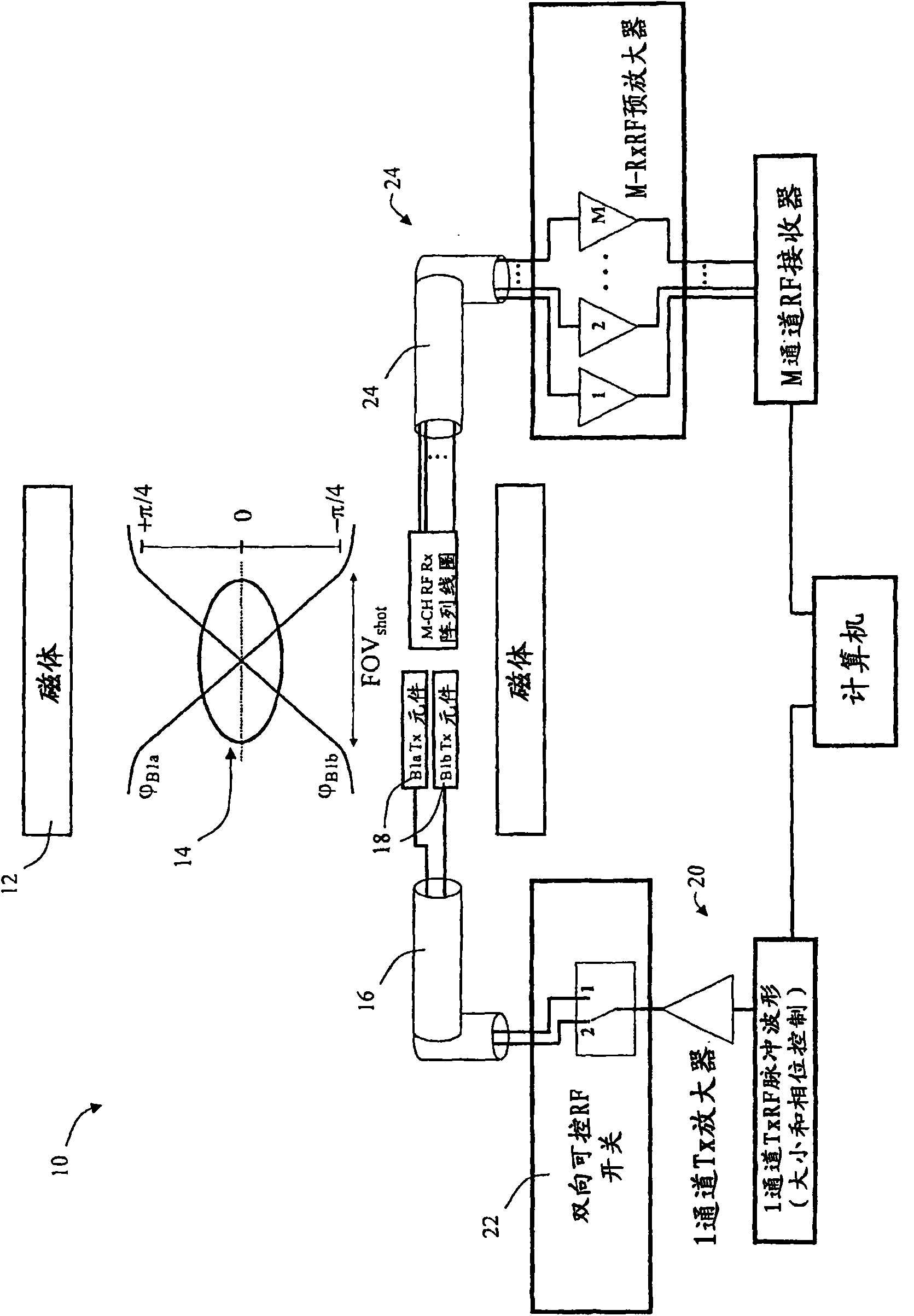
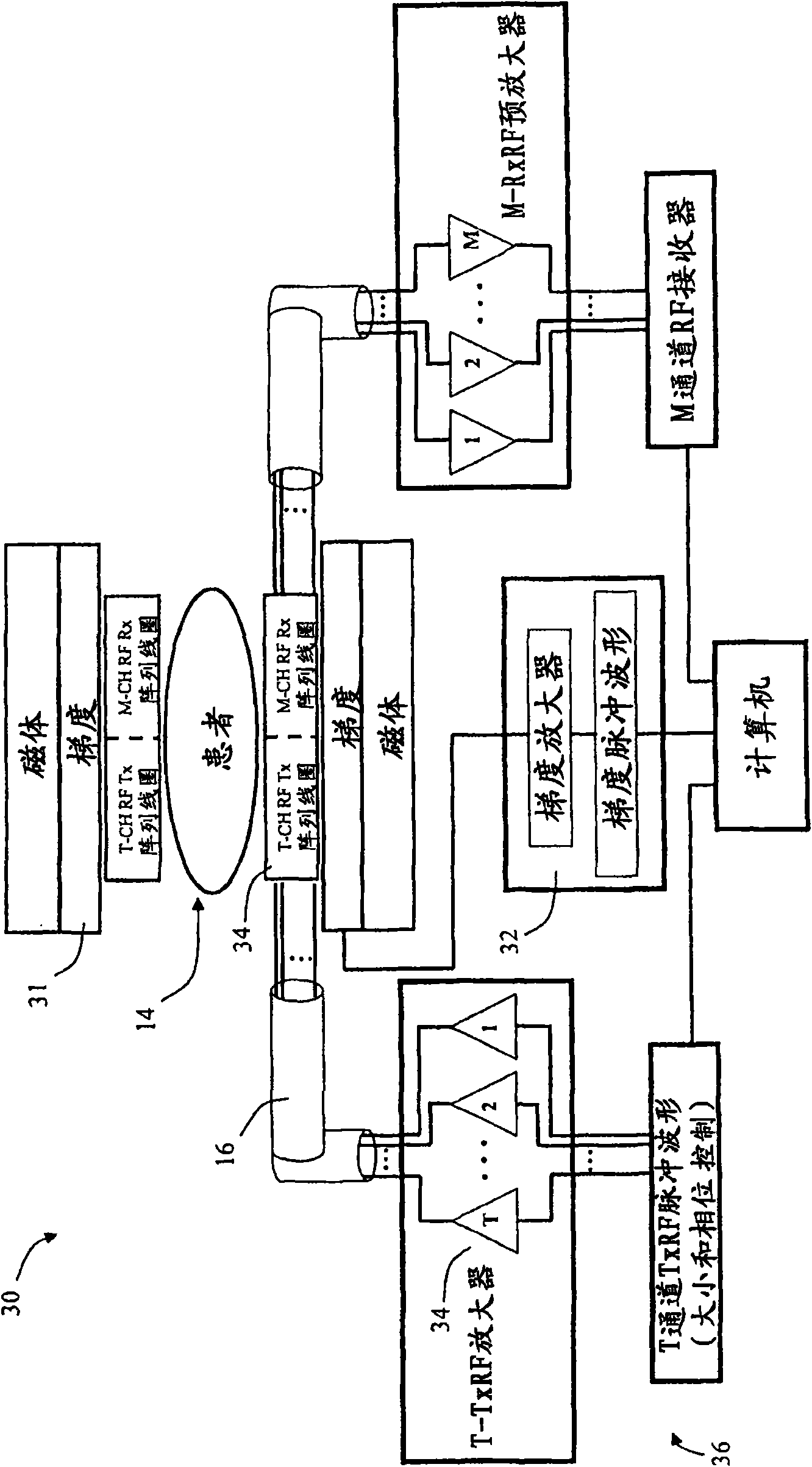
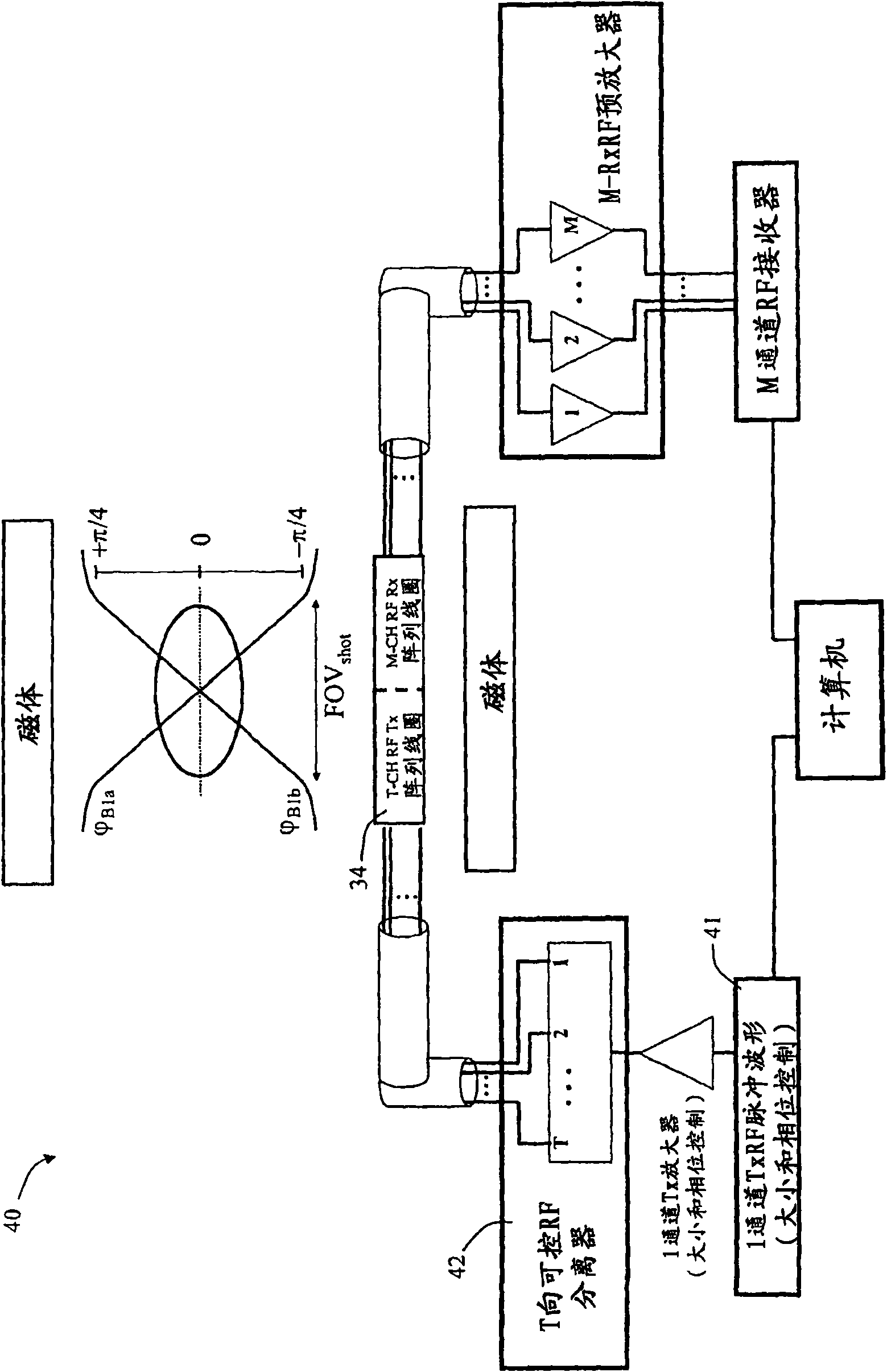
[0050] Herein, a method for slice selection in MRI processing is provided, which method comprises shifting the k-space weighting function by adding weights in one or more B1 fields used to deposit energy according to the desired k-space weighting function. Low flip angle RF pulses interspersed between focused pulses control the transmit array. The low flip pulse deposits energy such that if the phase encoding direction is a linear axis that coordinates the sample volume and the B1 field has a linear phase gradient, then the envelope described by the low flip pulse in the k-space weighting function, e.g. The lines relate to the desired spatially excited regions of the sample volume.
[0051] Here, mathematically idealized terms are used to represent the orientation and properties (constant, linear, uniform) of the fields and the array of coils or elements used to generate them. Those skilled in the art will appreciate that in the context of the examples, any idealization is in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com