Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus for repairing atrazine-contaminated soil
A technology of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and atrazine, which is applied in the field of microorganisms and can solve the problems of unsatisfactory effects of atrazine-contaminated soil
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0013] Specific embodiment one: the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi repairing atrazine-contaminated soil in this embodiment is Glomus mosseae (GM) HDSF1, which is preserved in the General Microorganism Center (CGMCC) of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee, The deposit number is CGMCC No.3012, and the deposit date is April 09, 2009.
[0014] In this embodiment, the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomusmosseae (GM) HDSF1 used to remediate atrazine-contaminated soil was collected from farmland soil polluted by pesticide atrazine residues in Yangmajiazi, Harbin.
[0015] Glomus mosseae (GM) HDSF1 was collected and purified according to the following steps: 1. The soil polluted by the pesticide atrazine residue was excavated at a depth of 0-30 cm, and then the arbuscular branches were separated and purified from the soil by wet sieving. Mycorrhizal fungal spores; 2. Soak the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spores in a mixed solution in which the mass concentrati...
specific Embodiment approach 2
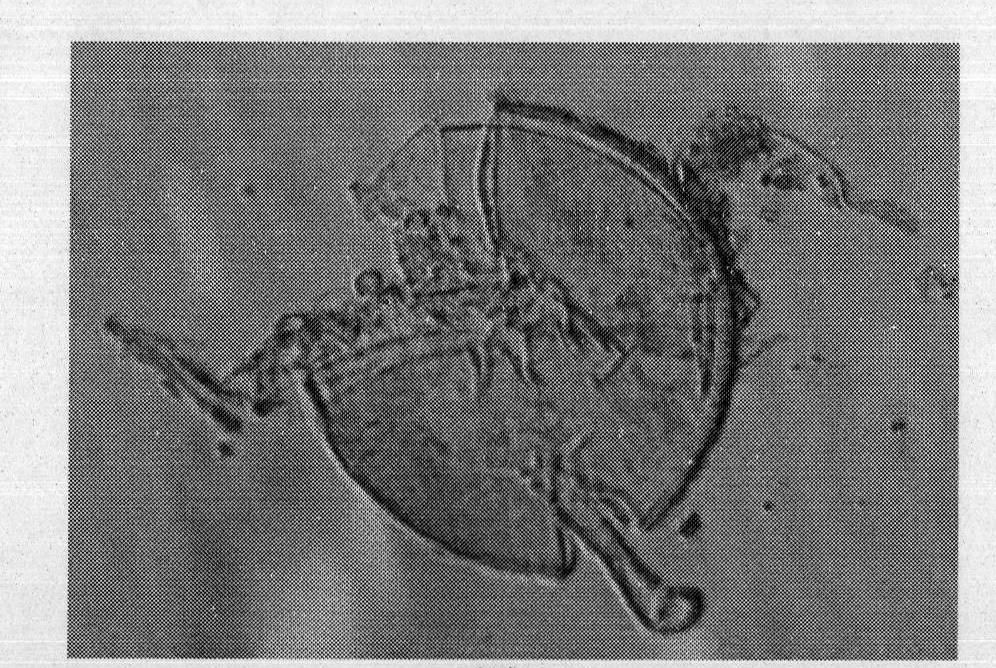
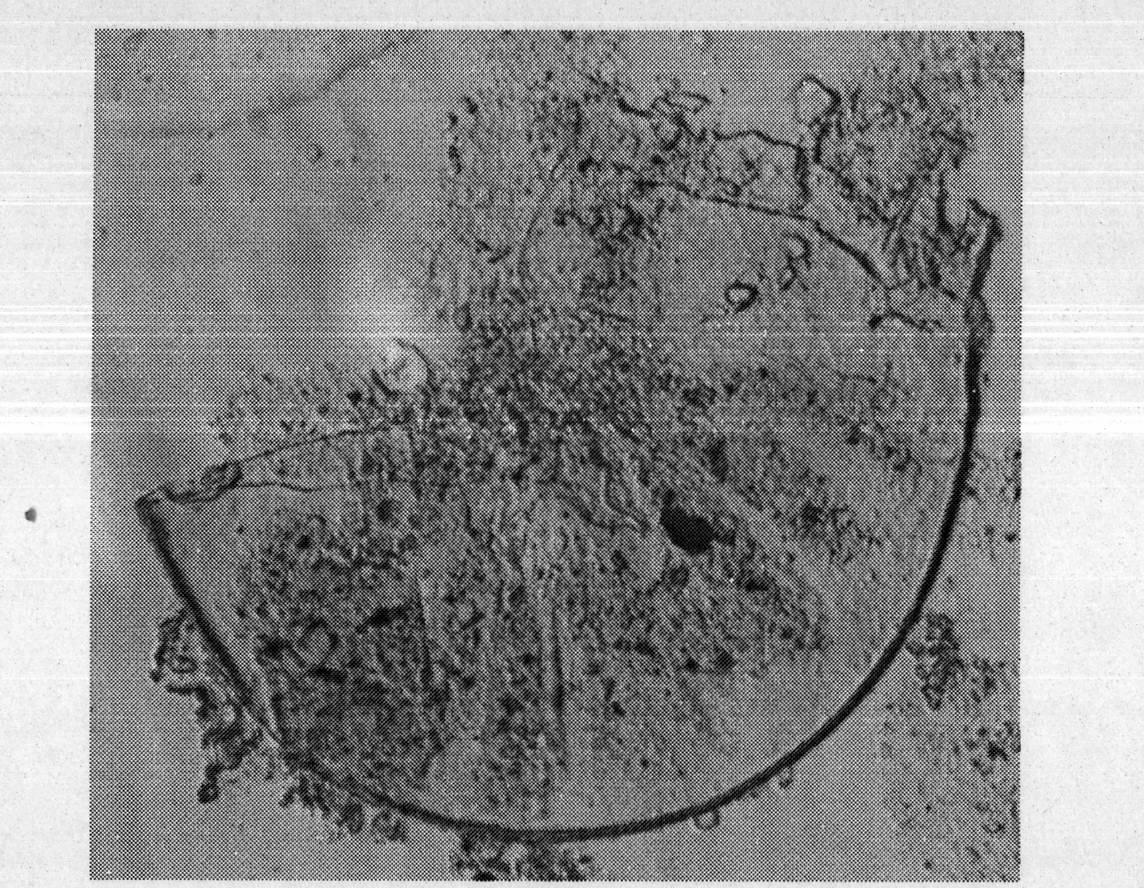
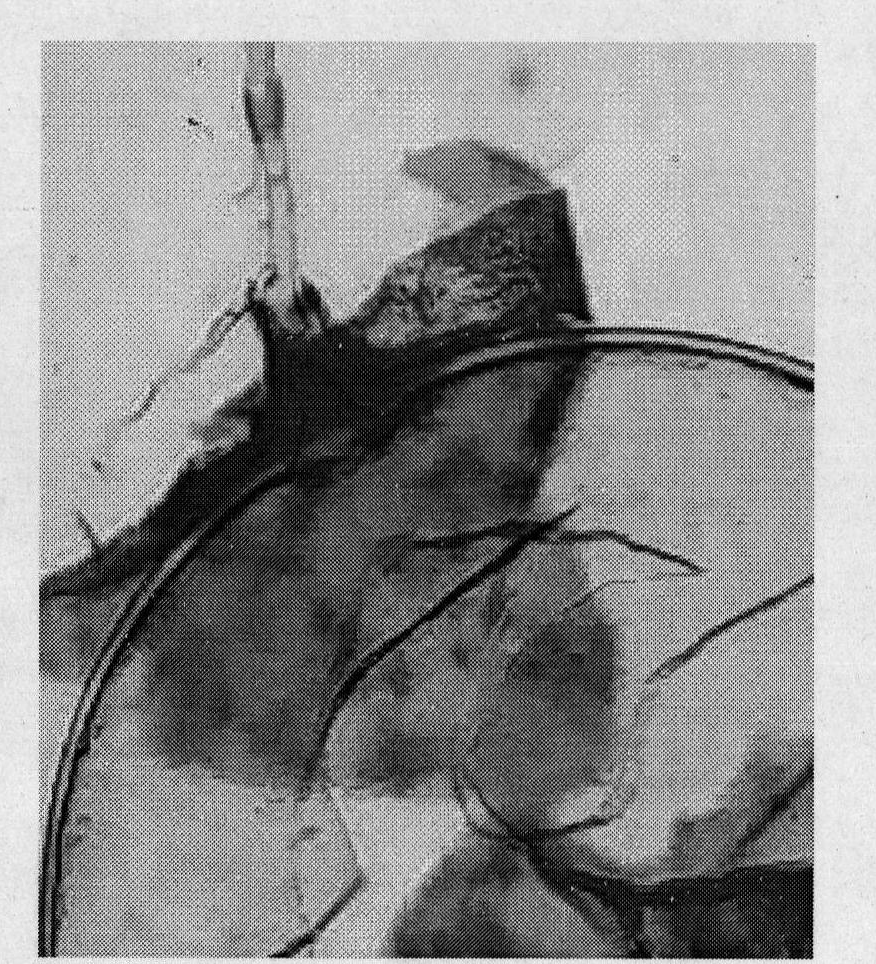
[0016] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the spores of Glomus mosseae (Glomus mosseae, GM) HDSF1 are yellow or brown, spherical, and the average diameter is 210 μm; mosseae, GM) HDSF1 conidia hyphae have a funnel-shaped base with a diameter of 20-30 μm; mature Glomus mosseae (GM) HDSF1 spore wall divides from outside to inside. 2 and L 3 two floors, L 2 The layer is light yellow, with a thickness of 1.2-1.6 μm, L 3 layer with L 2 The layers were separated, yellowish brown in color, and the average thickness was 4.5 μm. Others are the same as the first embodiment.
[0017] The L1 layer of mature Glomus mosseae (GM) HDSF1 spores has been shed.
[0018] mature Glomus mosei HDSF1 spores such as Figure 1~6 Shown (mature spores of 6 different G. mosei HDSF1).
[0019] The hyphae of Glomus mosseae (GM) HDSF1 have a curved thick septum that separates the spore contents from those of the hyphae. Through observation,...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0020] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: immature Glomus mosseae (Glomus mosseae, GM) HDSF1 spore wall divides from outside to inside. 1 , L 2 and L 3 3rd floor, L 1 The layer is located on the surface of the spores and is transparent, stained pink by Melzer's reagent, with an average thickness of 3.2 μm. Others are the same as the first or second embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com