Aluminum zinc series alloy sacrificial anode for electric water heaters
A sacrificial anode and electric water heater technology, applied in the field of aluminum-zinc alloy sacrificial anodes, can solve the problems of toxic heavy metals, low current efficiency of sacrificial anodes, polluted water quality, etc., achieve less secondary reaction products, improve current efficiency, and increase current efficiency effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
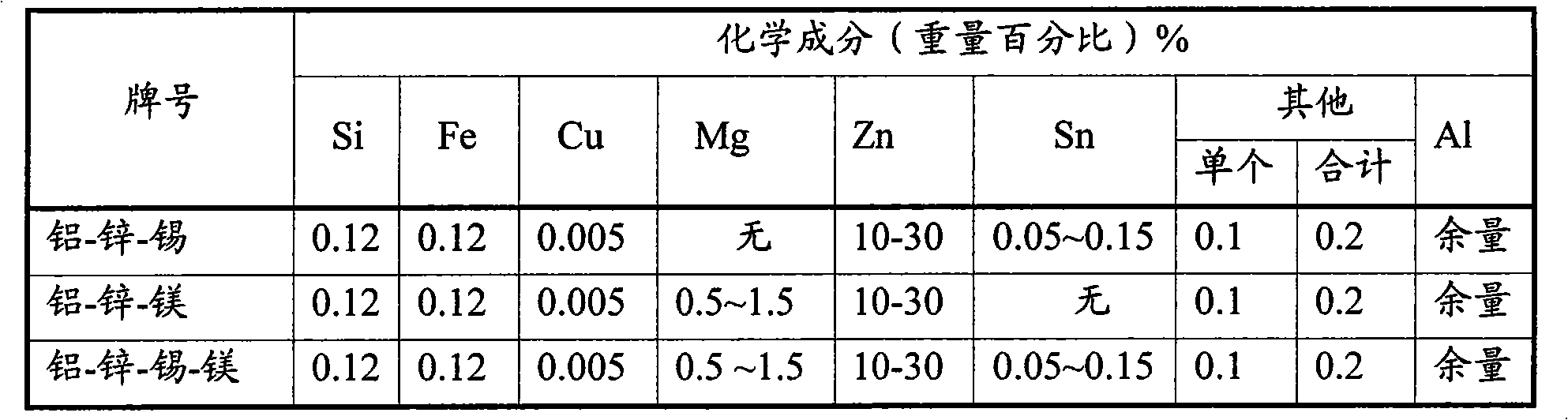
[0024] The weight percentage of each component of the aluminum-zinc alloy sacrificial anode material is: 30% zinc, 0.15% tin, 0.005% copper, 0.12% iron, 0.12% silicon; the rest is aluminum, the impurity content of a single element is ≤0.1%, and the impurity content of all other elements ≤0.2%.
[0025] During the preparation, graphite crucibles are used to hold aluminum ingots and zinc ingots, and the aluminum and zinc ingots are melted in a heating furnace, then tin is added to the molten aluminum, stirred with graphite rods, slag is removed, cast into ingots out of the furnace, and then extruded into rods. Made into aluminum-zinc-tin sacrificial anode. It is then cut into rods suitable for electric water heaters, and can also be directly cast into rods for electric water heaters.
Embodiment 2
[0027] The weight percentage of each component of aluminum-zinc alloy sacrificial anode material is: 20% zinc, 1.5% magnesium, 0.05% tin, 0.005% copper, 0.12% iron, 0.12% silicon; the rest is aluminum, and the impurity content of individual elements is ≤0.1%, others The impurity content of all elements is ≤0.2%.
[0028] During preparation, graphite crucibles are used to hold aluminum ingots and zinc ingots, and the aluminum and zinc ingots are melted in a heating furnace, and then elements of magnesium and tin are added to the molten aluminum, stirred with graphite rods, slag removed, cast into ingots out of the furnace, and then extruded It is made into a rod and made into an aluminum-zinc-magnesium-tin sacrificial anode. It is then cut into rods suitable for electric water heaters, and can also be directly cast into rods for electric water heaters.
Embodiment 3
[0030] The weight percentage of each component of the aluminum-zinc alloy sacrificial anode material is: 10% zinc, 1% magnesium, 0.005% copper, 0.12% iron, 0.12% silicon; the rest is aluminum, the impurity content of a single element is ≤0.1%, and the impurity content of all other elements ≤0.2%.
[0031] During preparation, graphite crucibles are used to hold aluminum ingots and zinc ingots, and the aluminum and zinc ingots are melted in a heating furnace, then elemental magnesium is added to the molten aluminum, stirred with graphite rods, slag is removed, cast into ingots out of the furnace, and then extruded into rods , made into Al-Zn-Mg sacrificial anode. It is then cut into rods suitable for electric water heaters, and can also be directly cast into rods for electric water heaters.
[0032] Among the above schemes, the aluminum-zinc-tin sacrificial anode and the aluminum-zinc-tin-magnesium sacrificial anode are suitable for the protection of the inner tank of electric ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com