Polarization-preserving fiber axis fixing method based on spatial diffraction light
A polarization-maintaining fiber, diffracted light technology, applied in polarized fibers, cladding fibers, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in establishing standard curves, limit the promotion of fixed-axis methods, etc. wide effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0040] The polarization-maintaining fiber in this embodiment is a panda-type polarization-maintaining fiber.
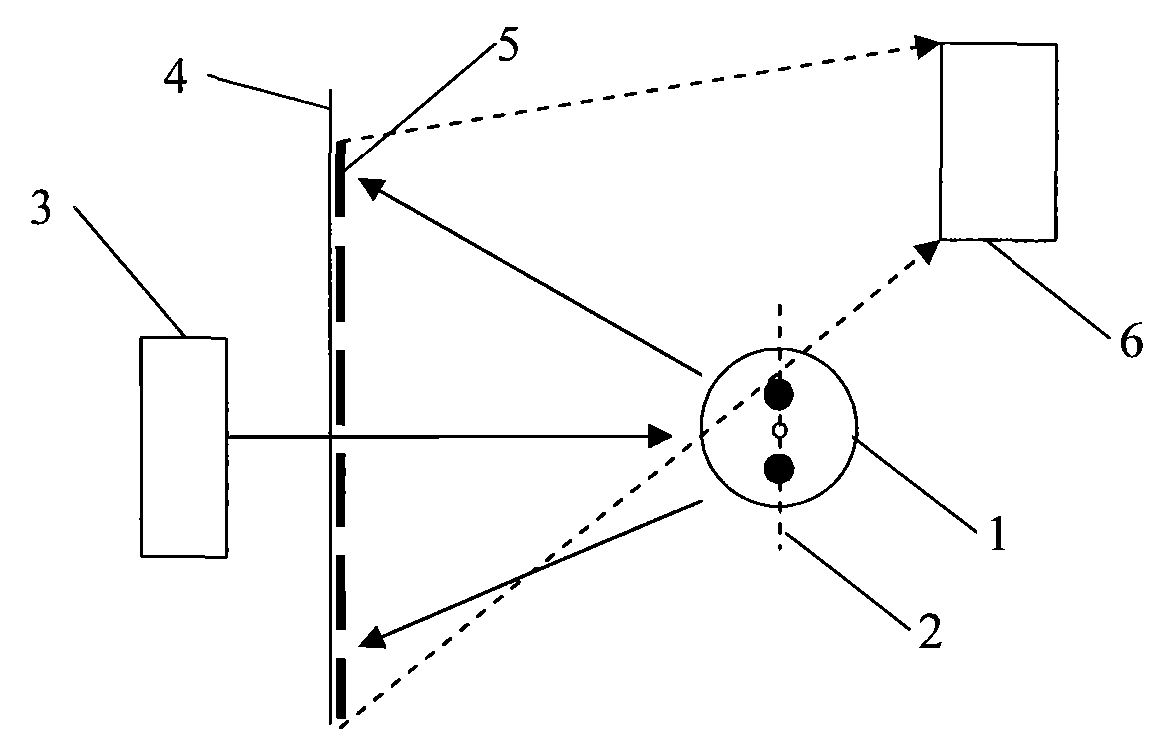
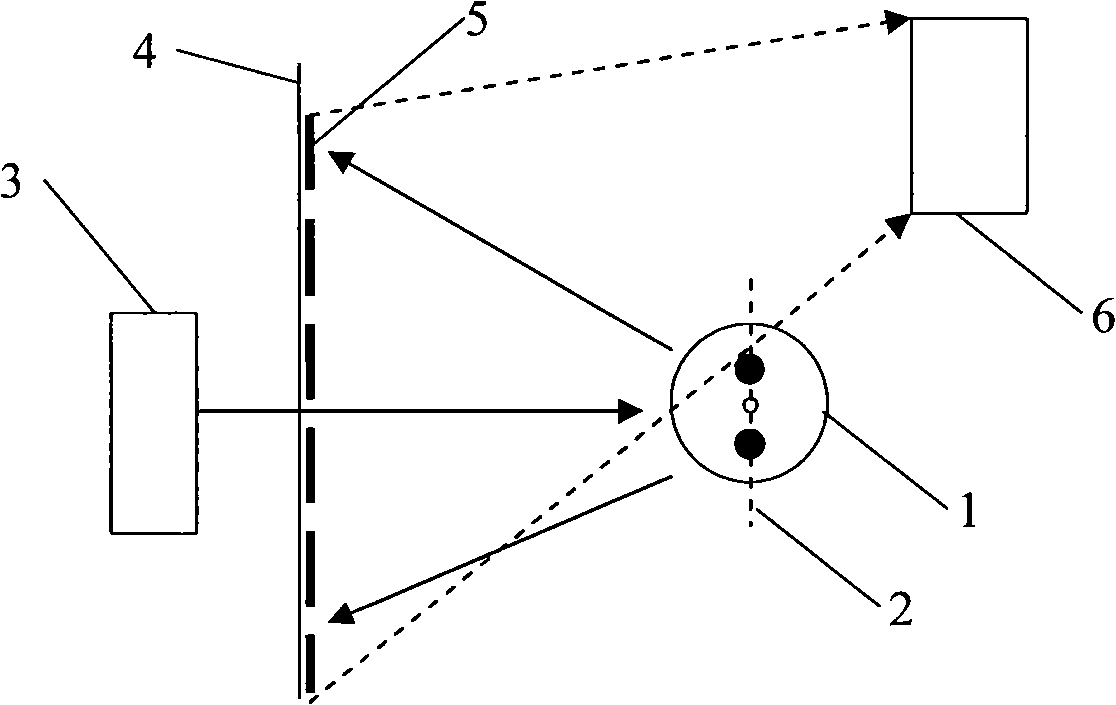
[0041] As shown in Figure 1, the laser beam emitted by the laser 3 is perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the polarization-maintaining fiber 1 and irradiates the side of the polarization-maintaining fiber 1 vertically, thereby forming backscattered light, which interferes with each other in space and Diffraction fringes 5 are formed on the imaging screen 4, and the digital camera 6 takes diffraction images and sends them to an image processor for processing. 2 represents the slow axis of the polarization maintaining fiber. The digital camera 6 of the present embodiment selects the CCD camera with lens for use.
[0042] The axis-fixing method of polarization-maintaining fiber based on spatially diffracted light specifically includes the following steps:
[0043] (1) Make the laser beam emitted by the LD laser 3 and the polarization-maintaining fiber 1 be on the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com