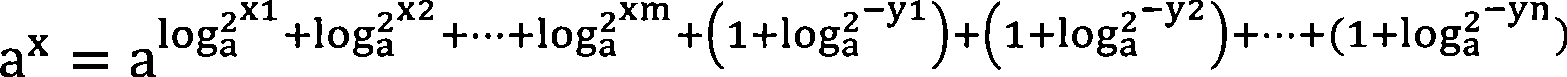Index operation method and device
A computing method and computing device technology, applied in computing, electrical digital data processing, digital data processing components, etc., can solve problems such as increasing multiplication operations and complex design
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
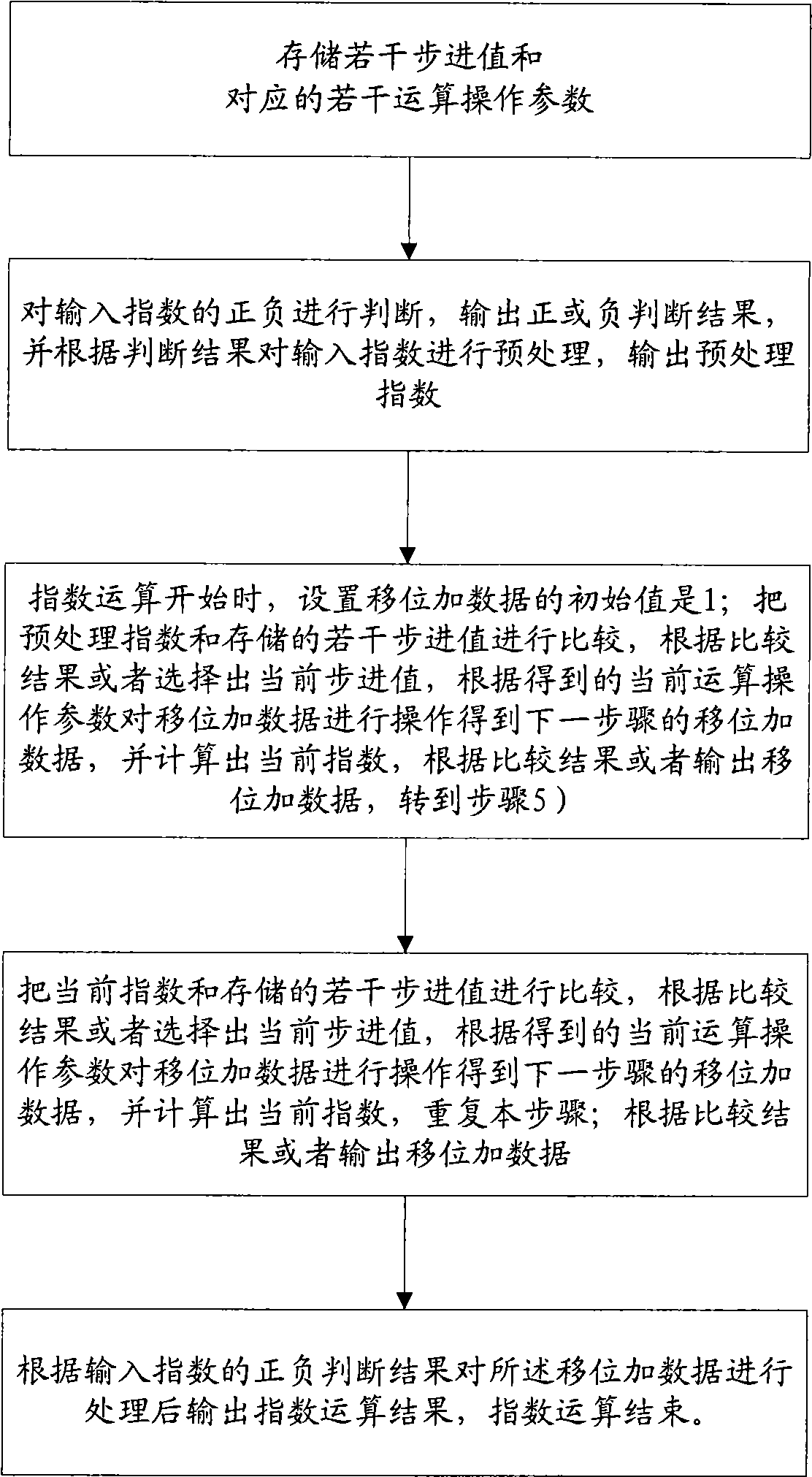
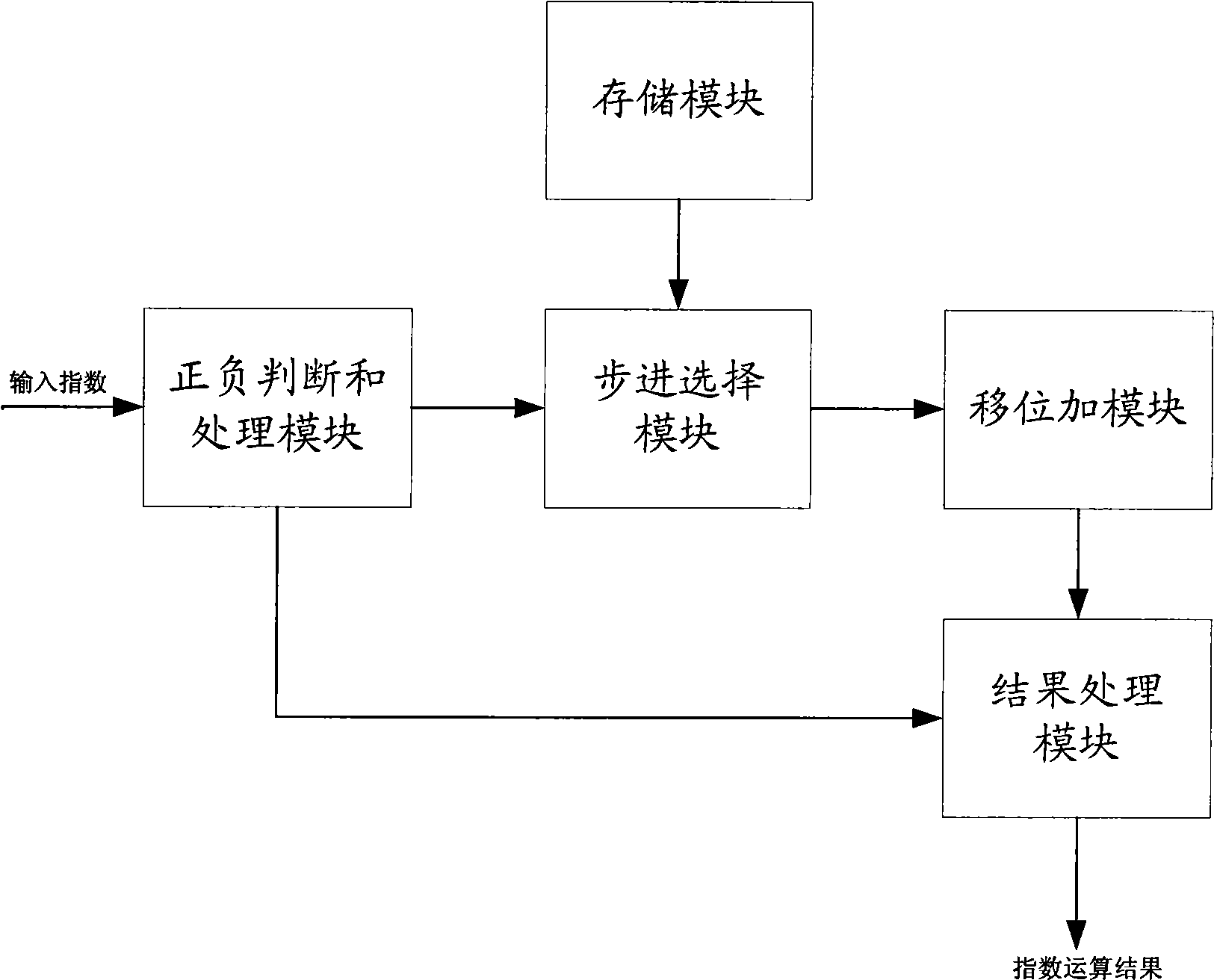
[0020] The idea of the present invention is: decompose the exponential operation into multiplication of several exponential operations, and the exponent in several exponential operations is the logarithm of the integer power of 2 or the value of the logarithm of the integer power of 2 plus 1, thus Convert the multiplication of exponent operations into simple shift operations and addition operations.
[0021] a x = a log a 2 x 1 + log a 2 x 2 + · · · + log a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com