Method for post-processing a signal in an audio decoder
An audio decoder and decoder technology, applied in the direction of instruments, speech analysis, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to apply models
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
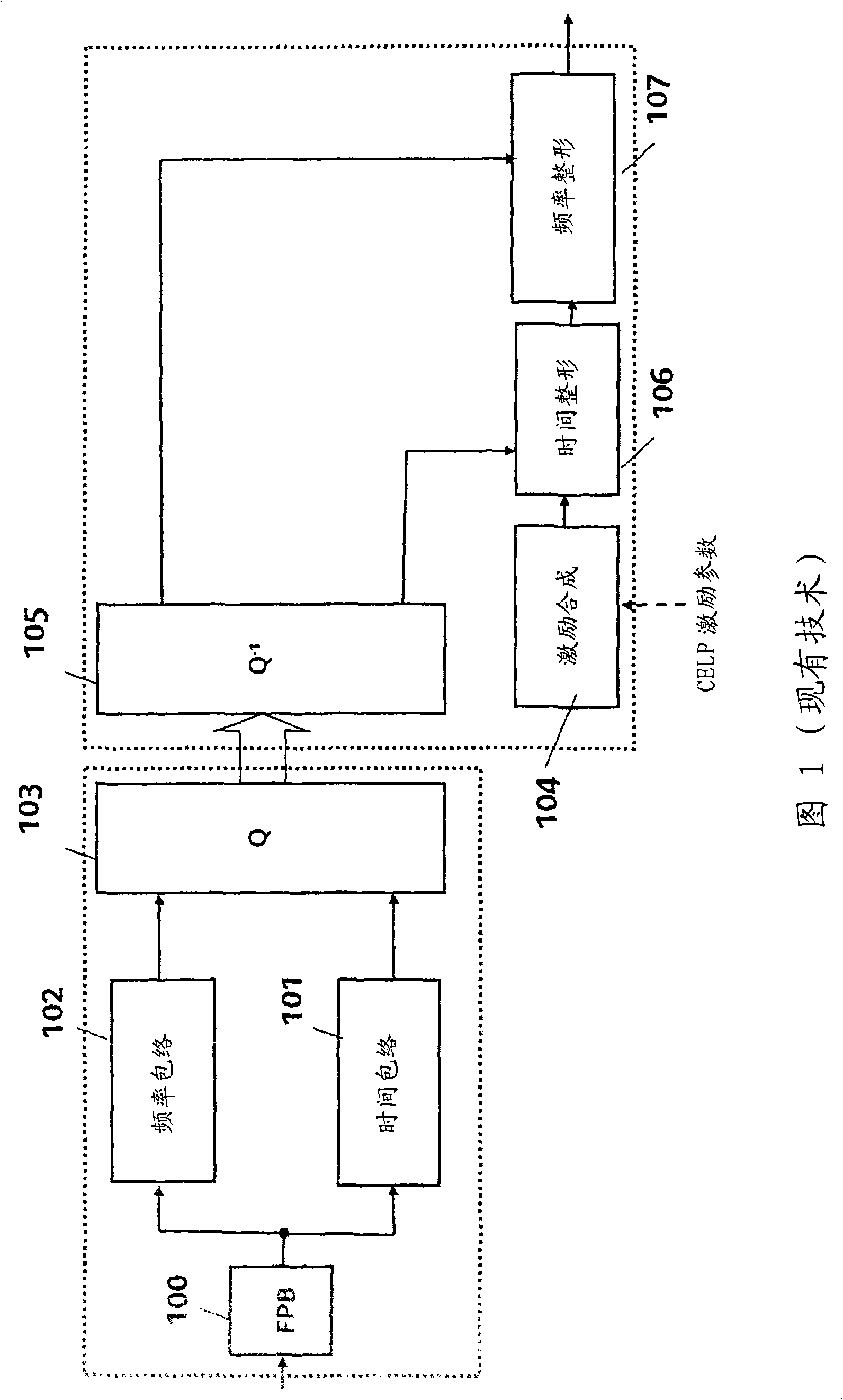
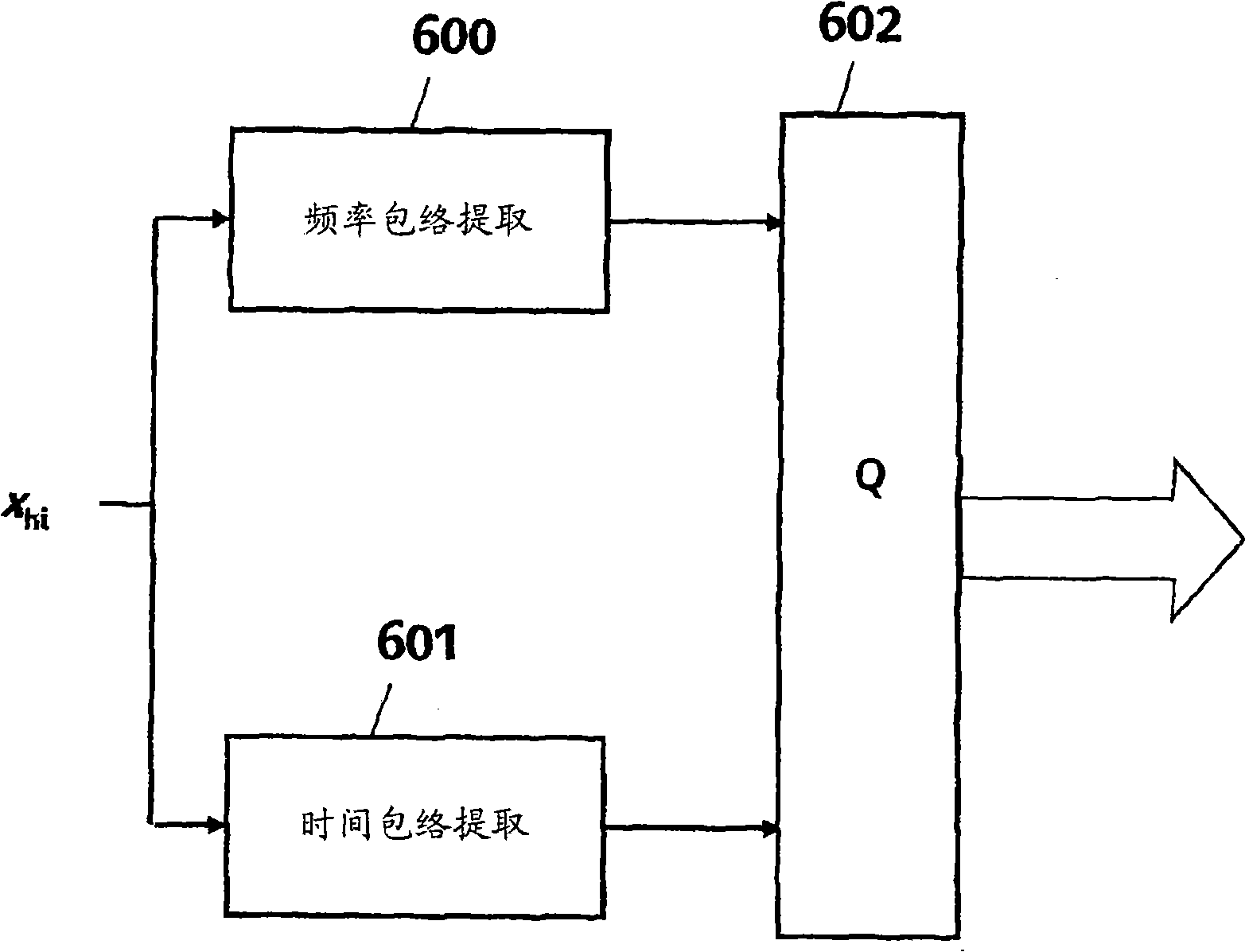
[0042] It should be remembered that the general context of the invention is sub-band hierarchical audio encoding and decoding at three bit rates (8kbps, 12kbps and 13.65kbps). In practice, the encoder always operates at a maximum bit rate of 13.65kbps, and the decoder can receive a core of 8kbps, and either or both enhancement layers of 12kbps or 13.65kbps.
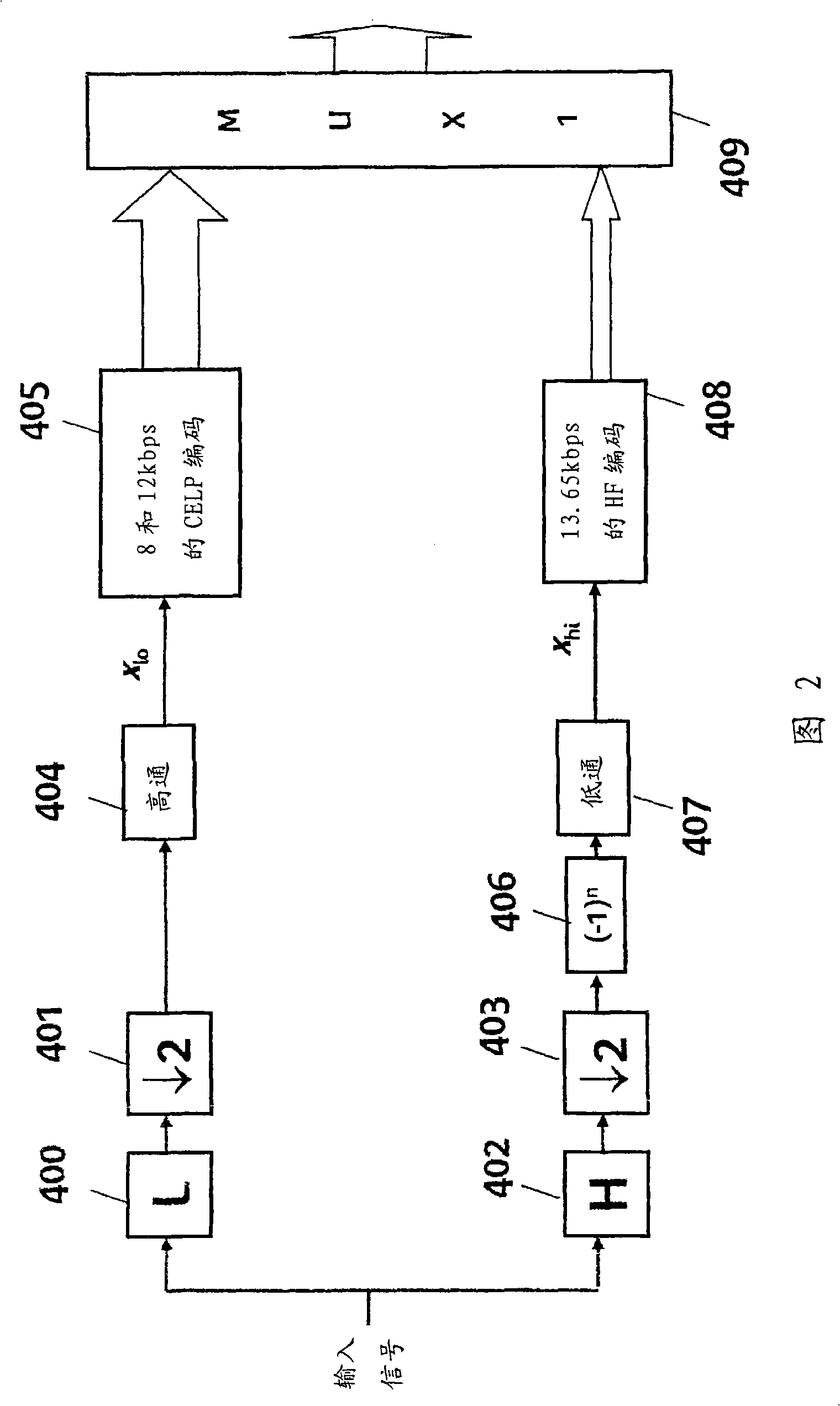
[0043] Figure 2 is a diagram of a hierarchical audio encoder.
[0044] First, the broadband input signal sampled at 16 kHz is divided into two sub-bands by filtering it using QMF (Quadrature Mirror Filter Bank) technique. The first frequency band (low band) in the range of 0 to 4000 Hz is obtained by low-pass (L) filtering 400 and decimation (decimation) 401, and the second frequency band in the range of 4000 Hz to 8000 Hz is obtained by high-pass (H) filtering 402 and decimation 403 Second band (high band). In a preferred embodiment, the L and H filter lengths are 64 and are in accordance with the paper "A filter famil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com