Method for detecting somatic cell number in raw milk
A technology of somatic cells and raw milk, applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome operation, inaccuracy, high cost, etc. The effect of easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
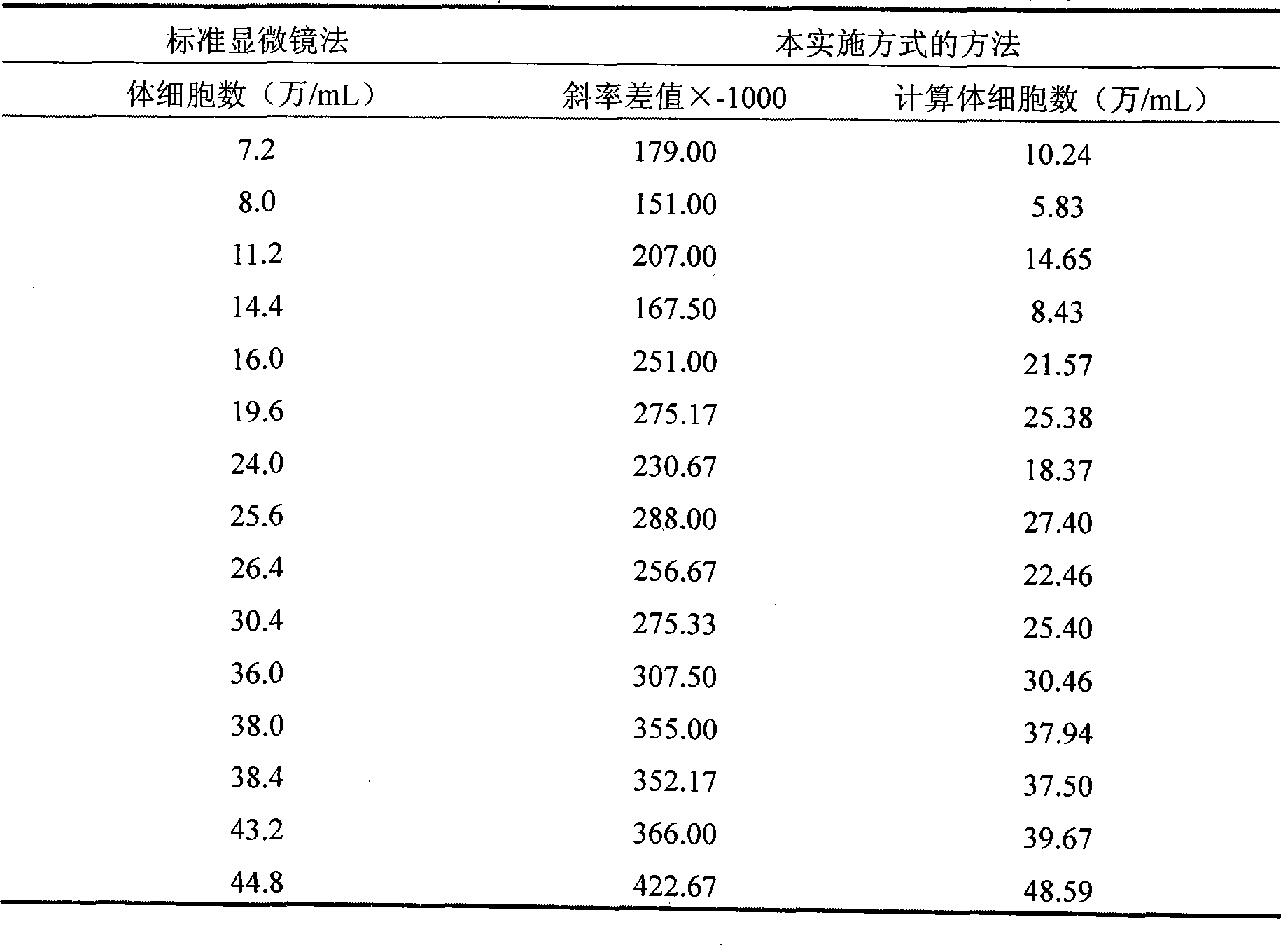
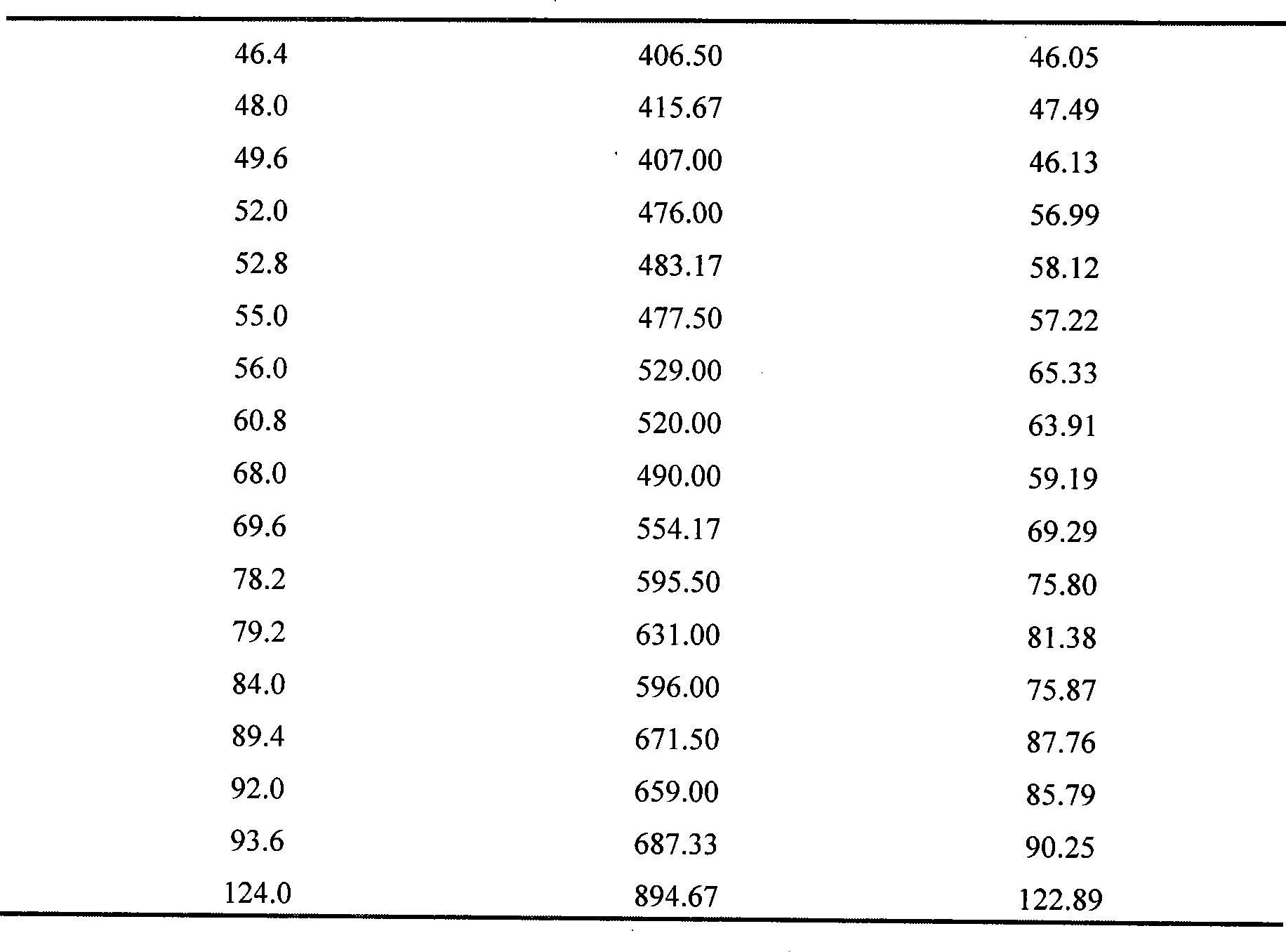
[0013] Specific Embodiment 1: The method for determining the number of somatic cells in raw milk in this embodiment is carried out as follows: 1. Pretreatment: Take two parts of the raw milk to be tested, named as sample 1 and sample 2 respectively, and the somatic cells in sample 1 Filter out to obtain the reference substance without somatic cells. Take the equal volume of sample 2 and the reference substance and add them to a transparent container, and preheat to 36-38°C; 2. Addition of reaction reagents: add ester solution, buffered saline solution and diazonium salt solution, each 1mL of sample 2 and reference substance need to add 0.01-0.1mL of ester solution, 0.01-0.1mL of buffered saline solution and 0.01-0.1mL of diazonium salt solution; 3. Determination of color Change: Immediately use the instrument to collect the color information of sample 2 and the reference substance after adding the reaction reagent in step 2, and record the time corresponding to the color inform...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0017] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in Step 1, the sample 2 and the reference substance were preheated to 37° C. respectively. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0018] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the ester in step 2 is naphthyl chloroacetate, indoxyl ester or pyrrolyl ester. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com