Method for direct communication between optical network units and passive optical network system
A technology of passive optical network and optical network unit, applied in the direction of optical multiplexing system, multiplexing communication, multiplexing system selection device, etc. Support P2P business efficiency is not high
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] First introduce the preamble structure of the Ethernet frame that this embodiment adopts, as figure 1 As shown, in this embodiment, the 4th to 5th bytes of the preamble carry the source LLID, that is, the LLID of the source ONU; the 6th to 7th bytes carry the destination LLID, that is, the LLID of the destination ONU.
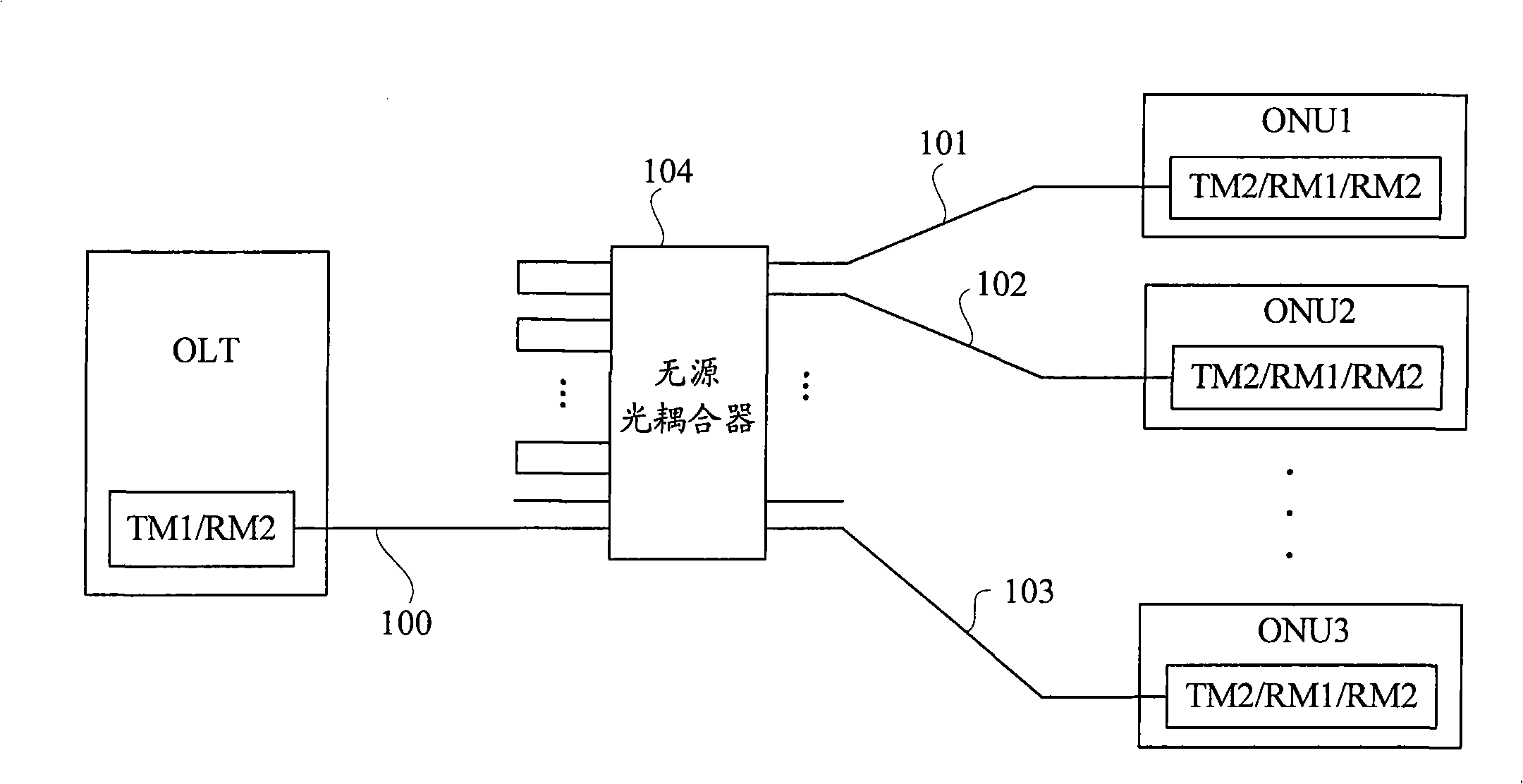
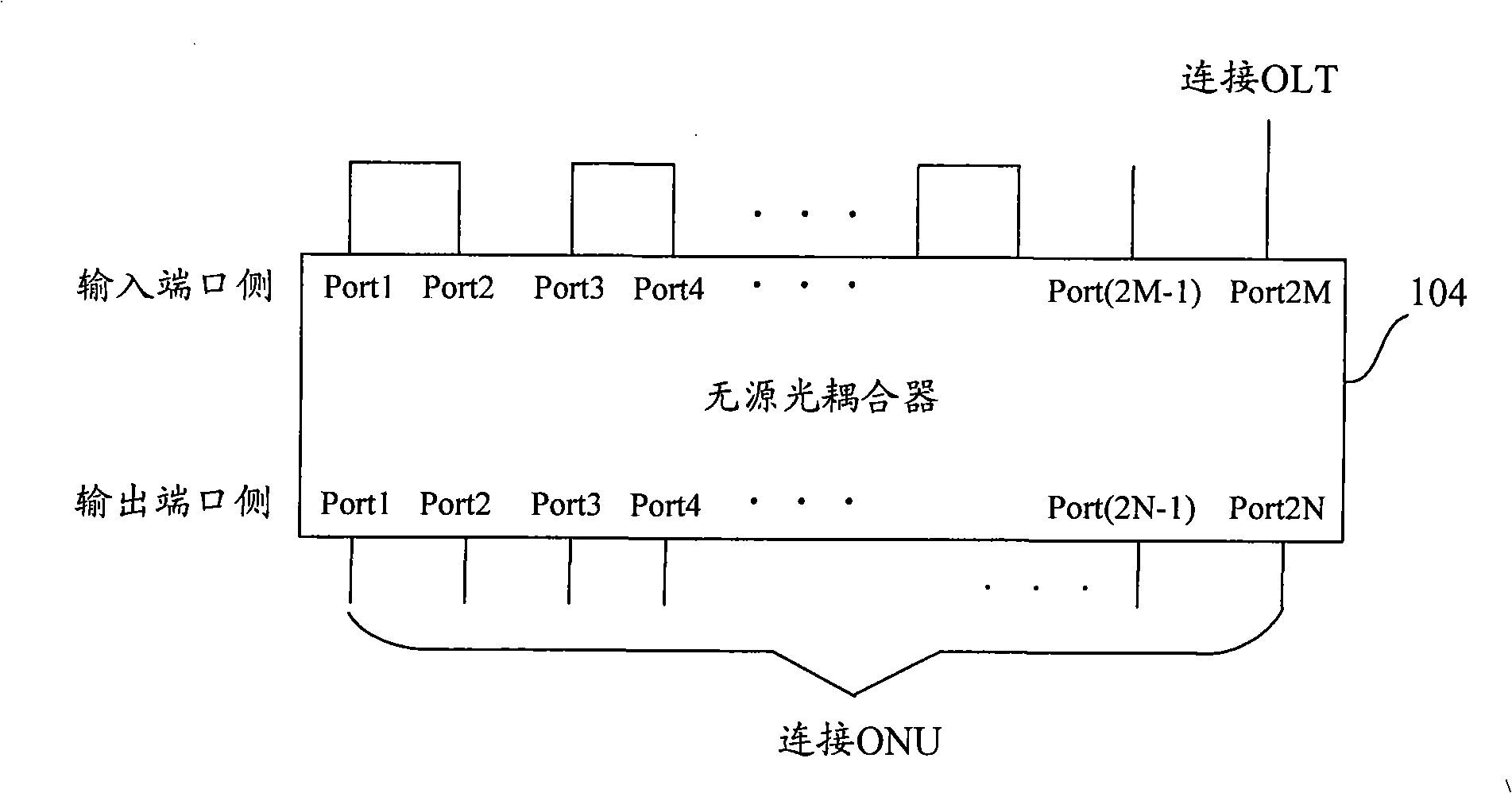
[0063] figure 2 It is a schematic structural diagram of the passive optical network system described in this embodiment. Such as figure 2 As shown, the OLT is provided with a set of optical transmitting and receiving modules TM1 / RM2, which are connected to the input port of the passive optical coupler through the main optical fiber 100 . The branch ratio of the passive optical coupler 104 (ie, the ratio of the input port to the output port) is 2M:2N, where M and N are both integers and M=N≧2. Each ONU is equipped with a set of optical transmitting and receiving modules TM2 / RM2 / RM1, which are respectively connected to the output port of the passive o...
Embodiment 2
[0100] Such as Image 6 As shown, the passive optical network system described in this embodiment includes an OLT, two passive optical couplers with a branch ratio of 2M:2N, and multiple ONUs. In this embodiment, the OLT is provided with two sets of optical transmitting and receiving modules TM1 / RM2, and each ONU is respectively provided with two sets of optical transmitting and receiving modules TM2 / RM2 / RM1. Please refer to Figure 7 , the first input port of the passive optical coupler 601 is connected to a set of optical transmitting and receiving modules of the optical line terminal OLT, and the first input port of the passive optical coupler 602 is connected to another set of optical transmitting and receiving modules of the optical line terminal OLT module, the remaining input ports of the passive optical coupler 601 are connected with the remaining input ports of the passive optical coupler 602 in pairs.
[0101] In this embodiment, each ONU specifically may include: ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com