Method for detecting aqueduct well by underwater robot
An underwater robot and aqueduct technology, applied in the direction of using optical devices, instruments, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of low measurement accuracy, high measurement difficulty, measurement interference from external factors, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
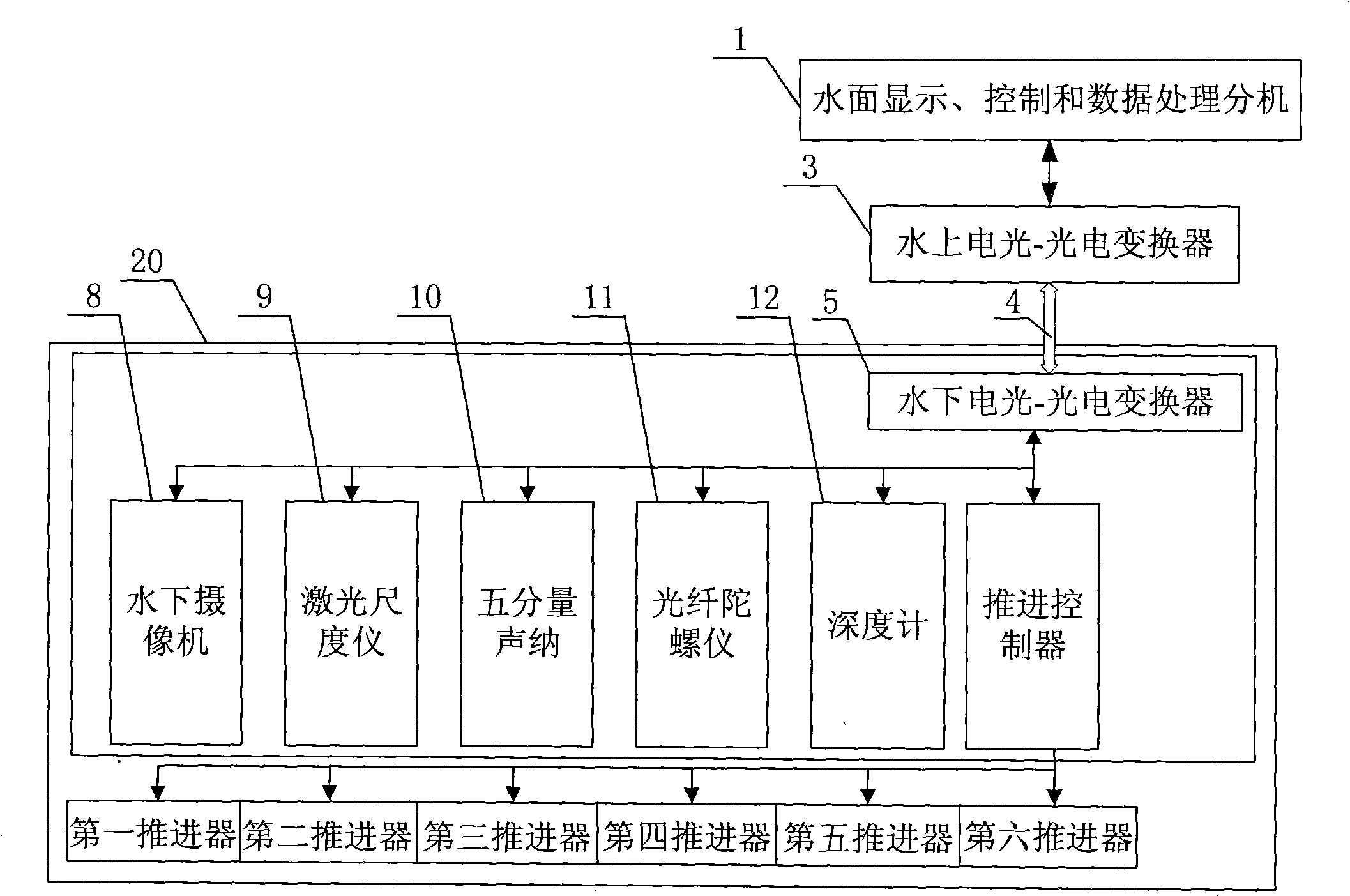
[0012] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 with figure 2 Describe this embodiment, in this embodiment, the underwater robot used for the inspection in the well of the aqueduct consists of a water surface display, control and data processing extension 1, an underwater camera 8, a laser scale 9, a five-component sonar 10, and a fiber optic gyroscope 11 , a depth gauge 12 and an underwater robot body 20;
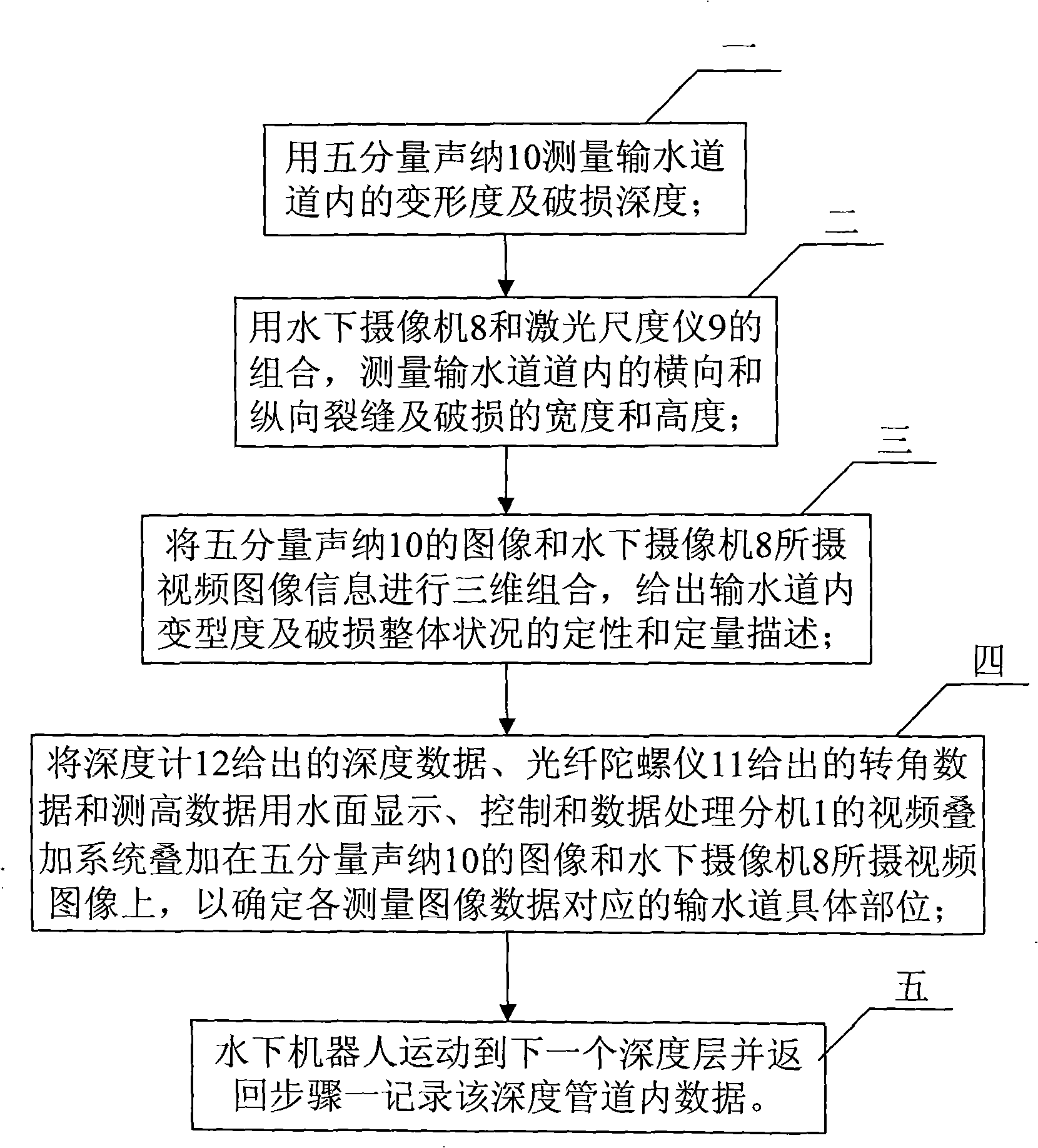
[0013] The steps of this embodiment are as follows:
[0014] Step 1: Measure the degree of deformation and damage depth in the water delivery channel with a five-component sonar 10;
[0015] Step 2: measure the width and height of transverse and longitudinal cracks and damage in the aqueduct with a combination of the underwater camera 8 and the laser scaler 9;
[0016] Step 3: Three-dimensionally combine the images of the five-component sonar 10 and the video image information captured by the underwater camera 8 to give qualitative and quantitative descriptio...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0020] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the five-component sonar 10 in step 1 is based on the principle of underwater acoustic ranging, respectively in four horizontal orthogonal directions and a vertical downward height measurement direction. Measure the data of five points, and with the movement of the robot, the water surface display, control and data processing extension 1 will connect the data of each measurement point transmitted from the underwater in real time into a line to form a circular image, so as to obtain a The deformation degree of the section and the measurement data of the damage depth. Other compositions and connection methods are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0021] Specific embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the underwater camera 8 in step 2 is driven by the movement of the underwater robot to perform a circular motion along the inner wall of the water delivery pipeline, so that the water delivery pipeline can be filmed Video image of the damage condition at the depth where the underwater robot is located on the inner wall. The parameters obtained for the video image of the damaged state are the length and width data of the damage. Other compositions and connection methods are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com