Gas measuring method and device thereof
A gas measurement and gas technology, applied in the measurement of color/spectral characteristics, etc., can solve the problems of difficult installation and debugging, limited measurement optical path, limited measurement accuracy, etc., to achieve low cost, reduce optical noise, and reduce optical noise. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] The following sections of this example describe a gas measurement device and method:
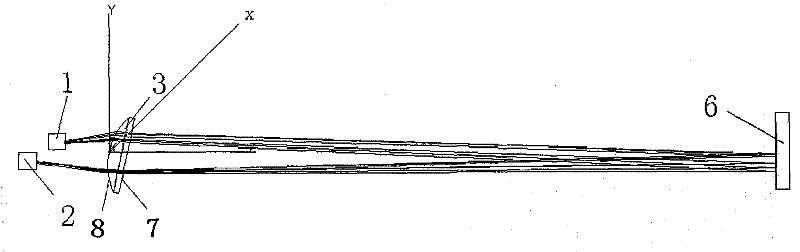
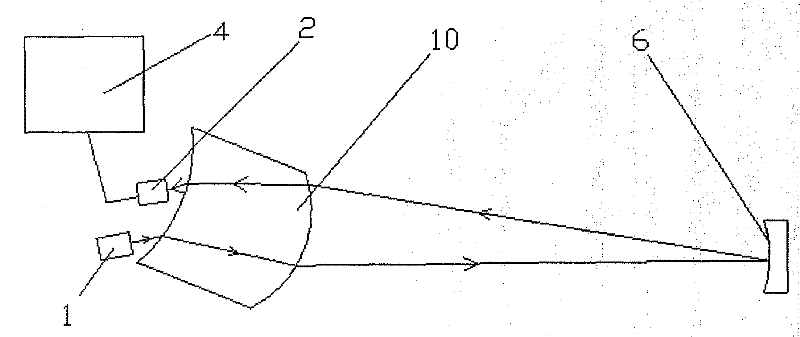
[0041] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, the gas measurement device includes a laser 1 , a sensor 2 , a plano-convex lens 3 , a concave mirror 6 , a support device 5 and an analysis unit 4 . The supporting device 5 is composed of a fixed cavity 11 and a measuring channel 12. One side of the measuring channel 12 is connected to the fixed cavity 11, and the other side is provided with a concave mirror 6. The laser 1, the plano-convex lens 3 and the sensor 2 are all installed in the fixed cavity 11. , the plano-convex lens 3 separates the laser 1, the sensor 2 from the gas in the measurement channel.
[0042] The laser 1 and the sensor 2 are arranged on the same side of the plano-convex lens 3, the plane of the plano-convex lens 3 faces the laser 1 and the sensor 2, and the position of the obliquely installed laser 1 in the Y-axis direction is lower than the sensor 2. Sensor 2 is...
Embodiment 2
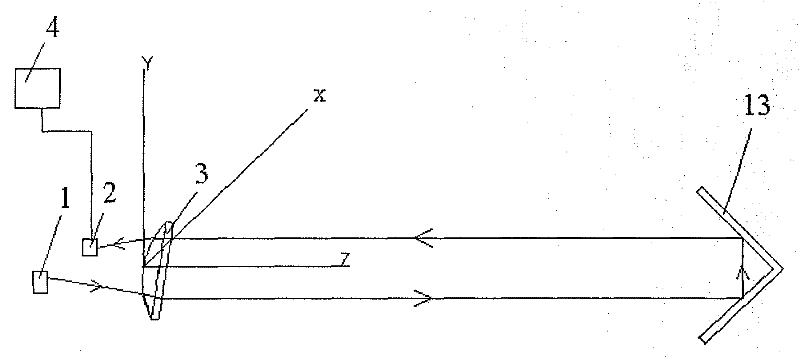
[0055] Such as Figure 4 , 5 As shown, this embodiment describes a gas measuring device and method, and the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is:
[0056] (1) The convex surface of the plano-convex lens 3 faces the laser 1 and the sensor 2, and the included angle between the main optical axis of the plano-convex lens 3 and the longitudinal axis of the measurement channel 12 is 13°.
[0057] (2) The angle between the central axis of the measuring light emitted by the laser 1 and the Z axis is 11.8°, so that the measuring light is obliquely incident on the optical curved surface 8 of the plano-convex lens 3 . The included angle between the central axis of the measuring light and the normal of the incident point on the optical curved surface 8 is 21°. In the present embodiment, the divergence angle of the measuring light is 13°, and the included angle between the measuring light and the normal of the optical interface at the incident point of the plano-convex ...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Such as Figure 6 , 7 As shown, this embodiment describes a gas measuring device and method, and the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is:
[0063] (1) The position of the laser 1 in the Y-axis direction is higher than that of the sensor 2, the convex surface of the plano-convex lens 3 faces the laser 1 and the sensor 2, and the included angle between the main optical axis of the plano-convex lens 3 and the longitudinal axis of the measurement channel 12 is 8 °.
[0064] (2) The angle between the central axis of the measuring light emitted by the laser 1 and the Z axis is 8.5°, so that the measuring light is obliquely incident on the optical curved surface 8 of the plano-convex lens 3 . The included angle between the central axis of the light beam and the normal line of the incident point of the optical curved surface 8 is 34°, and the divergence angle of the measured light is 13° in this embodiment. The method of measuring the light and its optical ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com