Traffic prioritization techniques for wireless networks
A wireless mesh network and prioritization technology, applied in the field of business prioritization technology for wireless networks, can solve the problems of insufficiently addressing the needs and complexity of wireless networks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
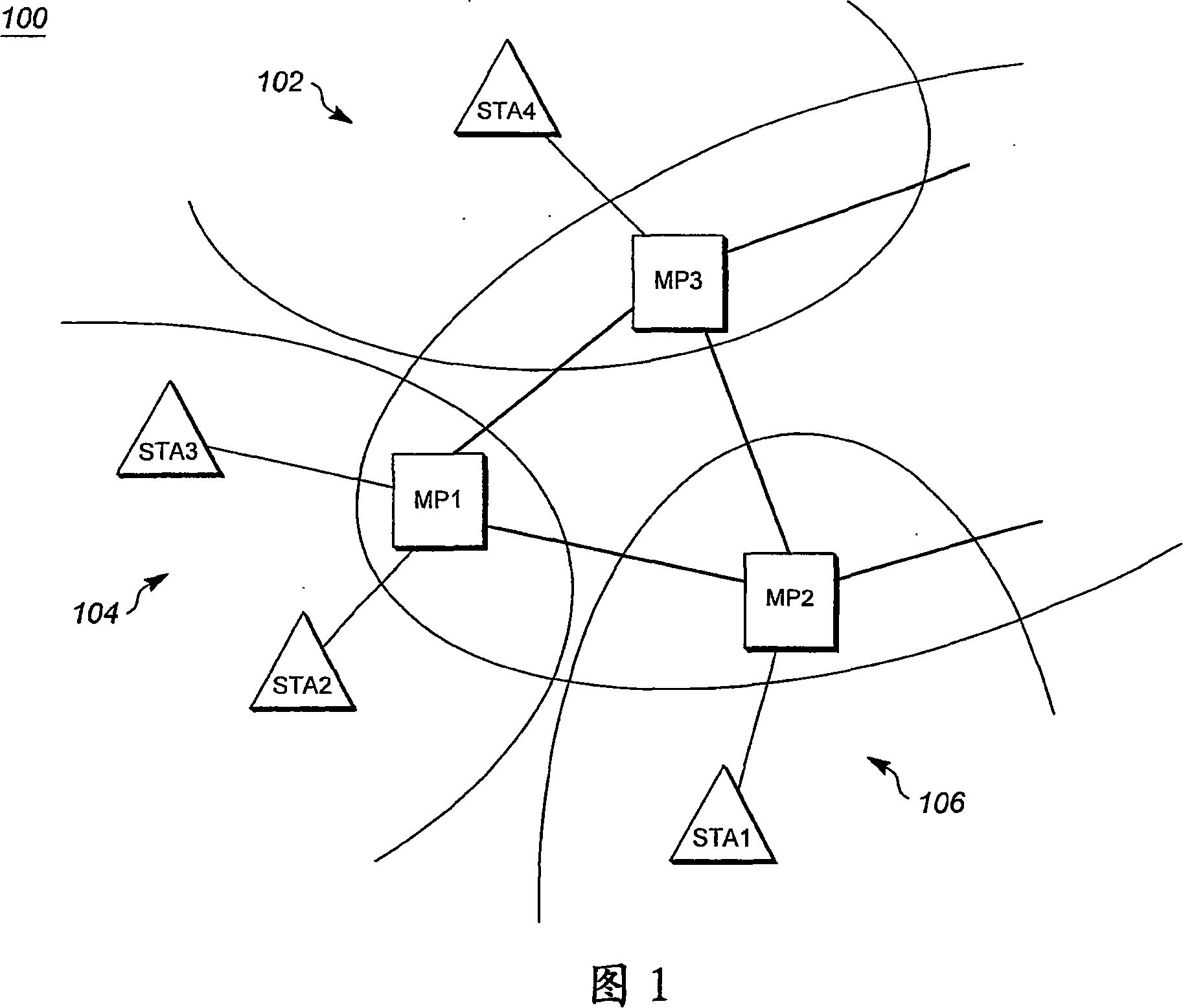
[0021] Referring to the drawings, in which like numerals indicate like elements, FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating a wireless mesh network 100 according to an exemplary embodiment.
[0022] According to an exemplary embodiment, a wireless mesh network may be a collection of mesh points (MPs) interconnected with wireless links. Each MP may typically be an access point, but may also be a station or other wireless node. For example, a wireless mesh network may employ a full mesh topology or a partial mesh topology. In a full mesh topology, each node (or mesh point) can be directly connected to each of the other MPs via wireless links. In a partial mesh topology, a mesh point may be connected to some of the other mesh points in the mesh network but not necessarily to all other mesh points in the mesh network.
[0023] In an example, the wireless mesh network 100 shown in FIG. 1 , the mesh points MP1 , MP2 , and MP3 may be connected to each other via wired links or wireless links....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com