Method and node equipment for improving mobile self-network grouping security
A mobile ad hoc network, node equipment technology, applied in security devices, data exchange networks, network traffic/resource management, etc. The effect of improving safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
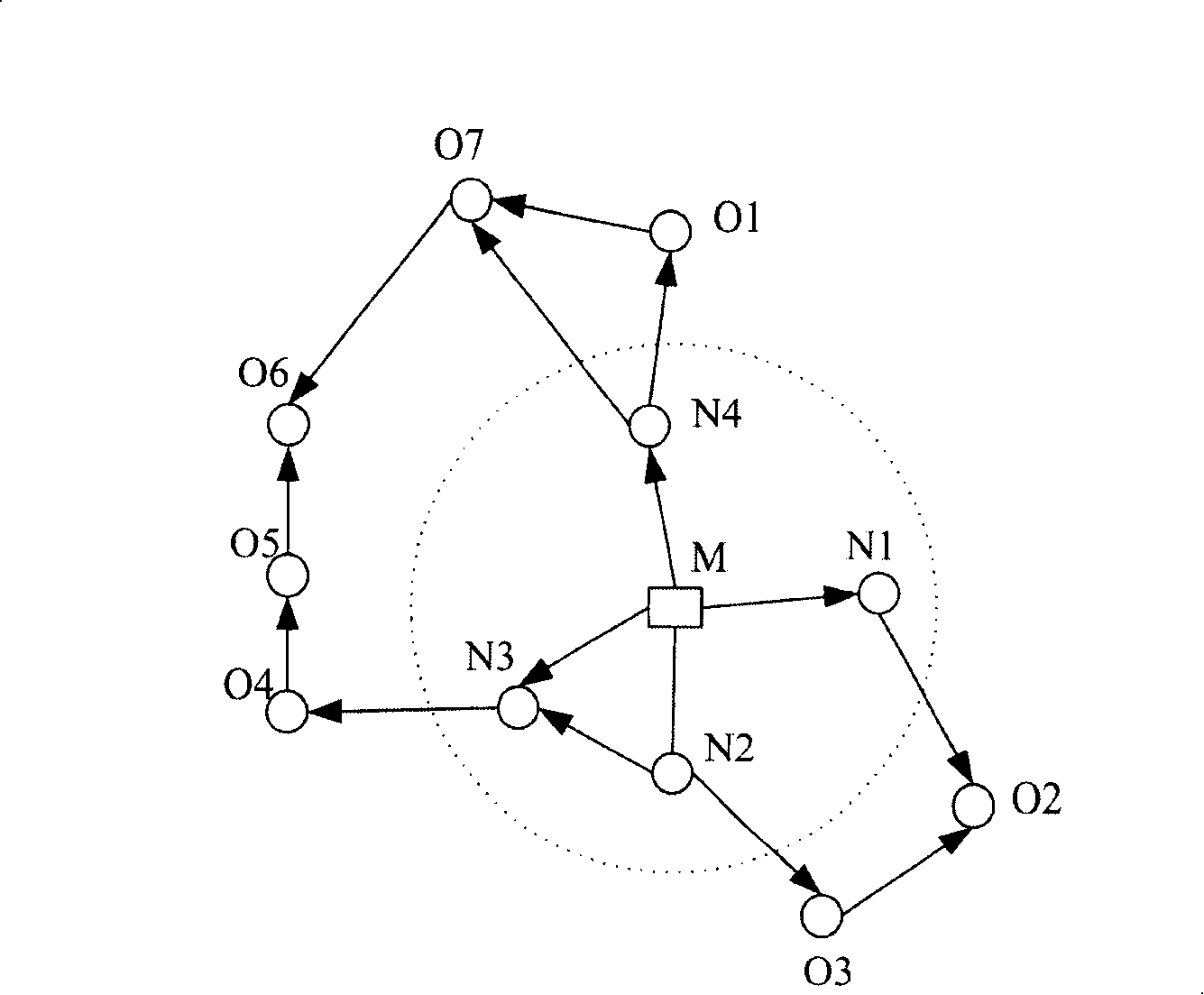
[0047] The route discovery process of AODV is as follows: the source node sends RREQ, and if the intermediate node has a fresh enough route to the destination node, it sends a route reply (Route Reply, RREP) to the source node; if the intermediate node does not have a fresh enough route to the destination node path, the RREQ is forwarded. The intermediate node will generate and save the corresponding routing table entry according to the RREQ. After the destination node receives RREQ, it will send RREP to the source node. When the source node receives the RREP, it selects an appropriate path, thus completing the route discovery process, and then the data packet is sent to the destination node along this path.
[0048] It can be seen that AODV sends RREQs to neighboring nodes by broadcasting, until the path to the destination node is found, the intermediate nodes will continue to broadcast this RREQ. When malicious nodes frequently send RREQs, the entire ad hoc network will be...
Embodiment 2
[0084]Compared with the first embodiment, the second embodiment mainly changes in the sequence of steps of increasing the RREQ counter and comparing the counter value with RREQ_th. In Example 1, first add 1 to C[A], and then compare C[A] and RREQ_th[A]; while in Example 2, first compare C[A] and RREQ_th[A], and then compare C[A] Add 1, that is, step 303 and step 304 are exchanged.
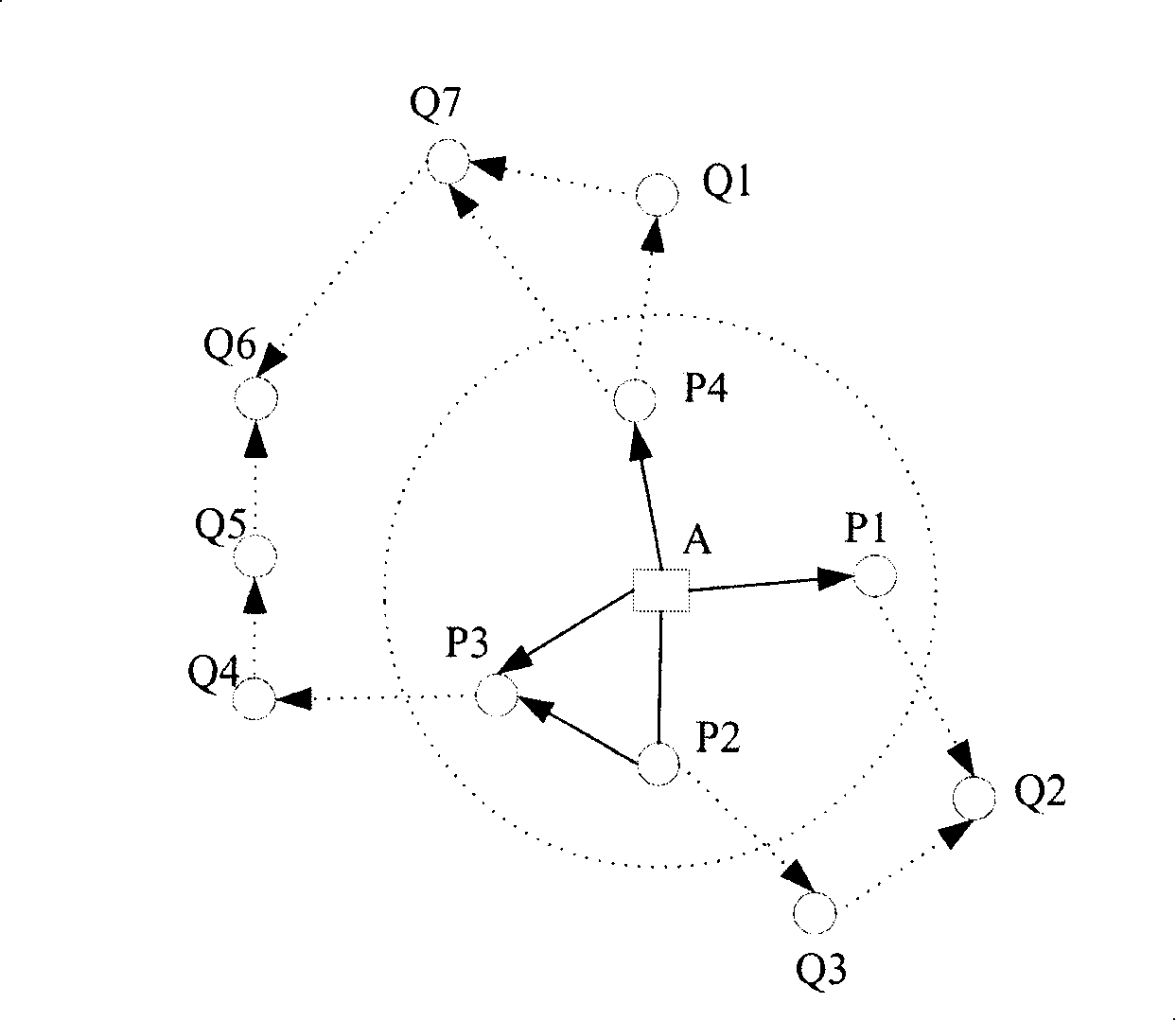
[0085] Also to figure 2 For example, node P1 sets RREQ_th[A]=3:
[0086] In Embodiment 1: when node P1 saves more than 3 RREQ routing entries from node A, it no longer saves routing entries for it, and does not forward RREQs for it at the same time, but the routing entry count value C[A] It will still be incremented, for example, when node P1 receives the fourth RREQ from node A, C[A]=4, when receiving the fifth RREQ, C[A]=5, and so on;
[0087] In the second embodiment: when the number of RREQ routing table entries from node A stored by node P1 exceeds 4, it will no longer save routing table i...
Embodiment 3
[0091] The working principle of ad hoc network DSR is similar to that of AODV. It also uses the source node to broadcast RREQ to find the route discovery process of the destination node. Among them, the intermediate node will generate and save the routing table entry for RREQ. The difference is that AODV records the routing information in the node, while DSR adds the routing information to the RREQ. When the destination node receives the RREQ, it will return the RREP to the source node according to the node position in the RREQ. DSR is a simple and effective routing protocol. It does not need to periodically update the routing information in the network, thereby omitting the routing overhead caused by maintaining routing information when there is no transmission task.
[0092] Because AODV does not maintain complete routing information and does not participate in the exchange of routing tables, it is a routing protocol that obtains routes on demand; and DSR is different from AO...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com