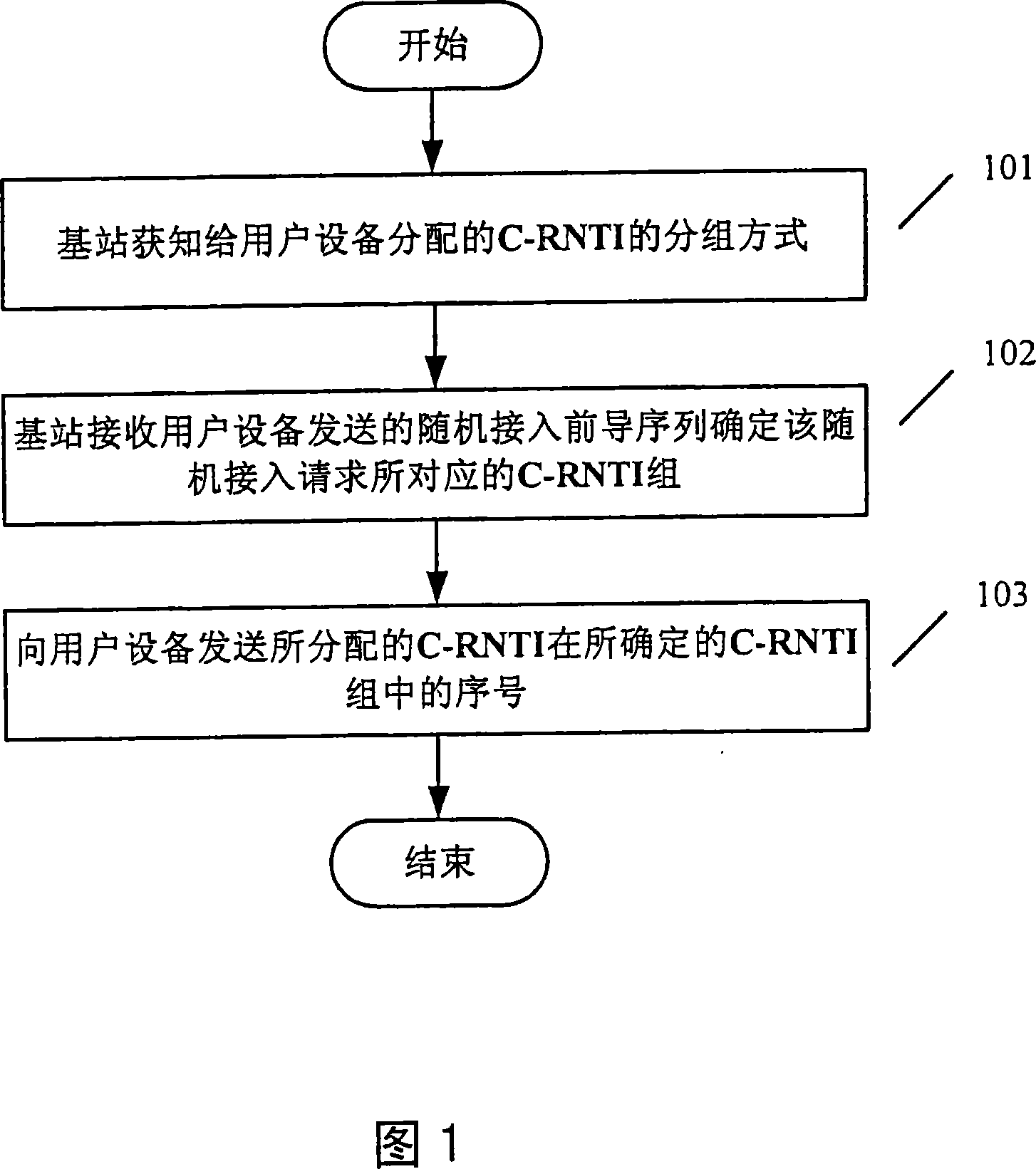
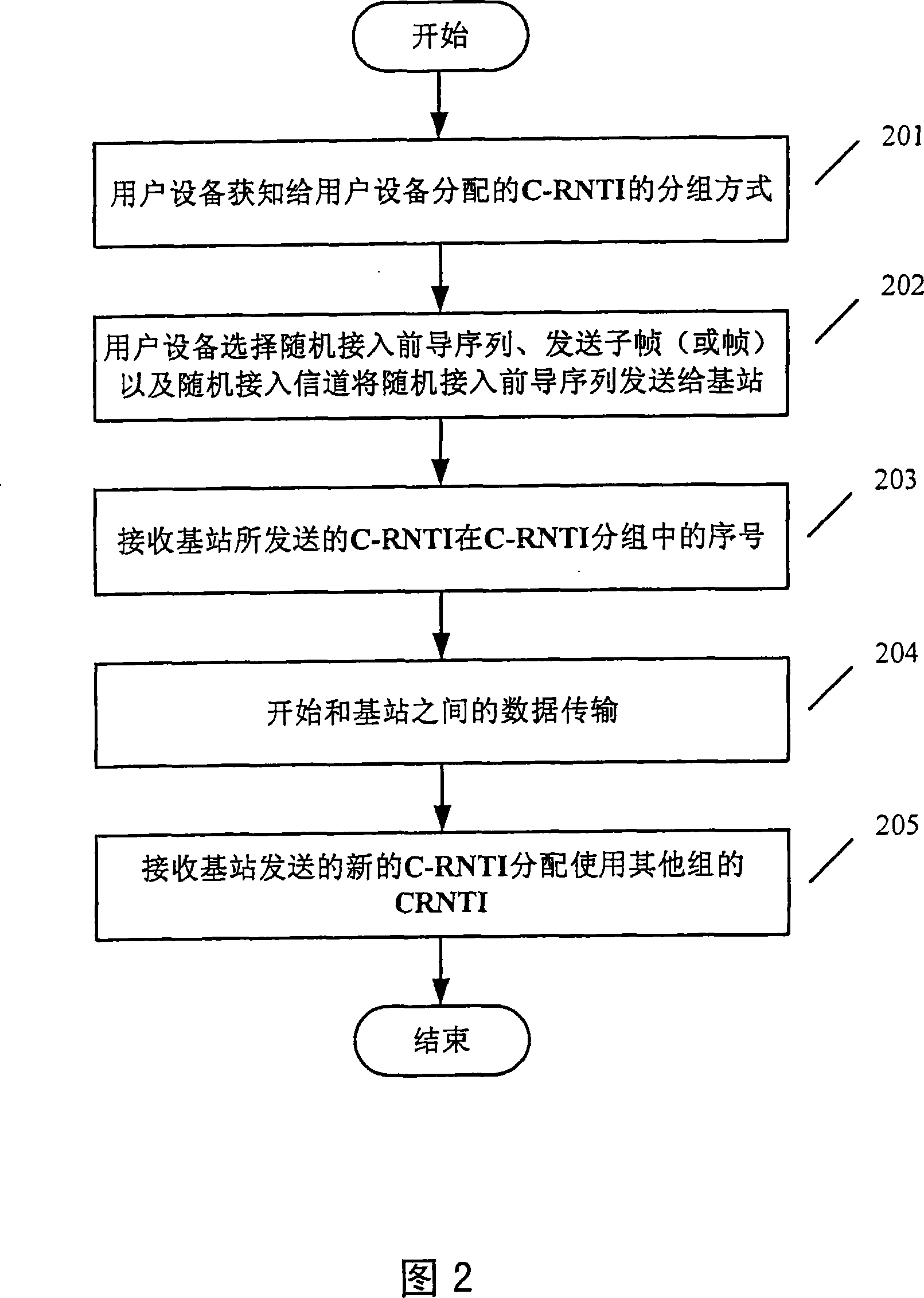
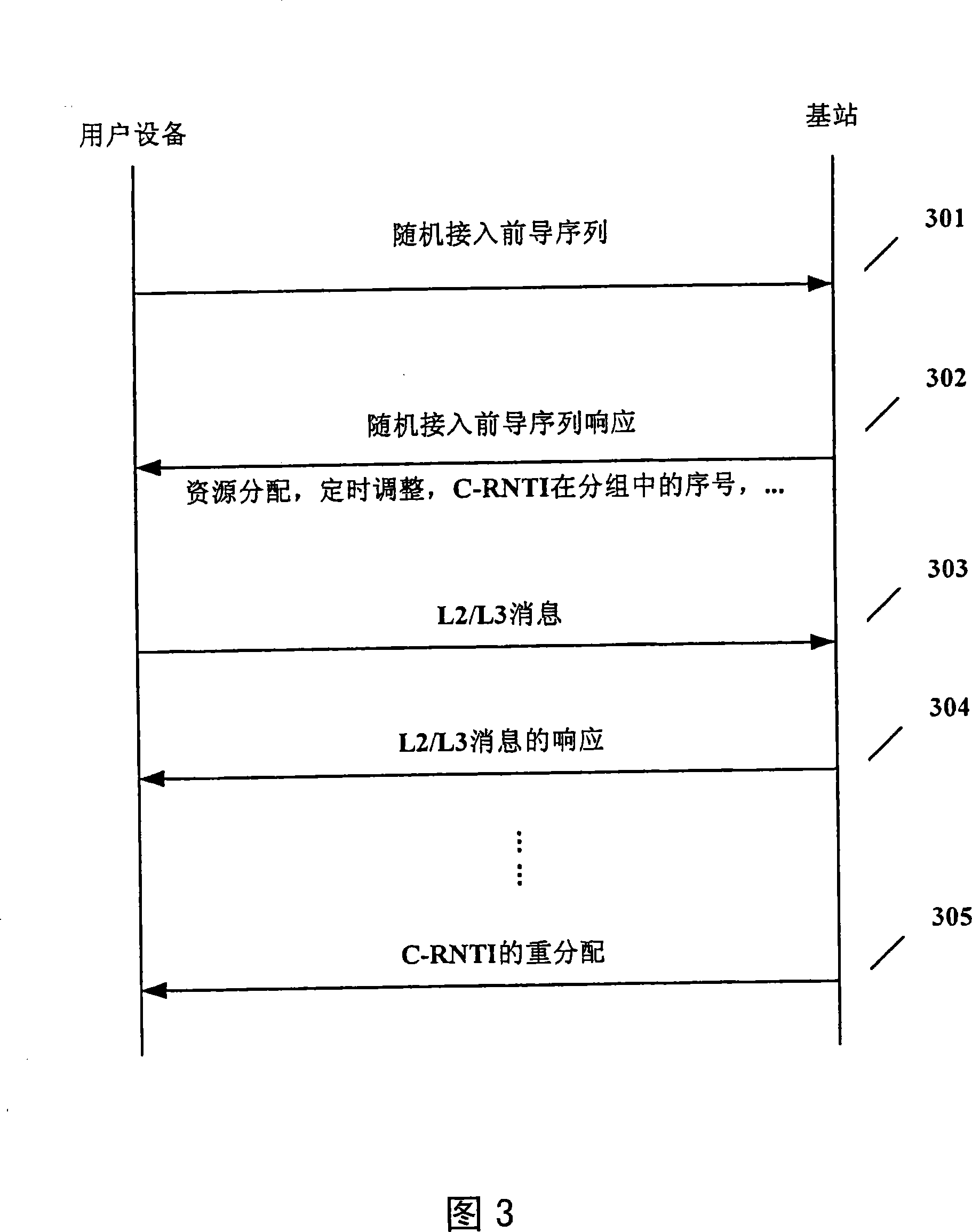
Method and device for distributing temporary recognition number of subdistrict wireless network
A network terminal and user equipment technology, applied in wireless communication, network data management, radio/inductive link selection and arrangement, etc., can solve problems such as long C-RNTI sequence length, heavy C-RNTI burden, and heavy signaling burden , to achieve the effect of optimizing the random access process, reducing the indication information bits, and reducing the signaling burden
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0145] The following assumptions are given here:
[0146] - The preamble sequence of random access is sent every 10ms interval;
[0147] - There are 4 subframes in every 10ms interval that can send the random access preamble;
[0148] - There is one random access channel (frequency band with 1.25MHz bandwidth) in each subframe that can send random access preamble;
[0149] - There are 64 random access preamble sequences available to the system, 32 of which are used to initiate an asynchronous random access request requiring C-RNTI allocation (the user equipment does not have a C-RNTI).
[0150] According to the above assumptions, the C-RNTI space of the system can be grouped as follows according to the method proposed by the present invention:
[0151] Table 5 The grouping method of the C-RNTI space in the first implementation of the C-RNTI allocation method proposed by the present invention in the embodiment
[0152] C-RNTI assignment
instruct
(...
Embodiment 2
[0159] The following assumptions are given here:
[0160] - The preamble sequence of random access is sent every 10ms interval;
[0161]- There are 4 subframes in every 10ms interval that can send the random access preamble;
[0162] - There is one random access channel (frequency band with 1.25MHz bandwidth) in each subframe that can send random access preamble;
[0163] - There are 64 random access preamble sequences available to the system, 32 of which are used to initiate an asynchronous random access request requiring C-RNTI allocation (the user equipment does not have a C-RNTI).
[0164] According to the above assumptions, the C-RNTI spatial grouping of the system can be given as shown in Table 5 according to the method proposed by the present invention.
[0165] It can be seen from Table 5 that the 65536 C-RNTIs in the C-RNTI allocation space are divided into 32×4=128 according to the different random access preamble sequences sent by the user equipment and the differ...
Embodiment 3
[0175] The following assumptions are given here:
[0176] - There are 64 random access preamble sequences available to the system.
[0177] According to the above assumptions, the C-RNTI spatial grouping of the system can be given as shown in Table 7 according to the method proposed by the present invention.
[0178] Table 7 Grouping method of C-RNTI space in embodiment 3
[0179]
C-RNTI allocation means
Show
leader sequence
sequence 0
sequence 1
...
sequence 63
group 0
Group 1
...
group 63
0000000000
C-RNTI 0
C-RNTI 1
...
C-RNTI 63
0000000001
C-RNTI 64
C-RNTI 64+1
...
C-RNTI 2 * 64-1
0000000010
C-RNTI 2 * 64
C-RNTI 2 * 64+1
...
C-RNTI 3 * 64-1
0000000011
C-RNTI 3 * 64
C-RNTI 3 * 64+1
...
C-RNTI 4 * 64-1
...
...
...
...
...
1111111110
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com