Viscous fluid-sealed damper
A technology of viscous fluid and shock absorber, which is applied in the field of shock absorption, and can solve the problems of poor bonding between the surrounding wall part 11 and the cover part 6, leakage of viscous fluid 10, long production time, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
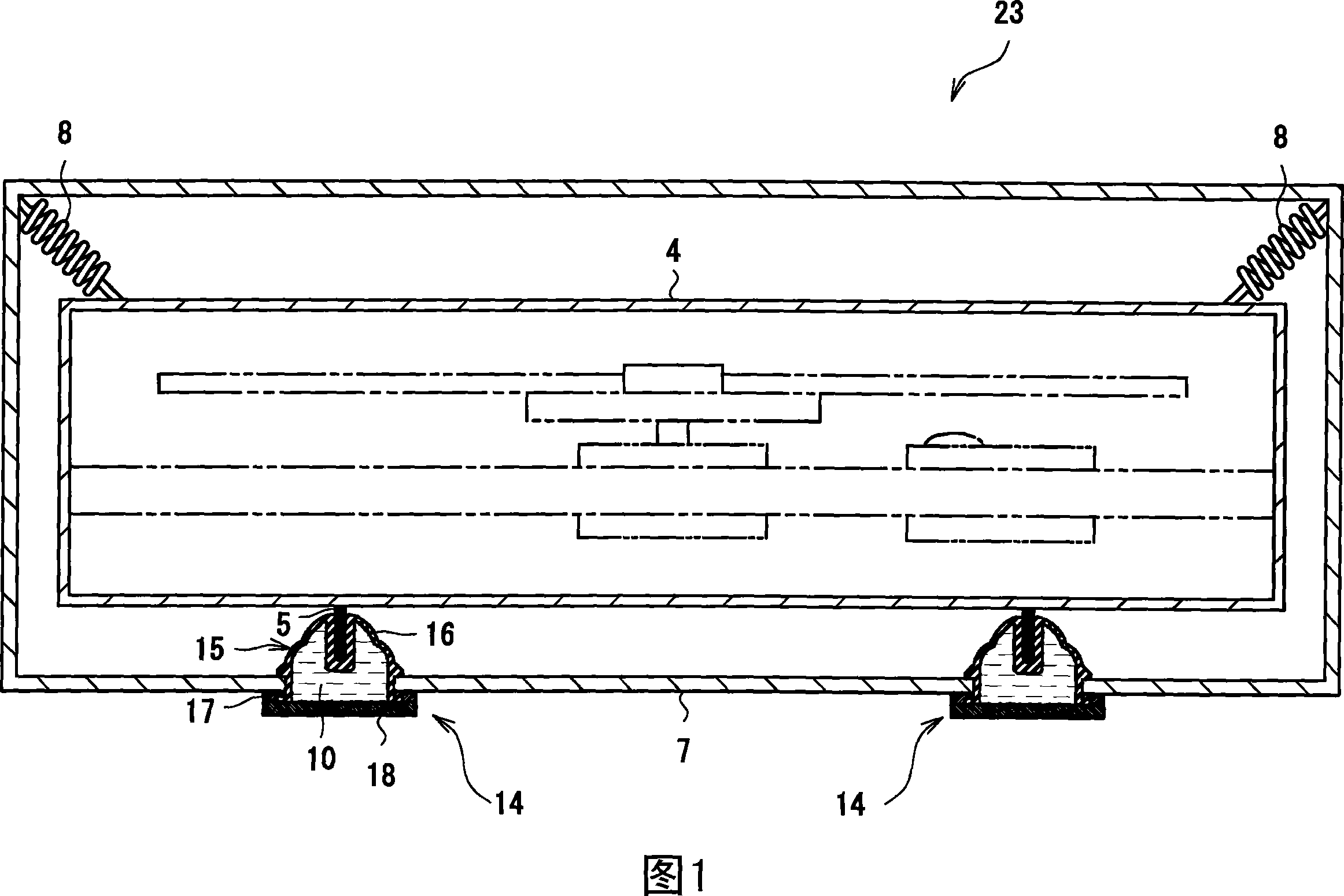
[0056] First Embodiment (Fig. 1 to Fig. 3)
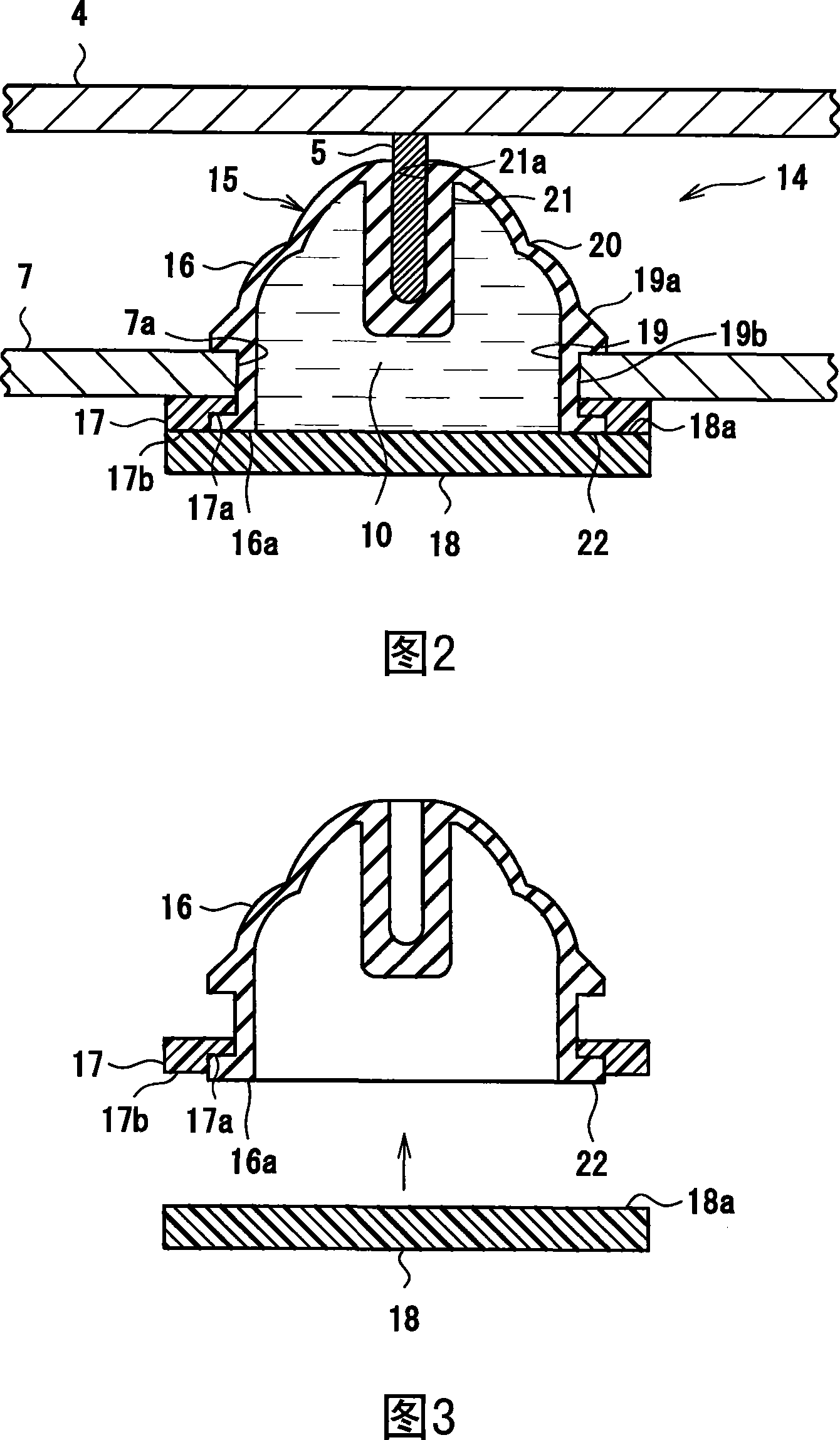
[0057] The viscous fluid-encapsulated damper 14 according to the first embodiment is shown in FIGS. 1 to 3 . The viscous fluid-enclosed shock absorber 14 of the first embodiment has a structure in which the viscous fluid 10 is enclosed in an airtight container 15 . The airtight container 15 is composed of a container body 16 , a sealing member 17 and a cover 18 .
[0058] The container body 16 is formed of a rubber-like elastic body, more specifically, butyl rubber, and has a hollow cup shape with one end open. The peripheral wall part 19, the flexible part 20, and the center attachment part 21 are formed from the opening end 16a side. Wherein, a flange portion 22 protruding outward is provided on the lower end side of the peripheral wall portion 19 along the entire circumference, and a protrusion 19a having an annular slope extending outward from the upper end side to the lower end side is provided on the upper end thereof. Betw...
no. 2 approach
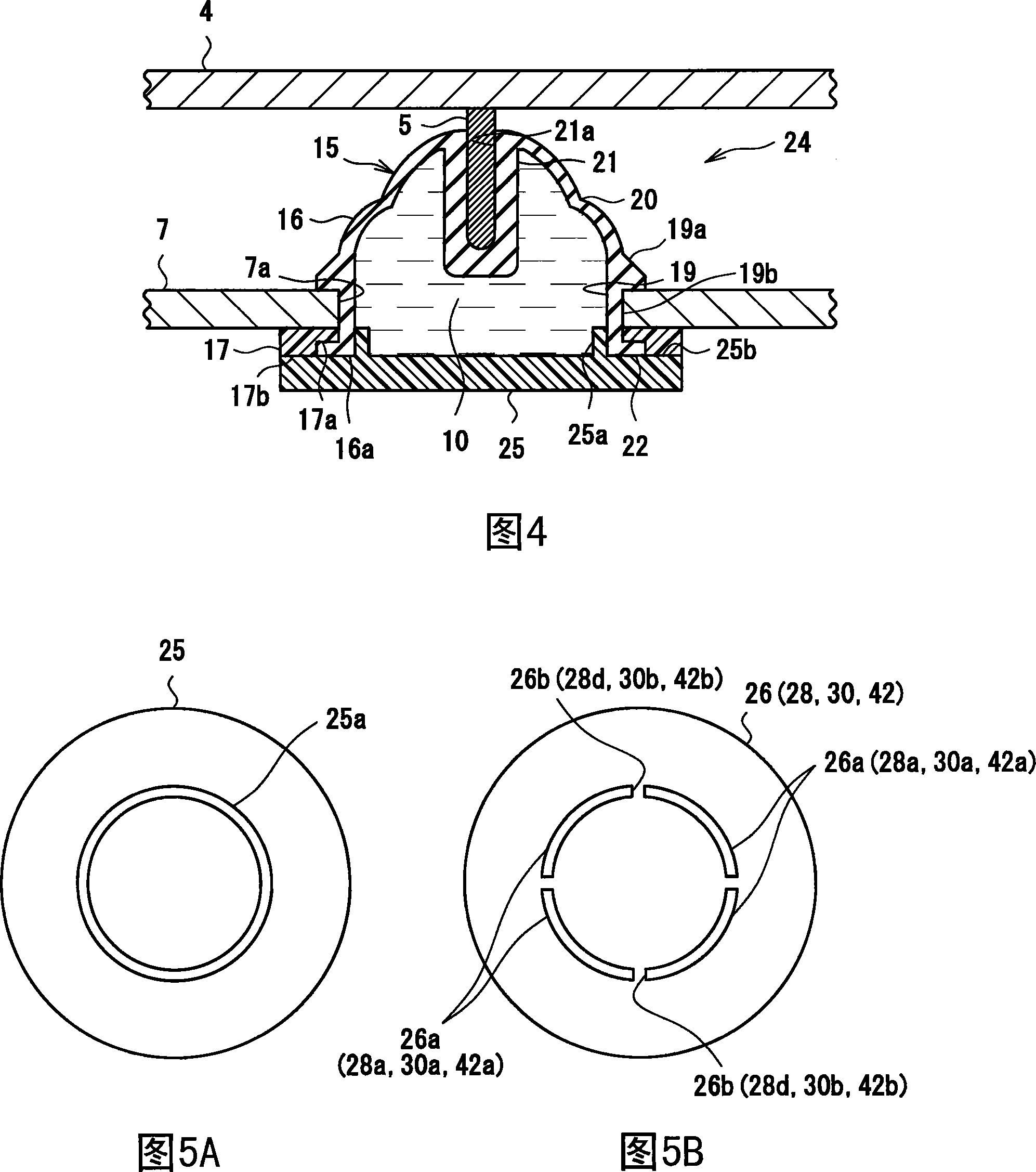
[0074] Second Embodiment (Fig. 4, Fig. 5A, Fig. 5B)
[0075] Encapsulation of the viscous fluid of the second embodiment into the damper 24 is shown in FIG. 4 , FIG. 5A , and FIG. 5B . The viscous fluid filled damper 24 in the second embodiment differs from the viscous fluid filled damper 14 in the first embodiment in the structure of the cover body 25 . The rest of the structure and its functions and effects are the same as those of the first embodiment.
[0076] The lid body 25 is formed with an endless annular protruding wall portion 25a that protrudes into the container body 16 and contacts the inner peripheral surface of the peripheral wall portion 19 of the container body 16 ( FIG. 5A ). The height of the protruding wall portion 25 a is the same as the thickness of the sealing member 17 . That is, the outer peripheral surface of the opening end 16a of the container body 16 is pressed by the sealing member 17 for compressing and holding the flange portion 22 of the peri...
no. 3 approach
[0082] Third Embodiment (FIG. 6)
[0083] Encapsulation of the viscous fluid in the shock absorber 27 of the third embodiment is shown in FIG. 6 . The viscous fluid filled damper 27 in the third embodiment differs from the viscous fluid filled damper 24 in the second embodiment in the structure of the cover body 28 . The rest of the structure and its functions and effects are the same as those of the second embodiment and the first embodiment.
[0084] Like the lid body 25 of the second embodiment, the lid body 28 is formed with an endless ring-shaped protruding wall portion 28a, and the protruding wall portion 28a protrudes into the interior of the container body 16 and is aligned with the inner periphery of the peripheral wall portion 19 of the container body 16. surface contact. Furthermore, a portion facing the fixed attachment surface 17b of the seal member 17 constitutes a fixed attachment surface 28b. However, the inner surface 28c of the lid body 28 is provided as a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com