Method for monitoring sensor function
A sensor and potential sensor technology, applied in the direction of instruments, scientific instruments, protection equipment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
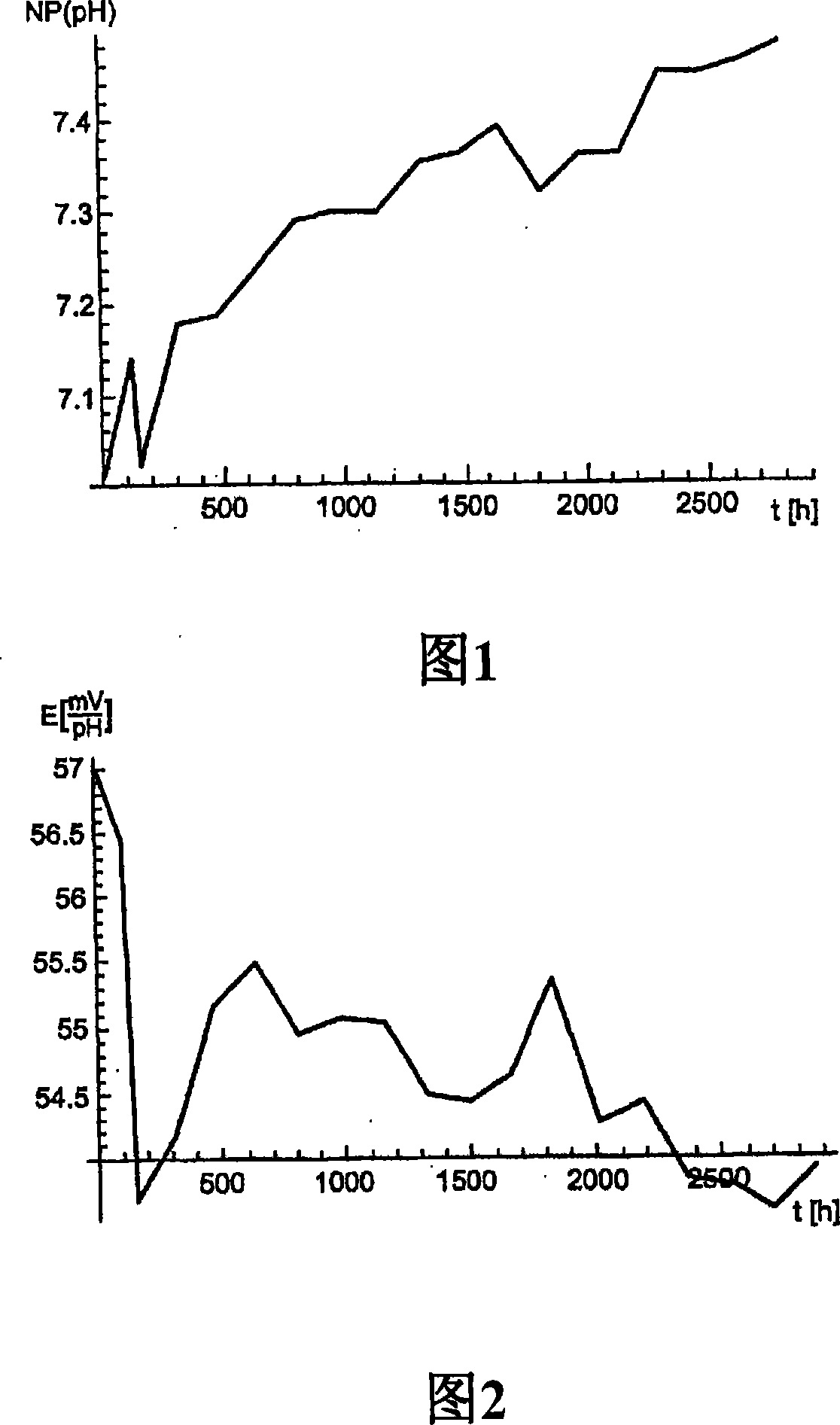
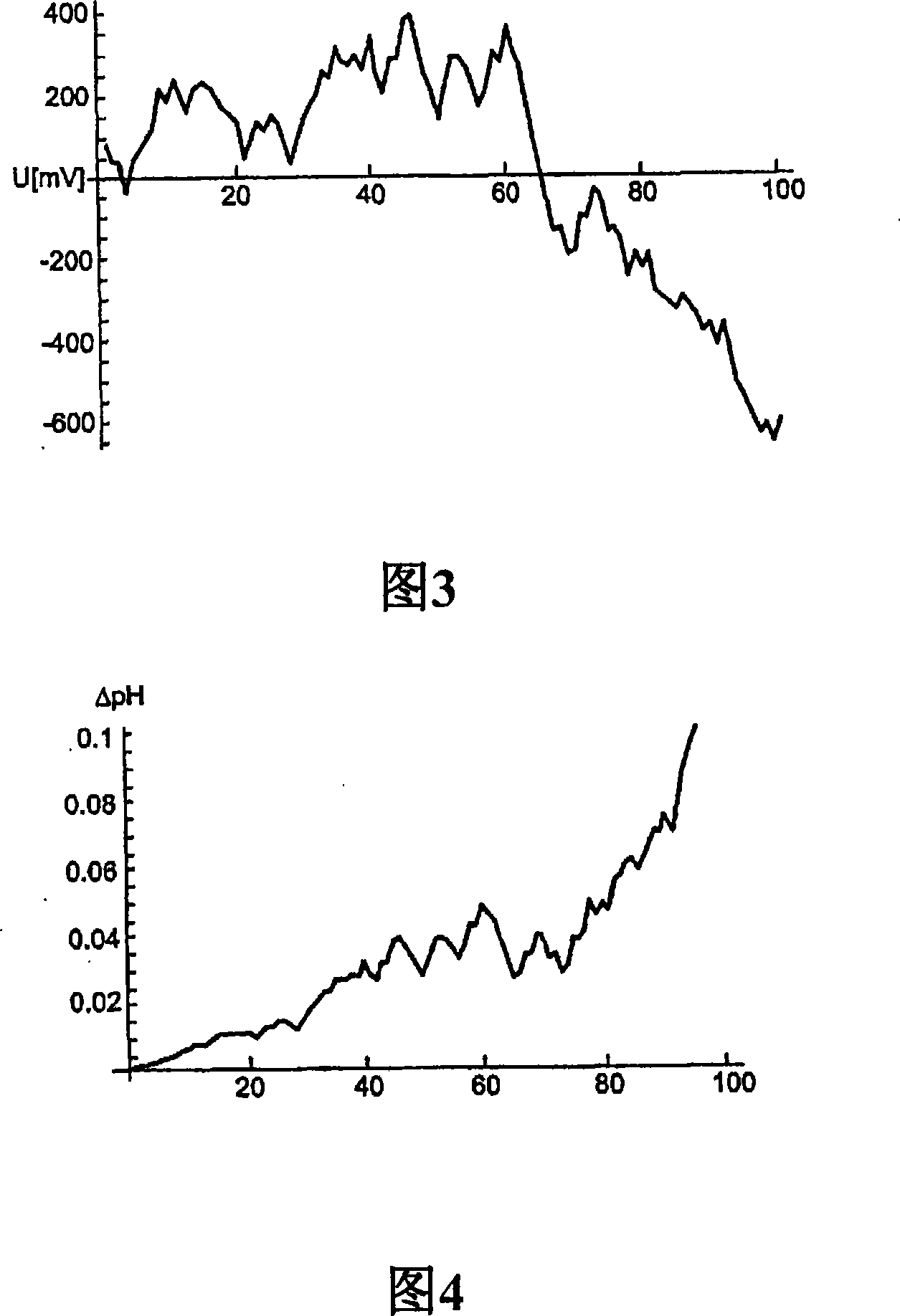
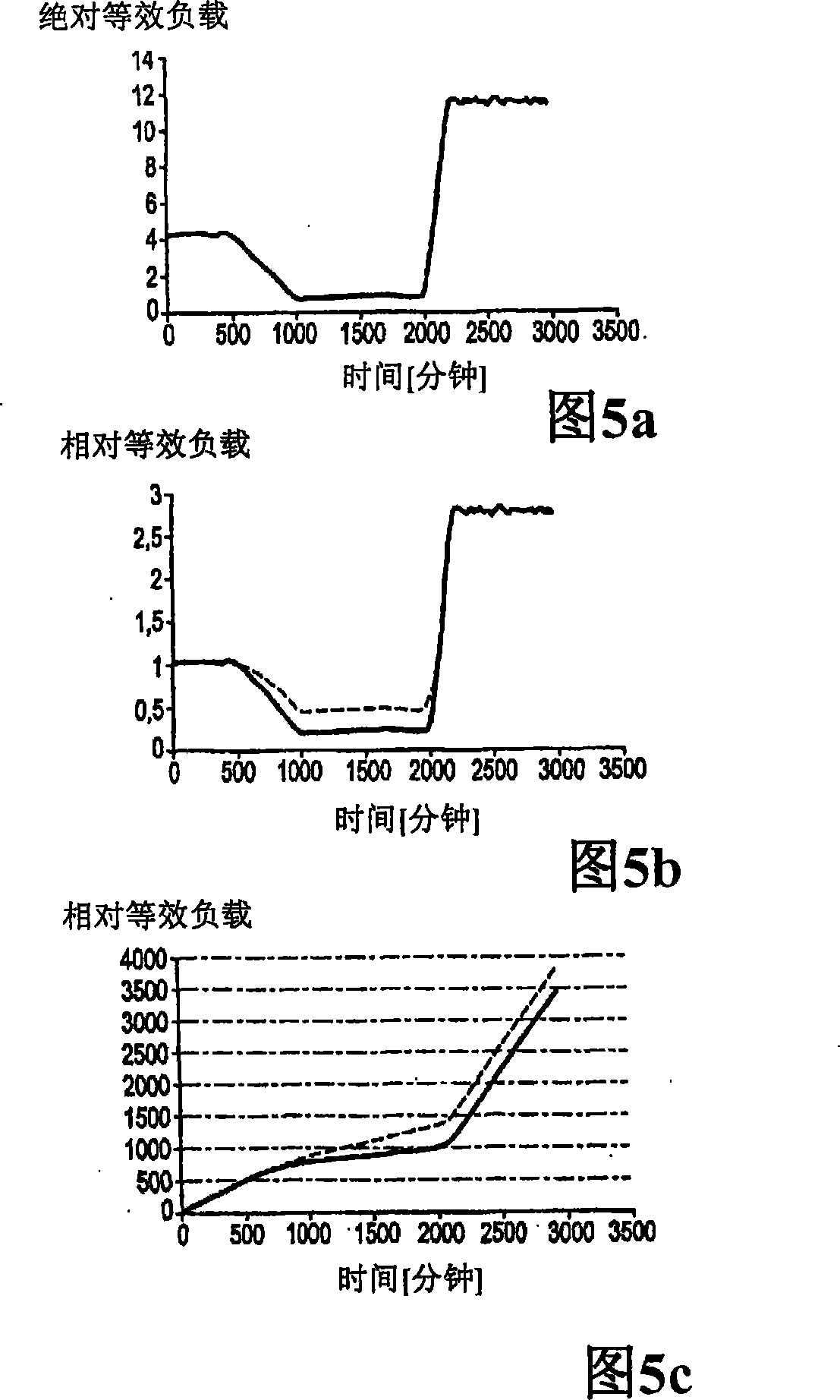
[0032] The graphs in Figures 1 to 4 relate to data from pH sensors. The basic characteristic quantities of the pH sensor are zero point NP and sensitivity E. These characteristic quantities must be calibrated at regular intervals to ensure the measurement accuracy of the measurement system.
[0033] Operating conditions affect changes in these characteristic quantities. The speed of change of these characteristic quantities reflects the operating conditions. Figures 1 and 2 show typical data for the time development of the zero point and sensitivity of a pH sensor. Each data point corresponds to a calibration value stored in the data set according to the present invention. Knowing the past time distribution, future changes can be inferred. In the simplest case, this is achieved by a smoothing function AE(t) for the sensitivity and ANP(t) for the zero point.
[0034] Figures 1 and 2 show the distribution of sensor data in 2820h. Determining the approximate development of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com