Method and device for multiplying and de-multiplying low speed service
A service multiplexing and demultiplexing technology, which is applied in the field of optical transport network, can solve the problems that OTN cannot bear the weight of data services and low-speed services cannot be multiplexed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
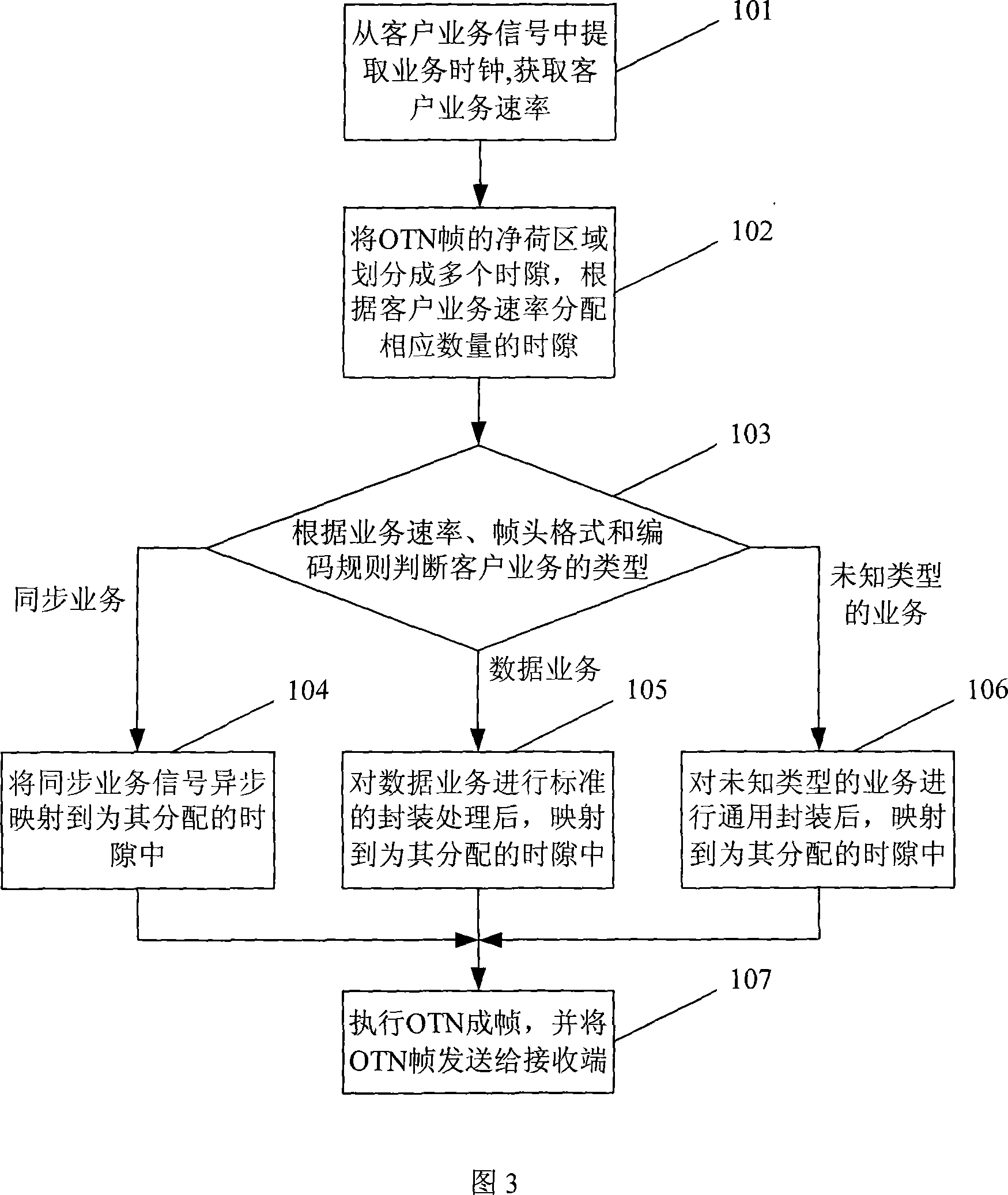
[0043] Referring to FIG. 3, an embodiment of the present invention provides a method for multiplexing low-speed services, which adopts a method of automatically identifying the type of low-speed services, and specifically includes the following steps:
[0044] Step 101: Perform clock data recovery processing on the accessed customer service signal to obtain the customer service rate.
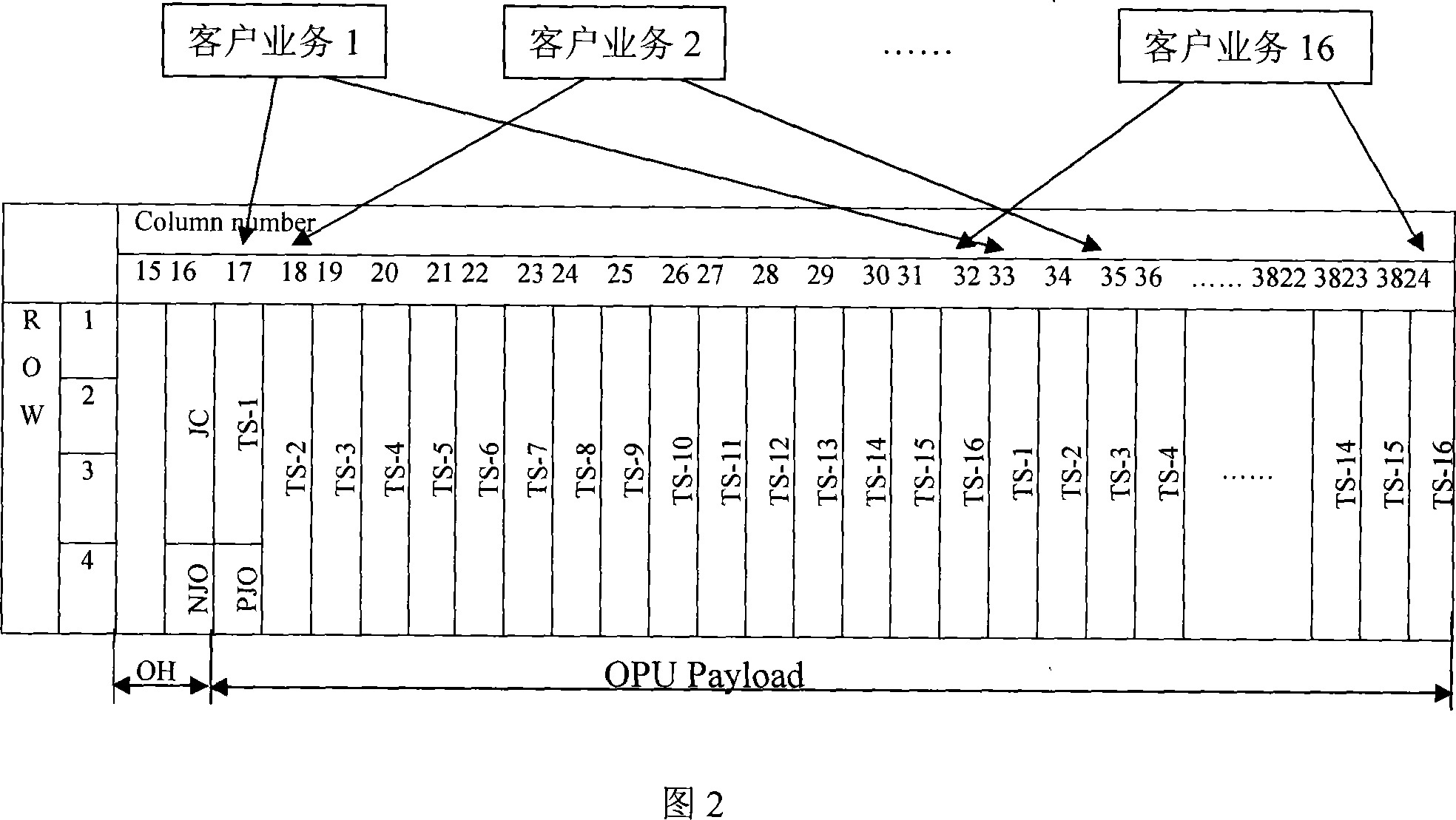
[0045] Step 102: Evenly divide the payload area in the OTN frame into multiple time slots, and allocate a corresponding number of time slots to each customer service signal according to the rate of each customer service signal.
[0046] All time slots have the same bandwidth, and the bandwidth of each time slot is the bandwidth of the payload area of the OTN frame divided by the number of time slots. There are various ways of allocating time slots to the OTN frame. For example, time slots can be allocated in a byte-interleaving multiplexing mode or a sequential mode, or can be allocated arbitr...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Referring to FIG. 6 , an embodiment of the present invention also provides a method for multiplexing low-speed services, which adopts a method of specifying a low-speed service type by a user, and specifically includes the following steps:
[0060] Step 201: The user specifies the customer service type and service rate, and the customer service types include synchronization service and data service.
[0061] Step 202: Evenly divide the payload area in the OTN frame into multiple time slots, and allocate a corresponding number of time slots for each customer service signal according to the rate of each customer service signal; all time slots have the same bandwidth , the bandwidth of each time slot is the bandwidth of the payload area of the OTN frame divided by the number of time slots. There are various ways of allocating time slots to the OTN frame. For example, time slots can be allocated in a byte-interleaving multiplexing mode or a sequential mode, or can be allo...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Referring to FIG. 8 , an embodiment of the present invention further provides a method for demultiplexing low-speed services, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0073] Step 301: Receive the OTN frame from the sender, and perform corresponding processing on the received OTN frame, including OTN framing, OTUk / ODUk layer overhead processing, and obtain OTUk OH, ODUk OH, OPUk OH, payload area, FEC , FAS and MFAS.
[0074] Step 302: Determine the mapping relationship between each time slot in the OTN frame and the client service according to PSI[2]-PSI[K+1] (K is the number of timeslots) in the OPUk OH, and determine the type of the client service.
[0075] Step 303: Determine the customer service type, if the customer service type is a synchronous service, go to step 304; if the customer service type is a data service, go to step 305; if the customer service type is an unknown type of service, go to step 306.
[0076] Step 304: Perform asynchronous demappin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com