Chromatographic exclusion agglutination assay and methods of use thereof
An aggregate, detected technology, used in measurement devices, biological testing, analysis by chemically reacting materials, etc., to solve problems such as lack of sensitivity and false positive results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0136] Embodiment 1: Detect Staphylococcus aureus
[0137] This example provides a device for the detection of methycillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureaus ("MRSA"). The feasibility and utility of the present invention was demonstrated with Pastorex Staph Plus (Biorad, #65356). As an experimental control, slide agglutination assays were performed on MRSA slurries according to the manufacturer's instructions. Moderate agglutination was observed in wells containing a mixture of test latex and MRSA, no agglutination was observed in wells containing a mixture of MRSA and control latex.
[0138] To identify suitable chromatographic media, suspensions of red latex test particles are applied to several types of media, including nitrocellulose and porous polyethylene. Choose a porous polyethylene membrane (Porex, Cat #181071) with suitable chromatographic properties. When untreated particles were applied to this membrane, the particles filled evenly into the pore volume, imparting ...
Embodiment II
[0141] Example II: Detection of Streptococcus agalactiae
[0142] This example provides a device for the detection of Streptococcus agalactiae ("StrepA").
[0143] Construct agglutination separation strips:
[0144] Materials for Constructing Agglutination Separation Strips:
[0145] -Millipore Nitrocellulose Membrane: 18 mm long, 6 mm wide (Millipore, Inc., Cat #PK002057; 100% Nitrocellulose Membrane)
[0146] - Bridge pads (Ahlstrom 1281; 90% cellulose fibers, 10% rayon, with traces of polyacrylamide wet strength resin and polyacrylamide dry strength resin)
[0147] - Absorbent pad (Ahlstrom 939; 100% cellulose with traces of polymide wet strength resin)
[0148] -Lexan backing plate (Lexan #8010)
[0149] Materials for construction of antibody capture strips:
[0150] -Millipore Nitrocellulose Membrane: 18mm long, 6mm wide (Millipore, Inc., Cat#PK002057)
[0151] - Bridge pads (Ahlstrom 1281)
[0152] - Conjugate pad (conjugate pad, Hollingsworth & Vose, H&V 7304 n...
Embodiment III
[0184] Example III: Detailed Practice of a Device for Detecting the Presence or Absence of One or More Analytes of Interest in a Test Sample
[0185] Implementation method
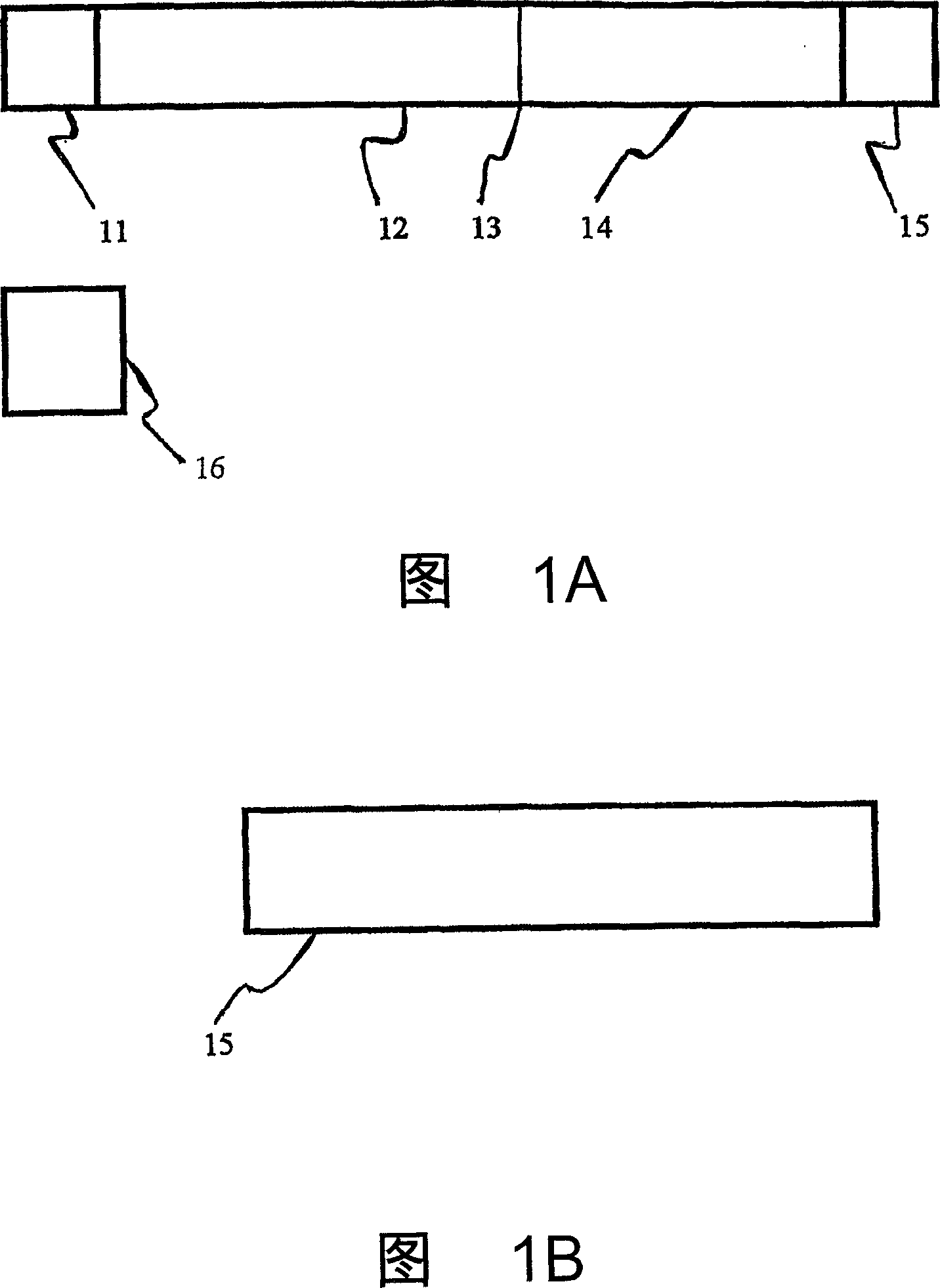
[0186] Referring to Figure 1A, the present invention includes an optional absorbent pad 11 fluidly connected to a first porous member 12 at one end thereof. The first porous part is in fluid communication with the second porous part 14 forming a connection 13 . An important aspect of the first porous member 12 of the present invention is that it is substantially capable of free passage of any detectable specific binding reagent through the first porous member 12 only when the detectable specific binding reagent is not bound to any analyte. . An important aspect of the second porous member 14 is that it is substantially capable of capturing or preventing any bound detectable specific binding reagent from flowing out of the second porous member 14, especially when the bound detectable specific binding reag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com