Variable valve system
A valve train, variable technology, applied in mechanical equipment, combustion engine, engine control and other directions, can solve problems such as valve body action angle and lift amount changes, and achieve the effect of avoiding the effect of temperature changes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0049] [Overall structure of variable valve train]
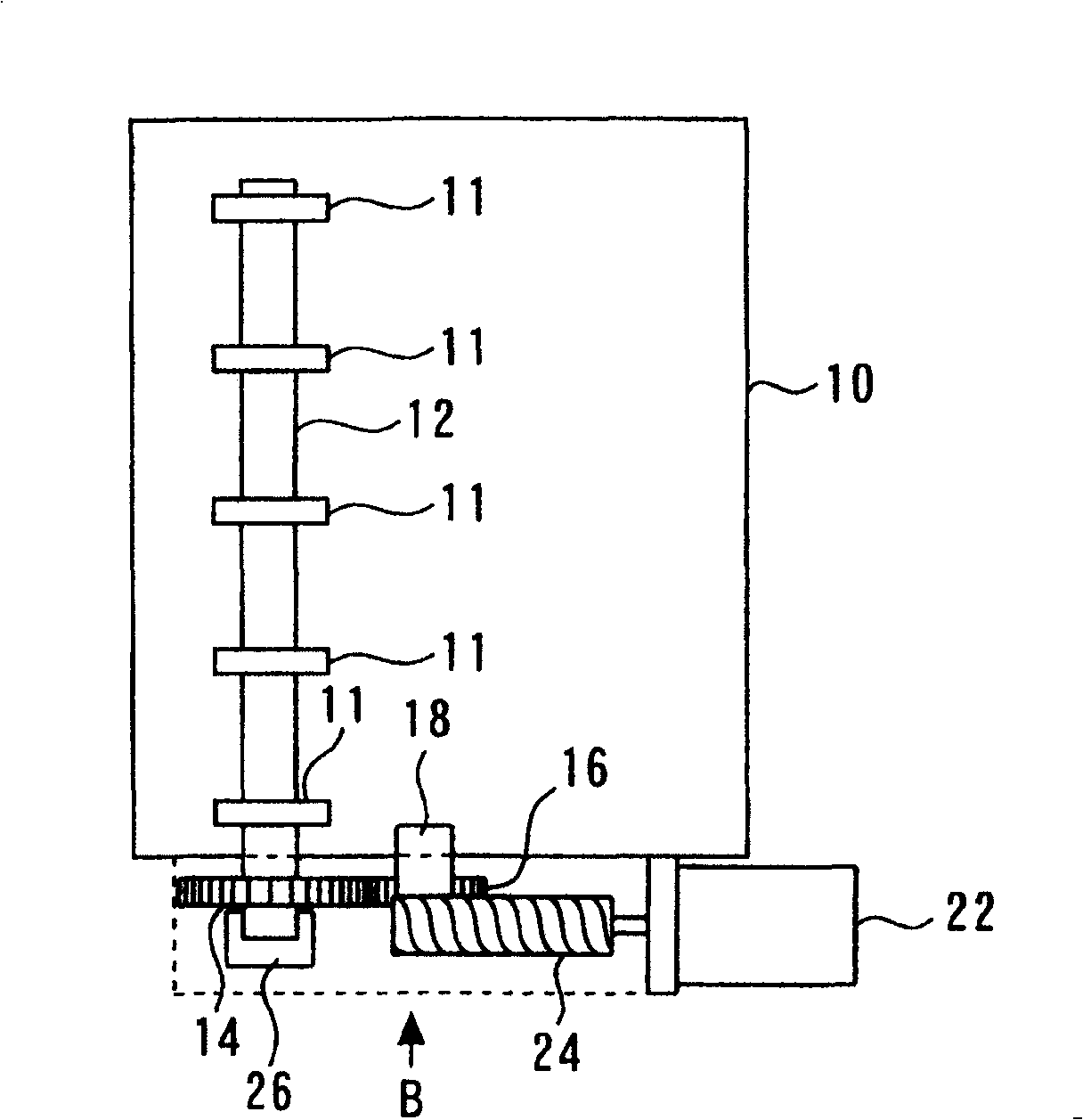
[0050] Figure 1A and 1B shows the overall structure of the variable valve train according to the first embodiment of the present invention; more specifically, Figure 1A is a plan view representing the entire variable valve train, and Figure 1B is from Figure 1A The side view when viewed from the B direction.
[0051] Figure 1A and 1B The illustrated structure includes a cylinder head 10 of an internal combustion engine. The cylinder head 10 has a plurality of control shaft bearings 11 located on both sides of each cylinder. The control shaft bearing 11 holds the control shaft 12 so that the control shaft 12 can rotate. The internal combustion engine of the present embodiment has four cylinders arranged in series. The control shaft 12 is arranged longitudinally across the four cylinders.
[0052] Each cylinder of the internal combustion engine has an intake valve and an exhaust valve, which are opened / closed synchr...
no. 2 example
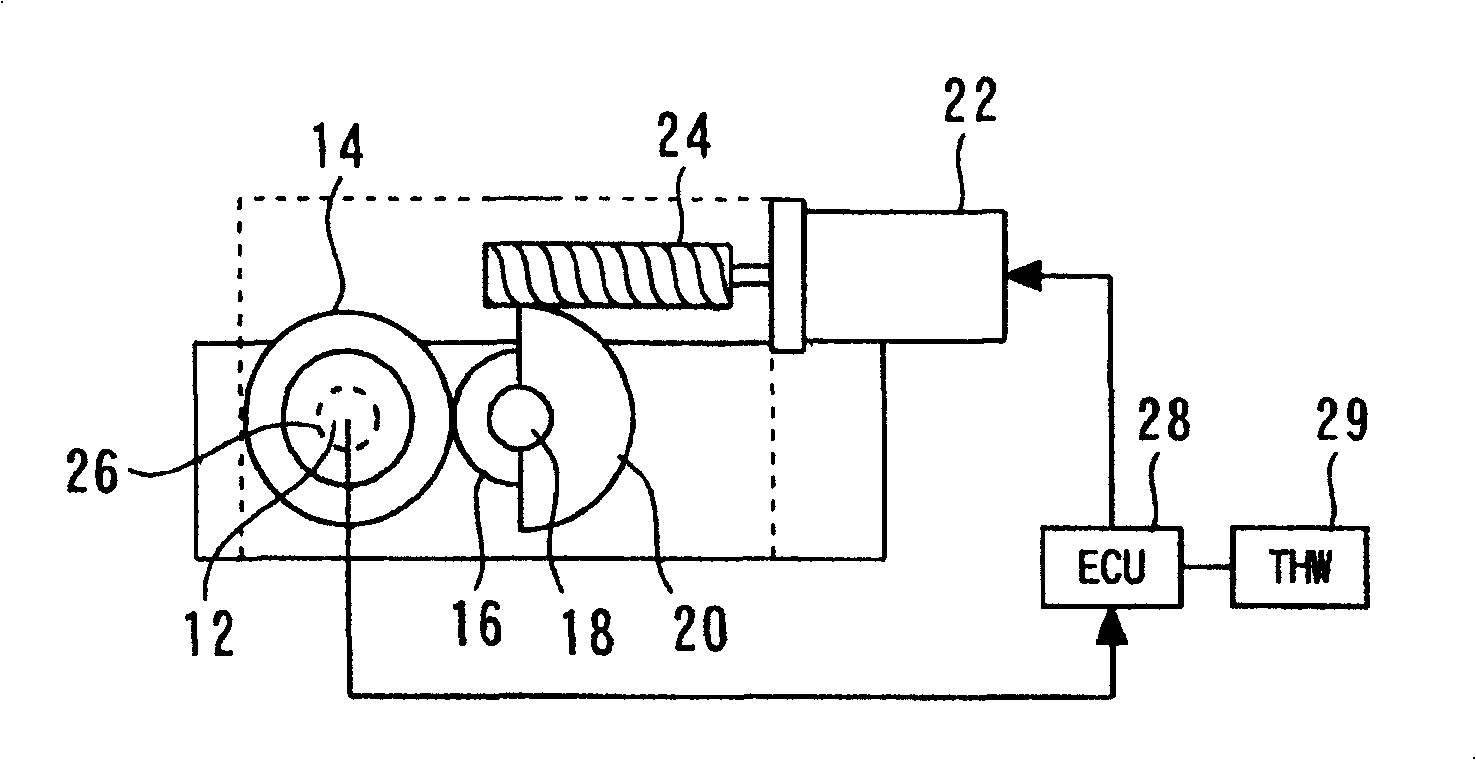
[0111] refer to Figure 1A to 5B describe the second embodiment of the present invention. The variable valve mechanism of the second embodiment has the same structure as that of the first embodiment. As far as the mechanism of the first embodiment is concerned, the components used to determine the distance between the control shaft 12 and the camshaft 72, that is, the distance L shown in FIG. The parts are made of materials with different linear expansion rates, and the angle of action can be corrected according to the ambient temperature of the cylinder head 10 to avoid the influence of thermal expansion and thermal contraction.
[0112] However, in the case of the variable valve mechanism of the second embodiment, the part for determining the distance L (that is, the cylinder head 10), and the part between the control shaft 12 and the camshaft 72 (that is, the first arm part) 44 and the second arm member 46) are made of materials with the same linear expansion rate to avoid...
no. 3 example
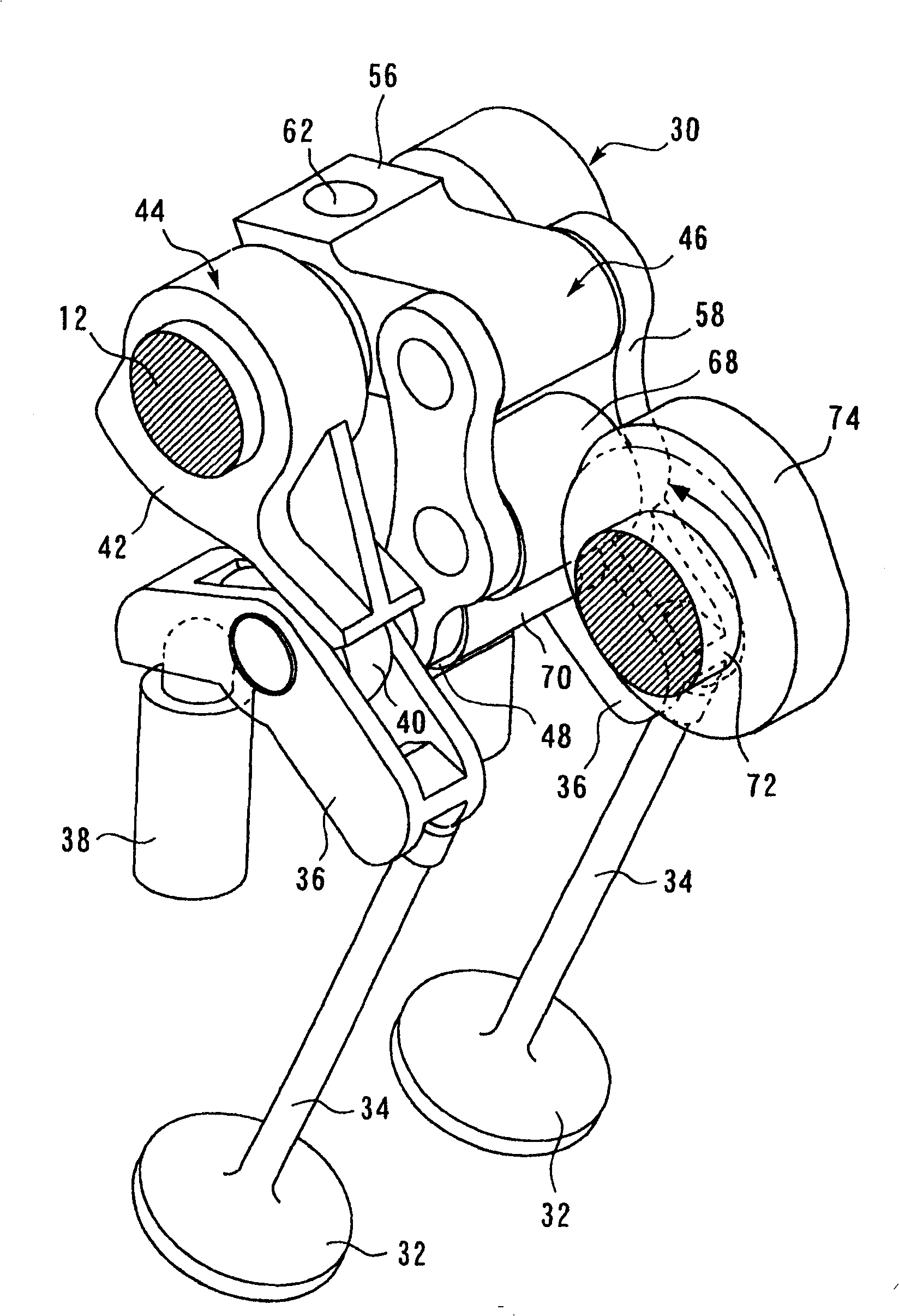
[0116] A third embodiment of the present invention is described with reference to FIGS. 8 to 10 . The variable valve mechanism of the third embodiment has the same structure as that of the first embodiment.
[0117] [Problems of the variable valve mechanism according to the present embodiment]
[0118] In order to properly operate the internal combustion engine, it is necessary to properly set the operating angle and the lift amount according to the operating state of the internal combustion engine. More specifically, when the internal combustion engine is started, it is necessary to set the operating angle and lift amount to be suitable for starting. However, when the internal combustion engine is stopped, the operating angle and the lift amount are not always set to a state suitable for starting the internal combustion engine. Therefore, for an internal combustion engine equipped with a variable valve train, it is necessary to correct the operating angle and lift amount wi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com