Volume control for audio signals
a volume control and audio signal technology, applied in the field of audio signal processing, can solve the problems of increased headroom from dolby a-type to dolby sr and digital releases, serious dialogue intelligibility problems, and inability to match the increase in power amplifier and loudspeaker capability with the increase in headroom, so as to reduce the maximum loudness, reduce the overall loudness, and avoid complaints
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
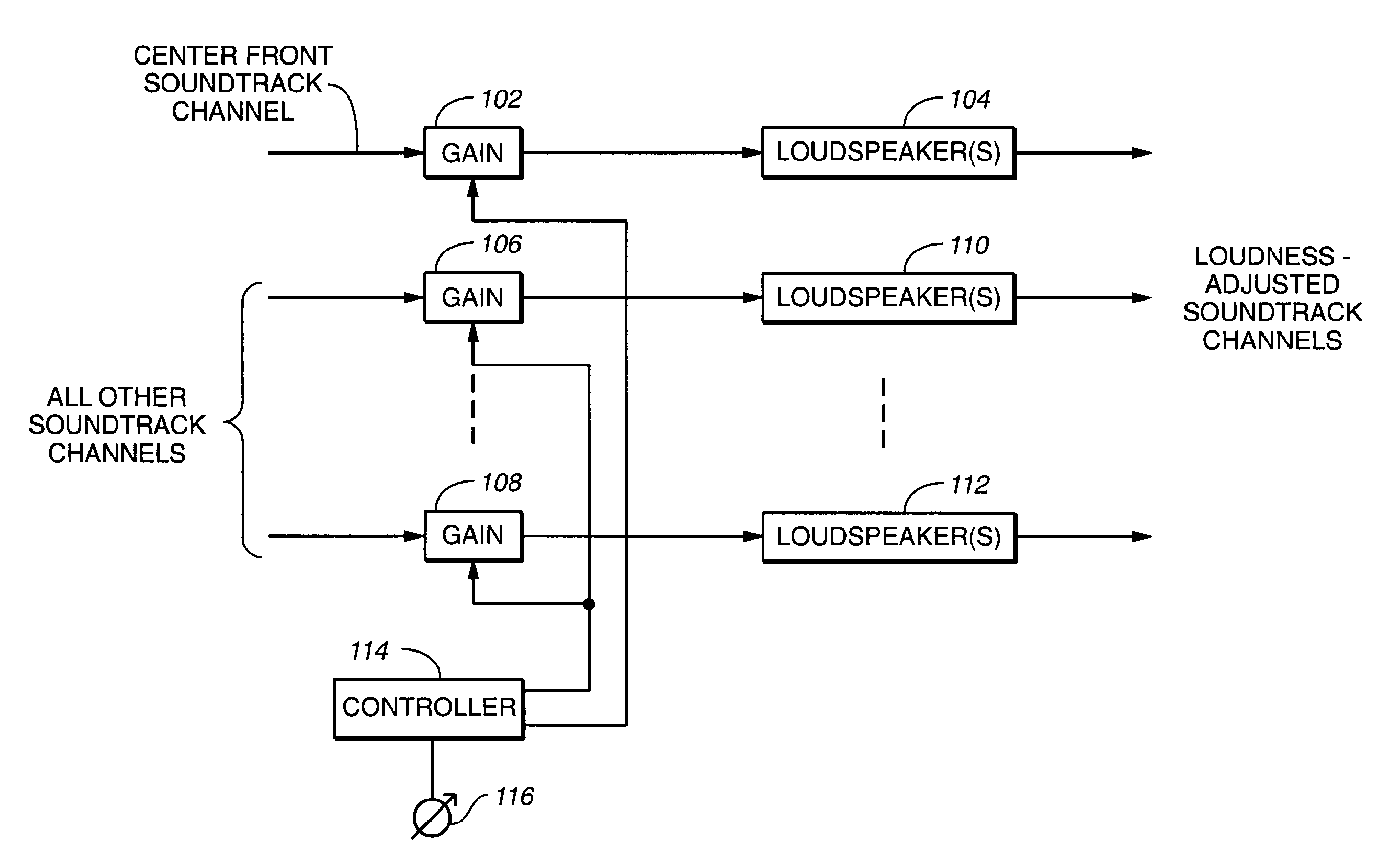
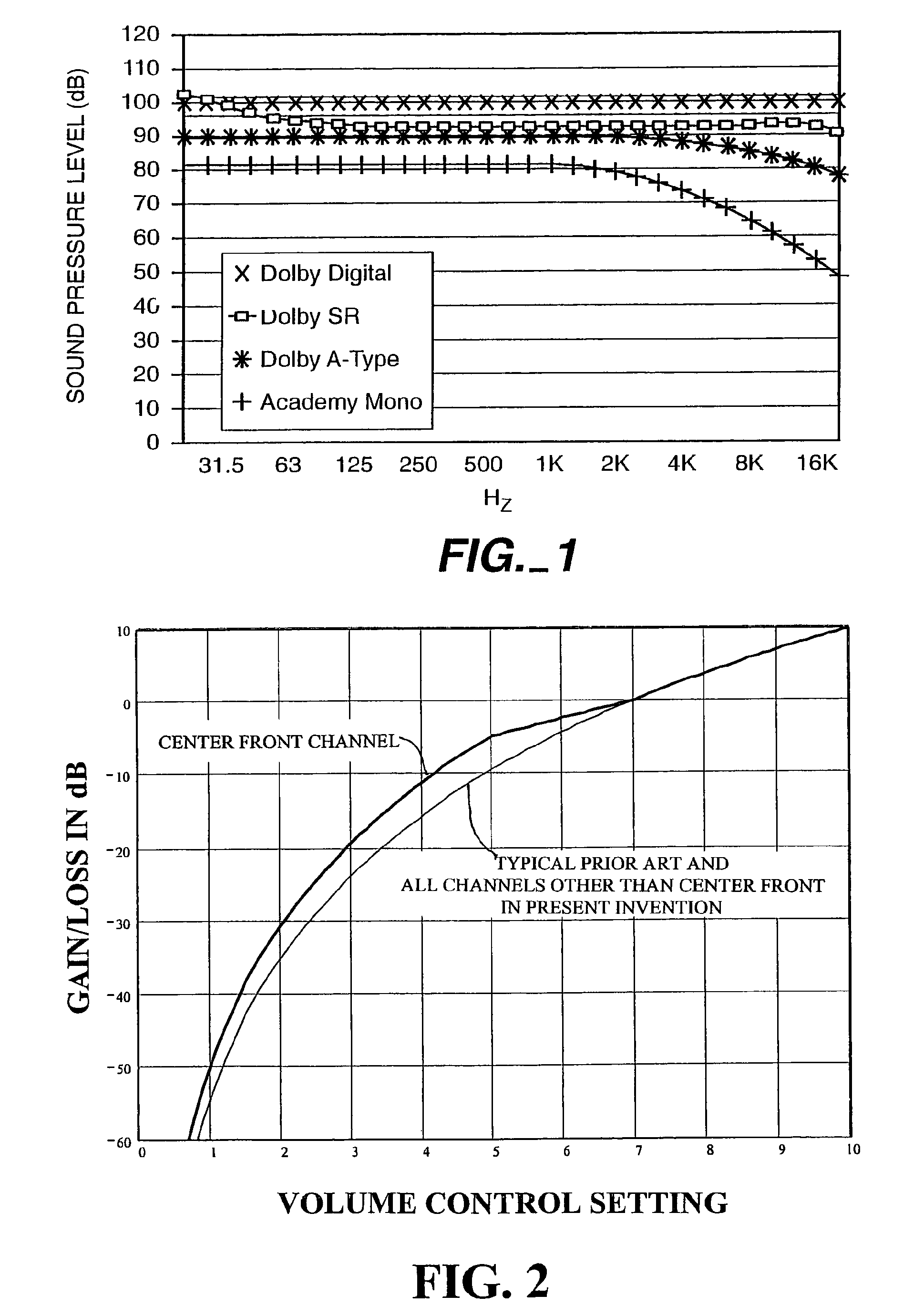
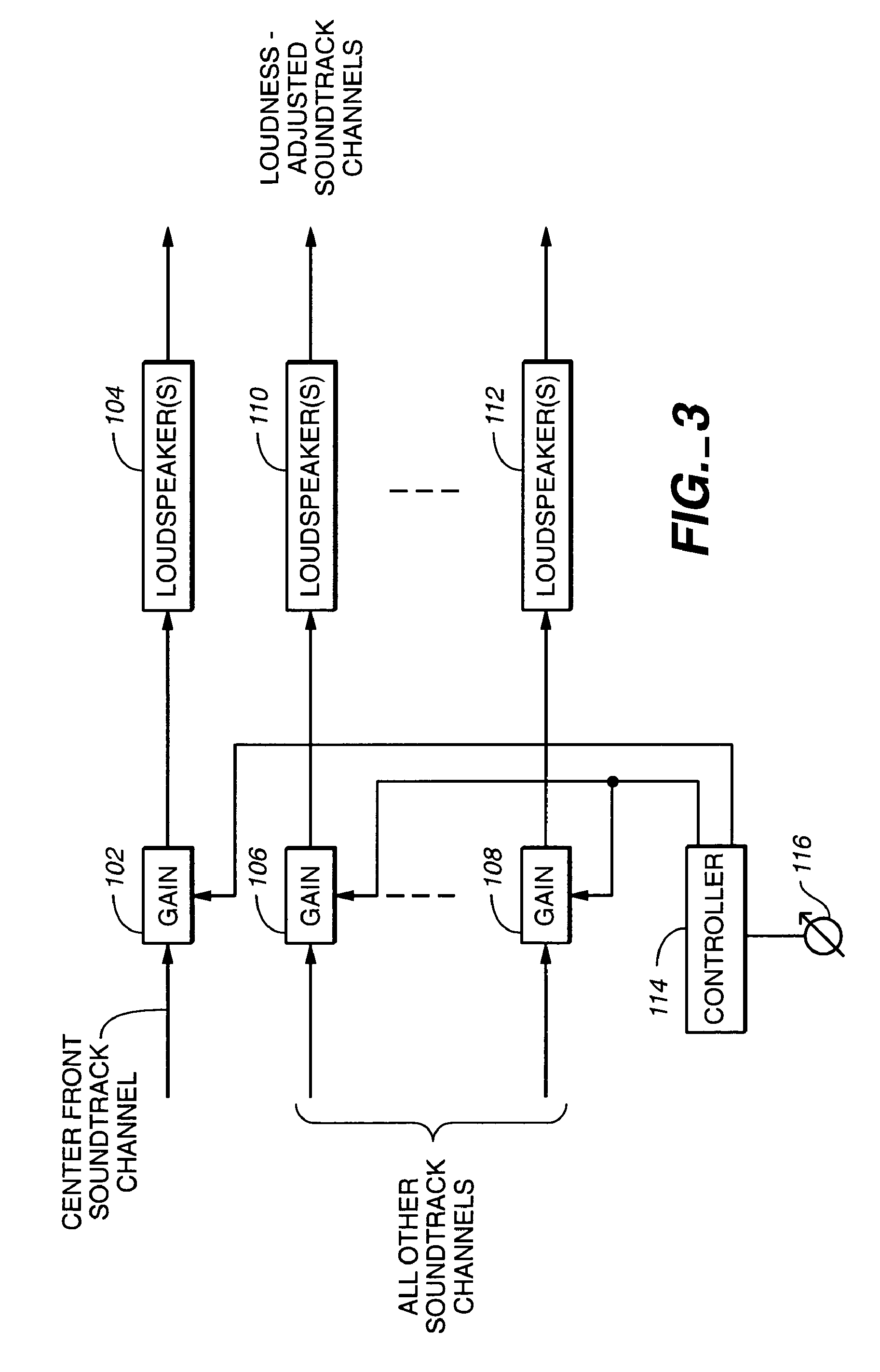
[0020]FIG. 2 illustrates idealized curves of gain / loss as a function of volume control setting, for the center front channel (upper line) and for each of the remaining channels (lower line). The lower line also shows the typical gain / loss for all channels (rather than channels other than the center front channel, as in the present invention) as a function of volume control setting in prior art motion picture sound equipment. While the characteristic responses shown in the example of FIG. 2 are practical and useful ones, the precise characteristics are not critical. For example, the lower characteristic curve need not be the same as in the prior art gain / loss for all channels versus volume control setting The characteristics shown in the figures are just one example of suitable characteristics that fall within the scope of the invention
[0021]Still referring to FIG. 2, it will be seen that the gain of the center front channel has a first relationship to the volume control settings and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com