Radiation-emitting device
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
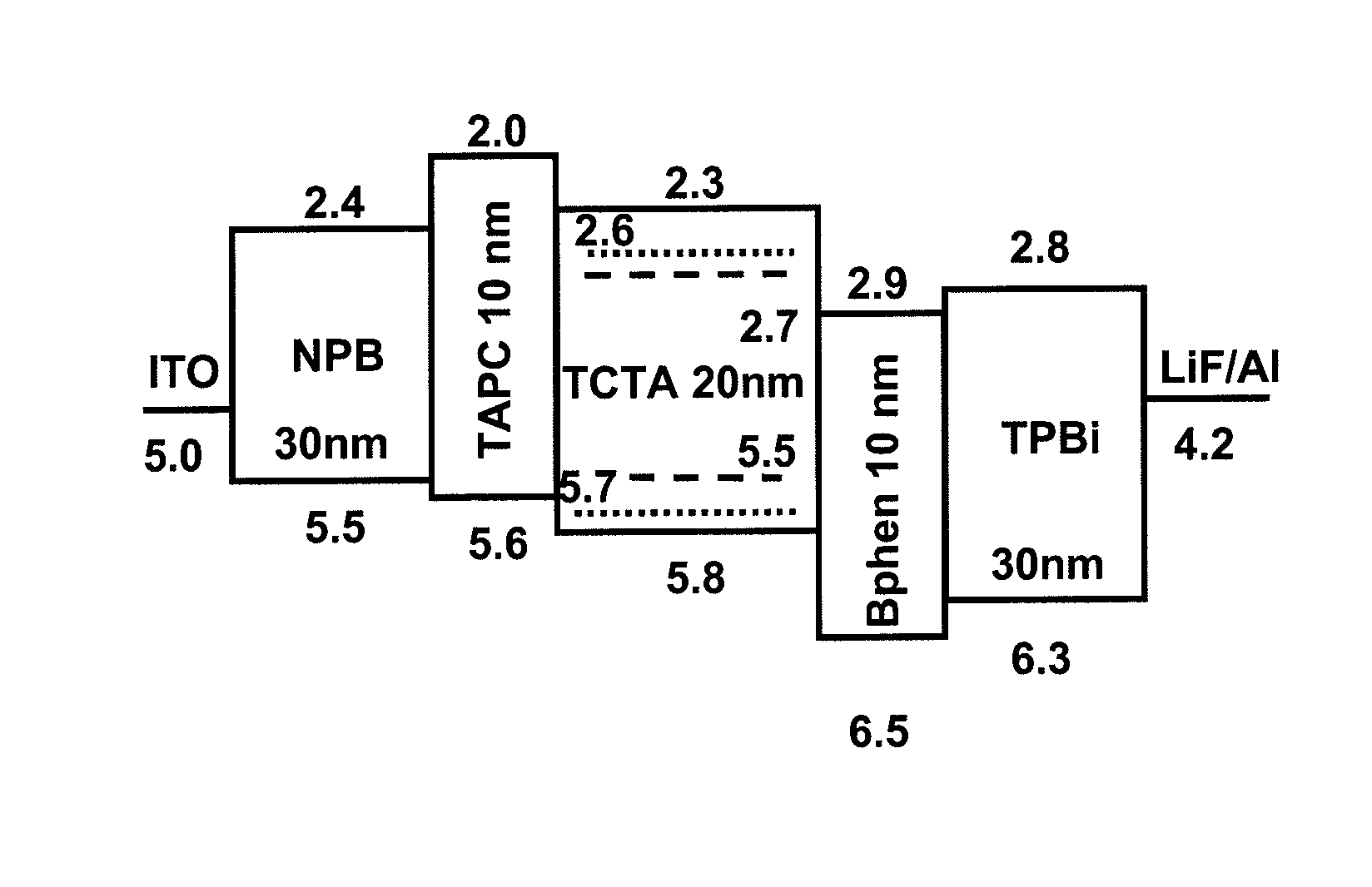
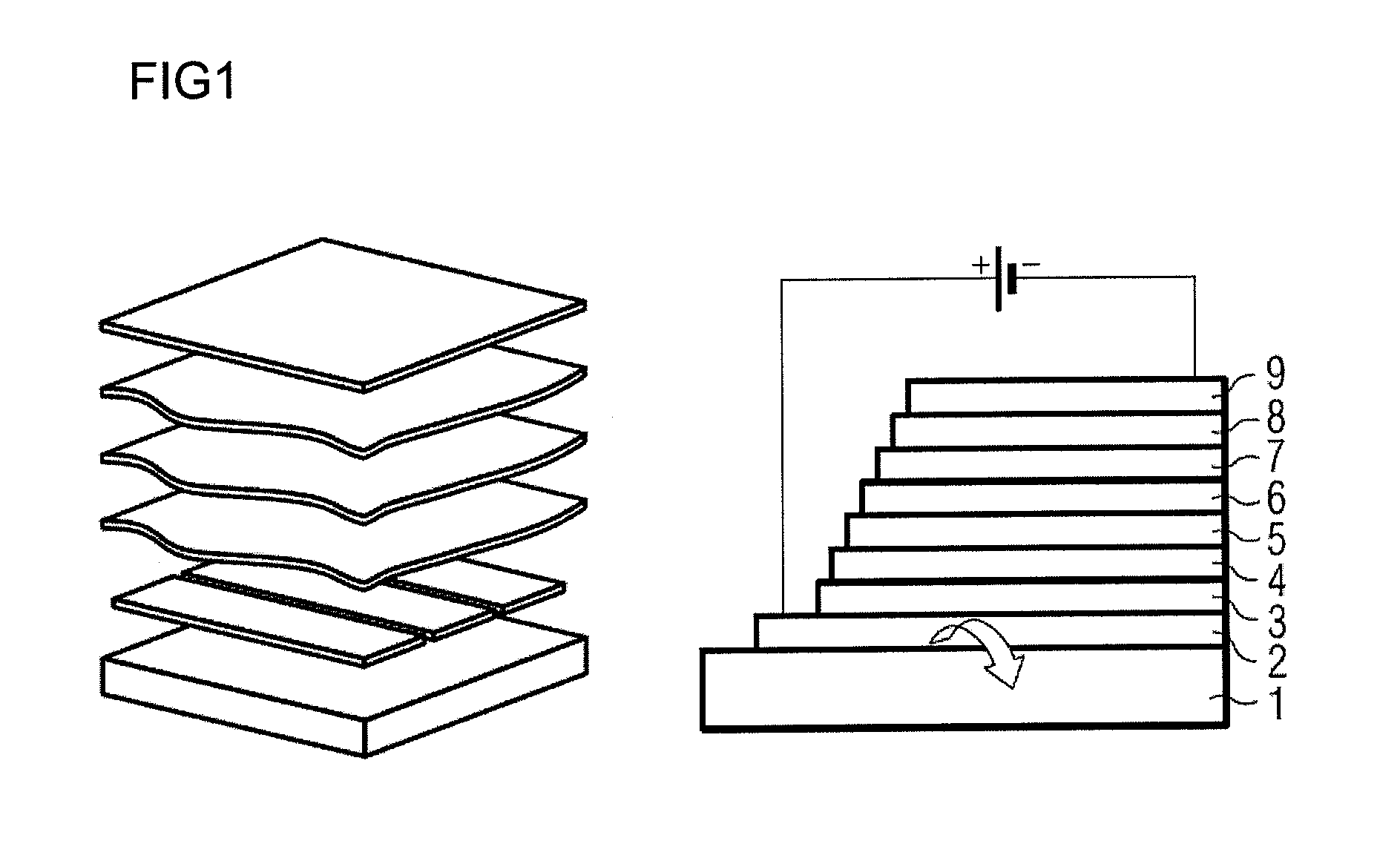
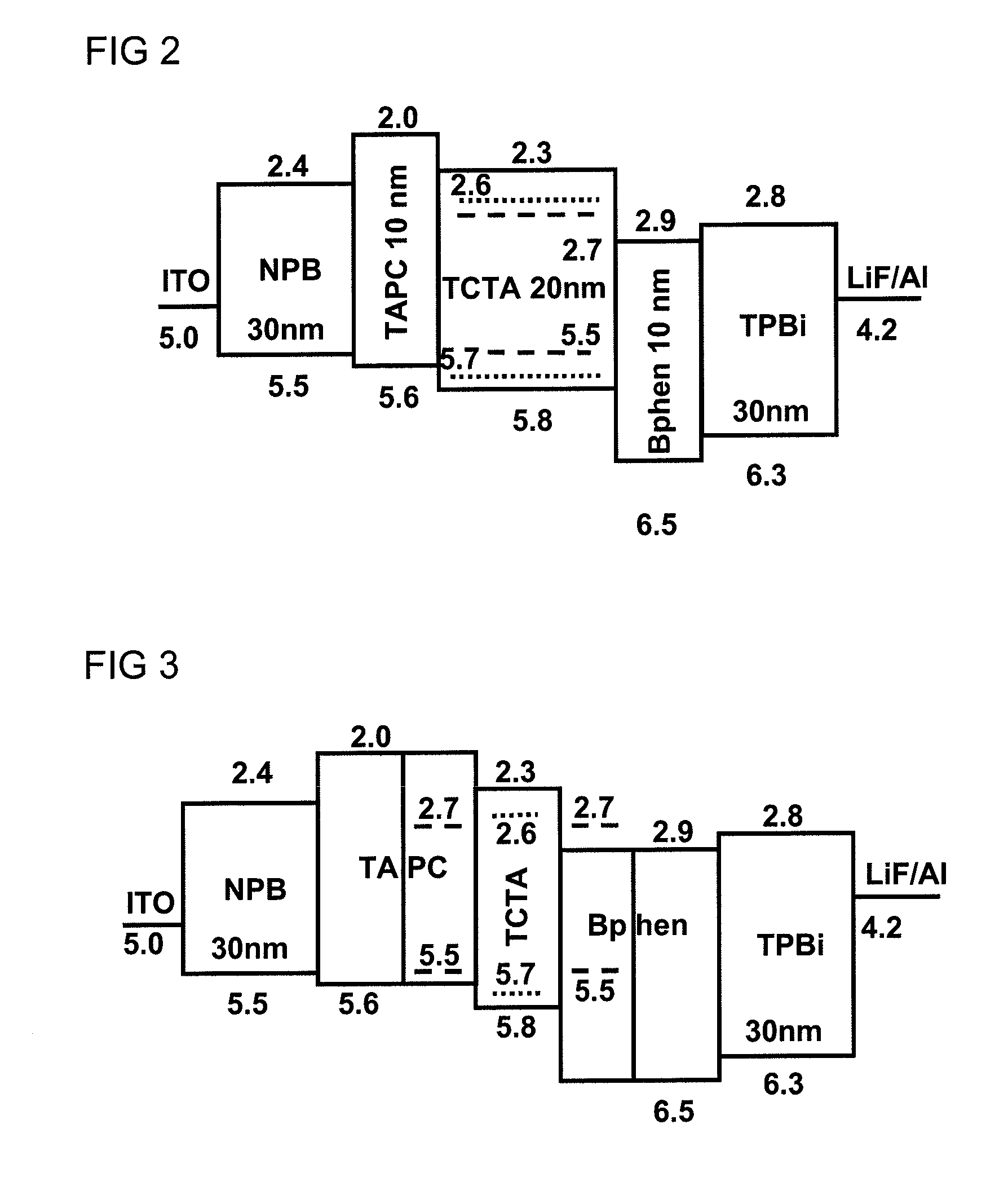
[0058]FIG. 1 shows the schematized layer construction of an organic, radiation-emitting component. From bottom to top, the following layer construction is realized: at the very bottom is the substrate 1, which may, for example, be transparent and may also be made of glass. Atop it is a lower electrode layer 2, which may, for example, be a transparent conductive oxide such as indium tin oxide (ITO). This lower electron layer may function as anode or as cathode. Disposed above this electrode layer 2 is a hole injection layer 3, above which in turn is disposed a hole transport layer 4. Disposed above the hole transport layer 4 is the organically active layer, the emission layer 5. Where the radiation-emitting device comprises more than one emission layer 5, the first emission layer is followed by the further emission layers, optionally separated by exciton blocking layers.
[0059]Lying on the emission layer or on the two or more emission layers is the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com