Power holdup circuit
a power holdup circuit and power technology, applied in emergency power supply arrangements, electrical equipment, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the power factor of the system, reducing the useful power of the system, and reducing the useful power of the reactive power, so as to achieve a low design complexity and high power factor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
CRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0022]The present invention will become fully understood from the detailed description and the accompanying drawings, wherein:
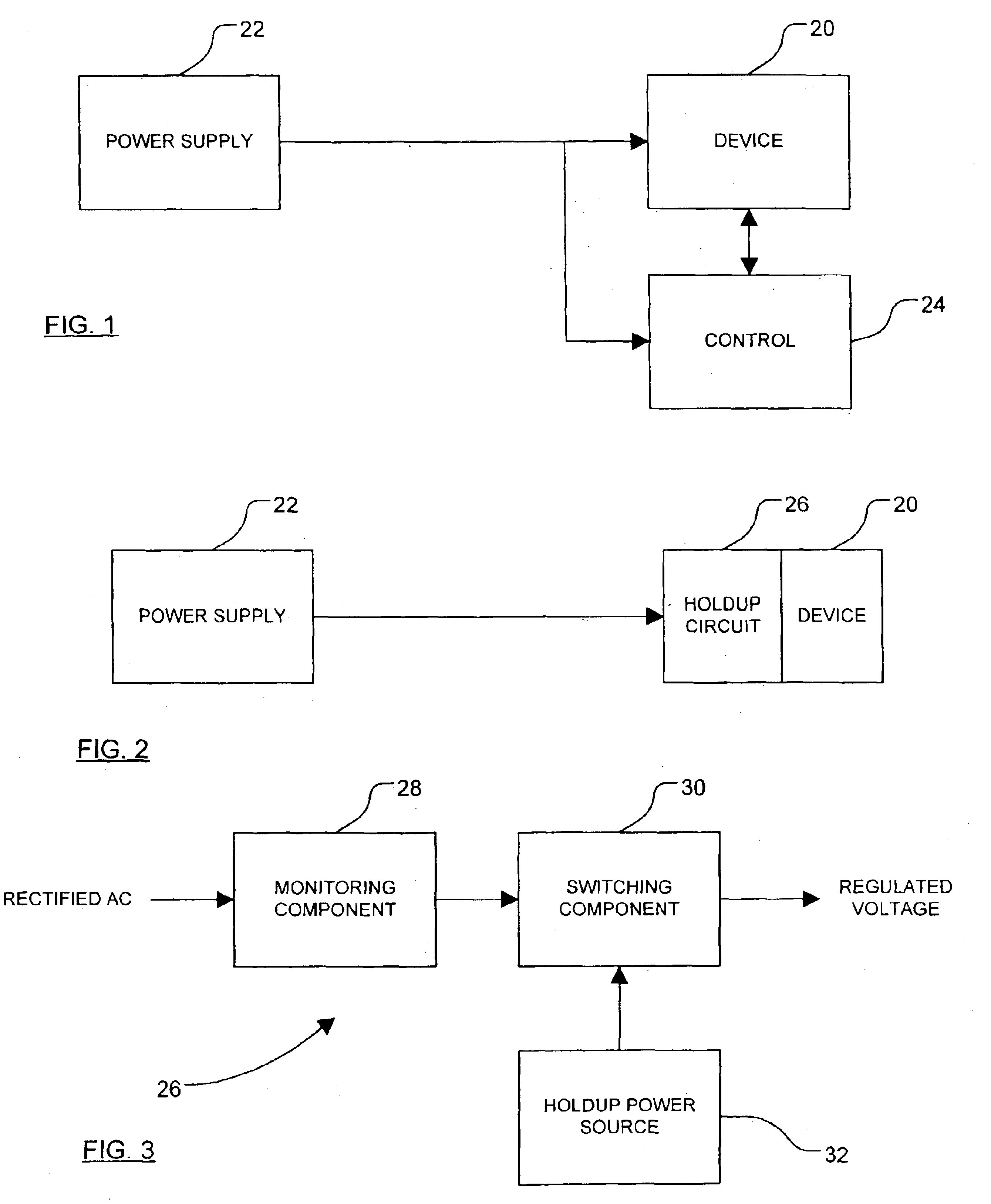
[0023]FIG. 1 is a simplified block diagram of a known system for providing power factor correction;
[0024]FIG. 2 is a simplified block diagram of a system having a holdup circuit constructed according to the principles of the present invention therein;
[0025]FIG. 3 is a simplified block diagram of a holdup circuit of the present invention;
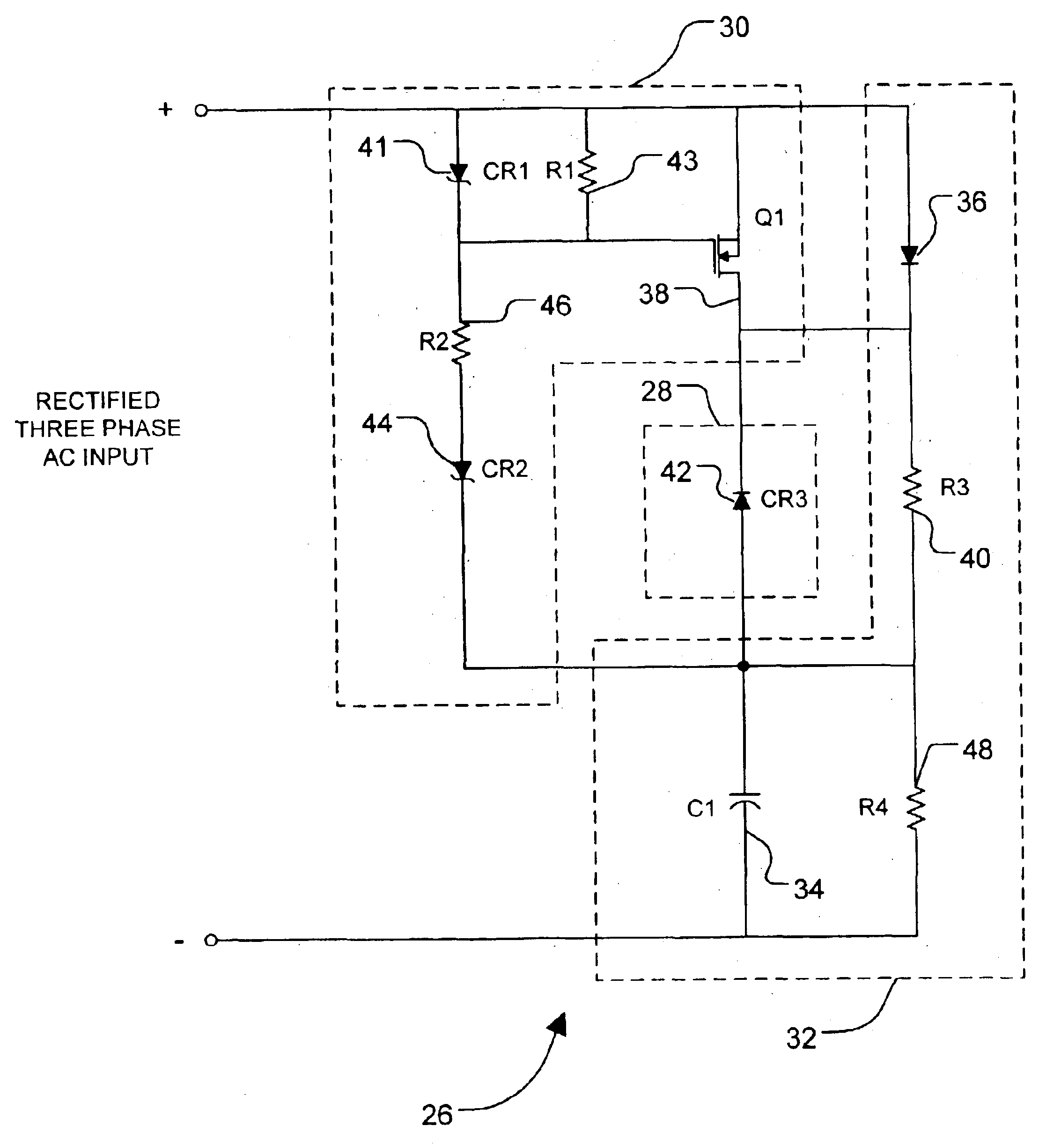
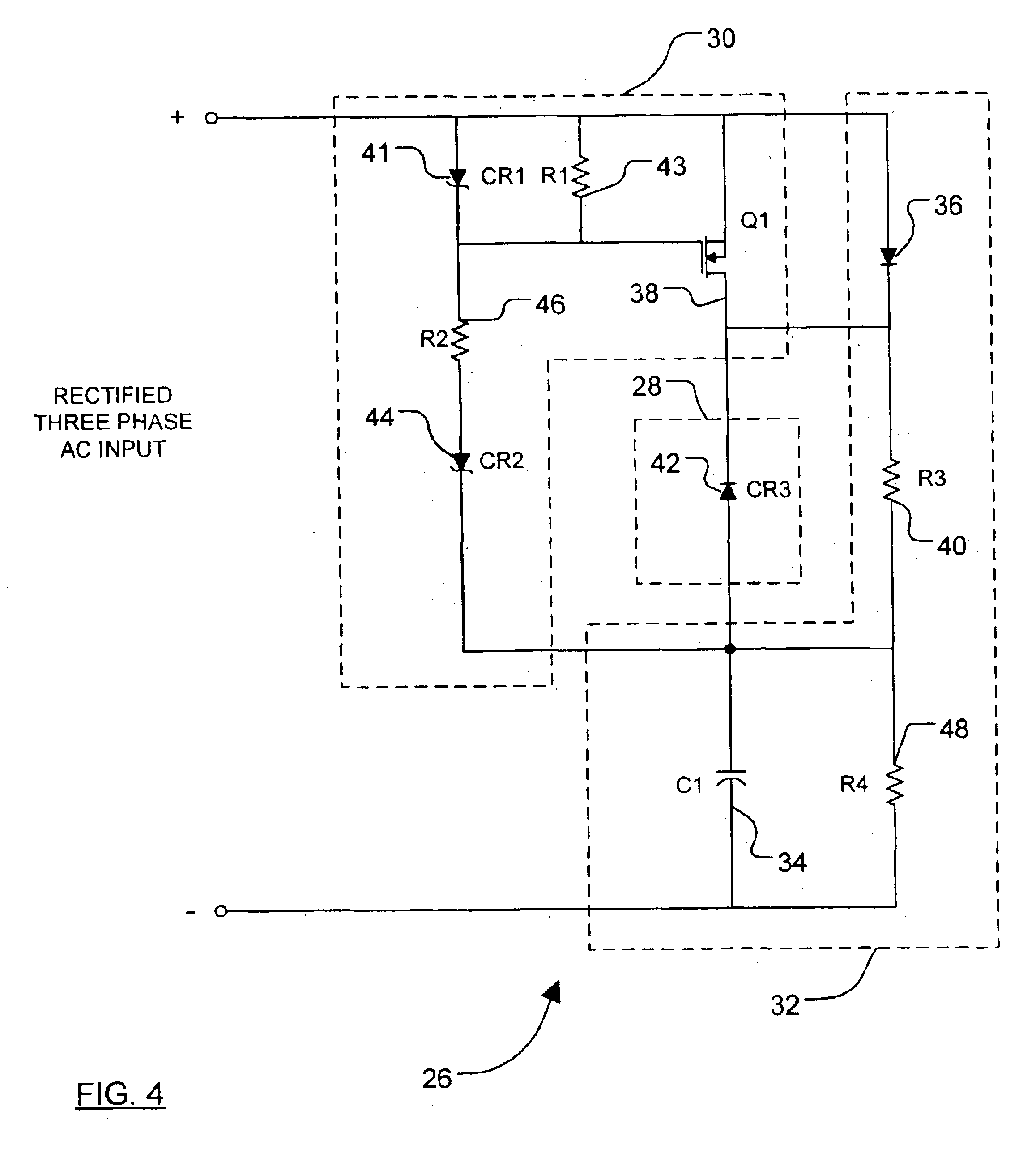
[0026]FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram of a holdup circuit of the present invention; and
[0027]FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram of another embodiment of a holdup circuit arranged in accordance with the principles of the present invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[0028]The following description of the present invention is merely exemplary in nature and is in no way intended to limit the invention, its application, or uses. Thus, although the application of the present invention as disclosed herein is generally direc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com