Methods and Systems for Generation of Balanced Secondary Clocks from Root Clock
a technology of secondary clocks and clock edges, applied in the direction of pulse automatic control, pulse generation with predetermined statistical distribution, generating/distributing signals, etc., can solve the problem of digital spurs in the system, under-utilization of clock edges, and the number of parallel hardware dependent on the division factor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
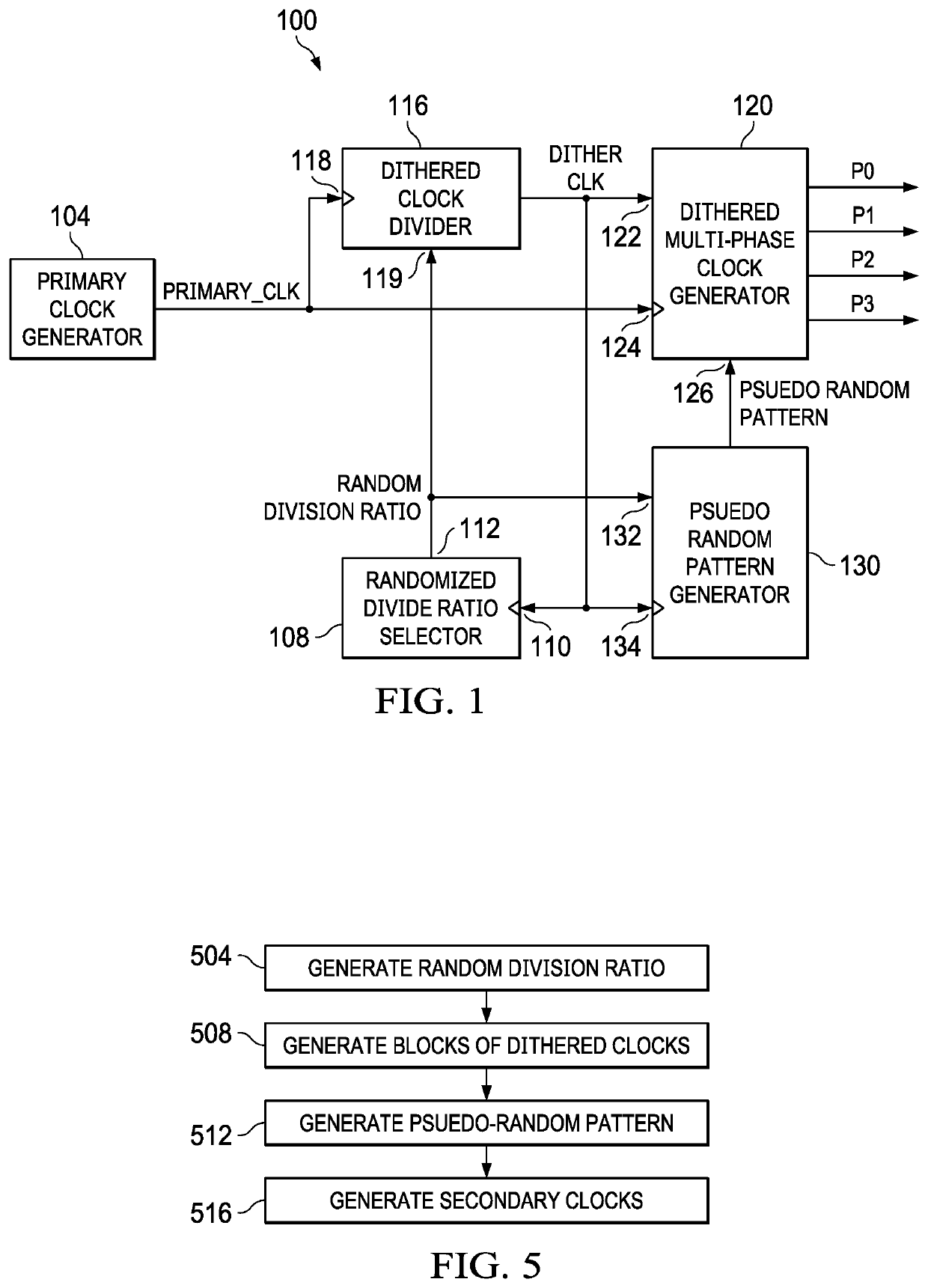
[0021]FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a system 100 of an example embodiment. The system 100 includes a primary clock generator 104 which provides a primary clock signal PRIMARY_CLK. The system 100 derives four secondary clock signals from the primary clock signal PRIMARY_CLK. The phases P0, P1, P2, and P3, which are the four secondary clock signals, are derived from multiple phases of PRIMARY_CLK. The secondary clock signals are also referred simply as different “phases.” Thus, the first secondary clock signal may be referred to as P0 phase, the second secondary clock may be referred to as P1 phase, the third secondary clock signal may be referred to as P2 phase, and the fourth secondary clock signal may be referred to as P3 phase. The phases P0, P1, P2, and P3 can be provided as clock signals to four parallel hardware (not shown in FIG. 1).
[0022]Although in the example embodiment of FIG. 1, four phases P0, P1, P2, and P3 are derived from the primary clock signal PRIMARY CLK, the syste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com