Antibodies against actin-binding protein girdin and methods of making and using the same
a technology of actin-binding protein and antibodies, which is applied in the field of application of actin-binding protein, can solve the problems of unknown molecular mechanism by which akt promotes cell motility, and achieve the effect of affecting cell migration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Identification of an Akt-Interacting Protein, Girdin / APE, Primary Structure Thereof and Expression Manner
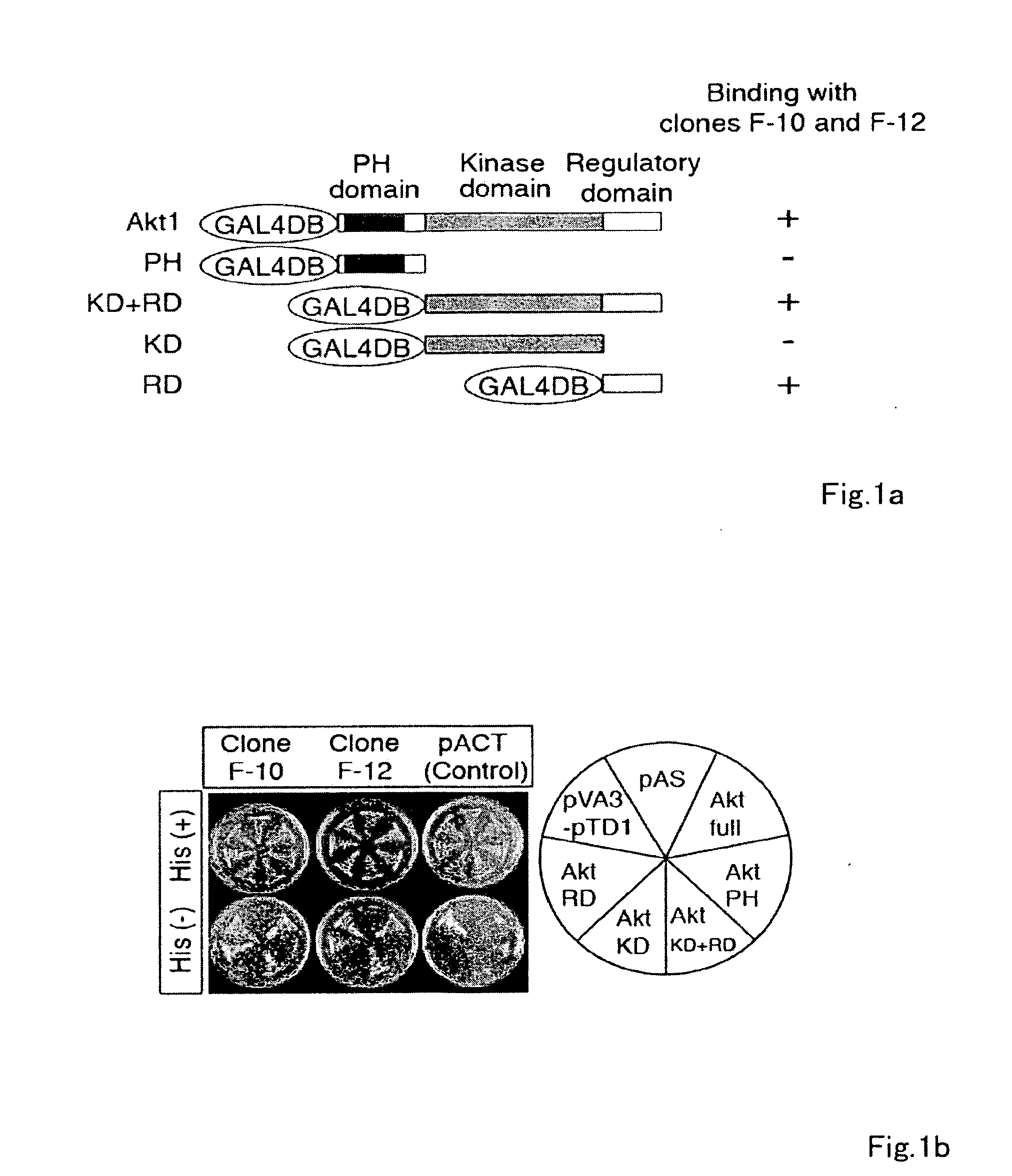
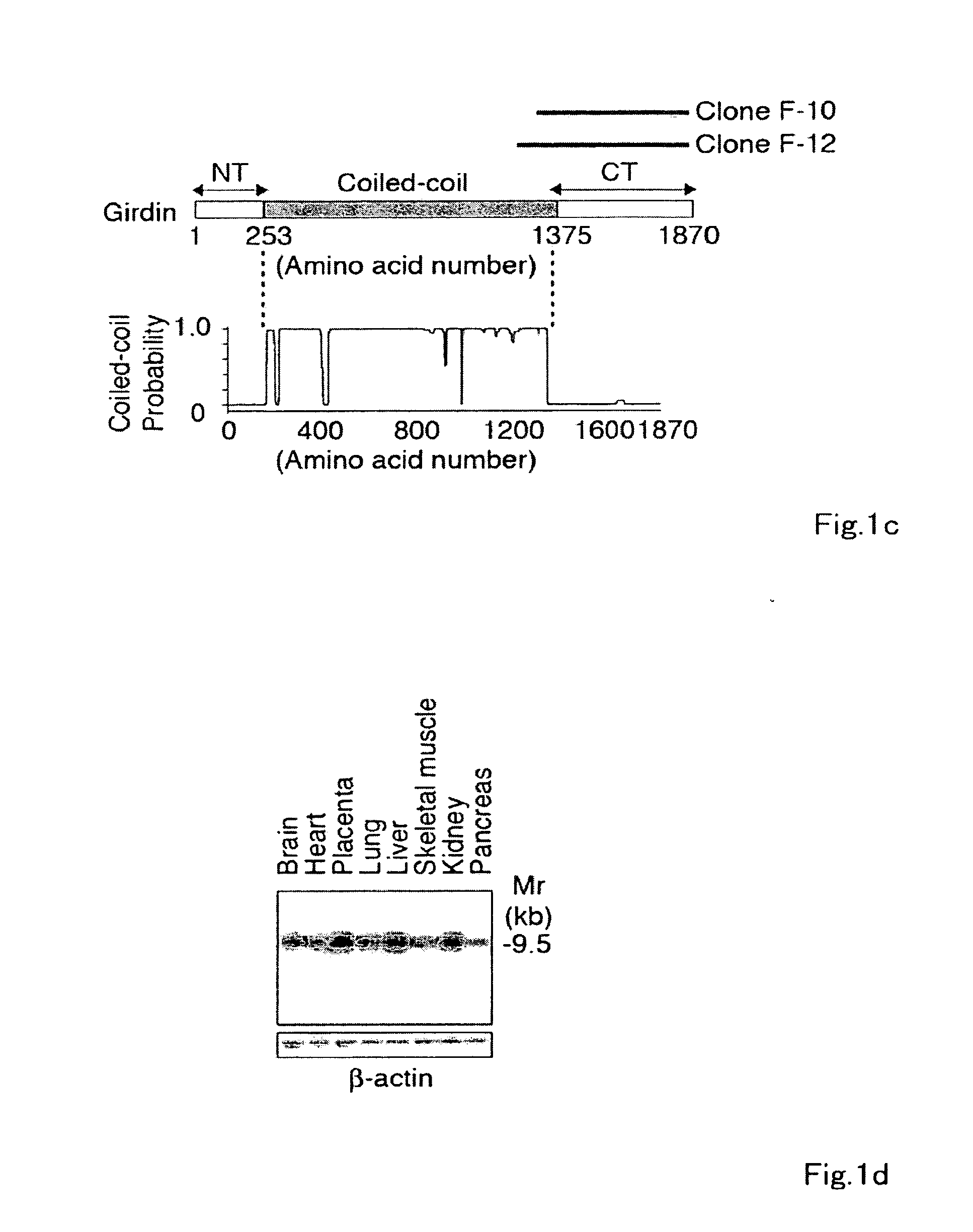
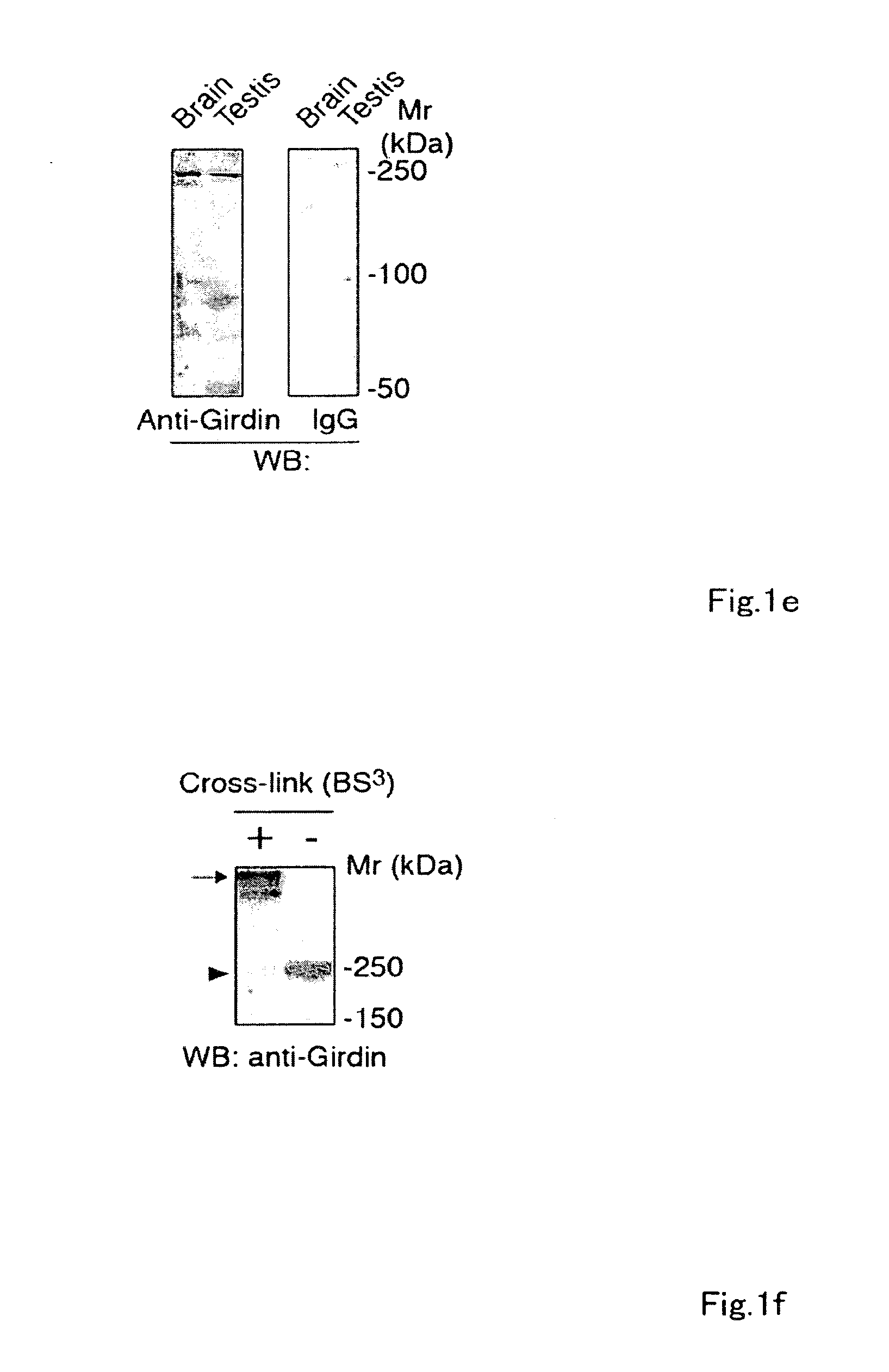
[0185]To identify novel Akt substrates, a yeast two-hybrid screen using full-length human Akt1 as bait was performed, and interacting proteins using a human fetal brain cDNA library were searched for. Two independent and overlapping clones (F-10 and F-12) encoding a novel gene product were identified. When expressed in yeast, the protein encoded by the F-10 and F-12 cDNAs was shown to interact only with the carboxyl-terminal regulatory domain (RD) of Akt1. Use of 5′-rapid amplification of cDNA ends (5′-RACE) provided a clone comprising the entire coding region with an additional 3.8-kb cDNA of contiguous 5′ sequence. The full-length cDNA included an open reading frame of 5610-bp (base pair) (GenBank™ / EMBL / DDBJ accession number AB201172) and was predicted to encode a novel protein of 1870 amino acids, which was designated Girdin, with a calculated molecular mass of 220 kilodalton...
example 2
Akt Phosphorylates Girdin In Vitro and In Vivo
[0189]In vitro and in vivo assays were initially used to ascertain if Girdin and Akt physically interact with each other. Neither in vitro binding nor immunoprecipitation assays using various fragments of Girdin and Akt demonstrated the formation of a stable complex of the two proteins (data not shown), suggesting that they may normally associate in a very transient manner, as observed for the interactions between protein kinases and their substrates. It has been established that Akt preferentially phosphorylates substrates that contain the sequence R-x-R-x-x-S / T. The amino acid sequence adjacent to a serine at position 1416 (Ser-1416, RERQKS) in the CT domain of Girdin had conformed to this consensus sequence. This was the only consensus site in the protein. Since the CT domain with the putative phosphorylation site was conserved in different mammalian Girdin homologues, consideration had been given to whether Akt phosphorylates Girdin....
example 3
Girdin Associates with Actin Filaments Via its C-Terminal Domain
[0193]To determine the subcellular localization of Girdin, Vero fibroblasts were immunofluorescently stained with the anti-Girdin Ab. As shown in (a) of FIG. 3a, the results showed that Girdin was colocalized with the actin stress fibers in quiescent cells. When the cells were stimulated with EGF (50 ng / ml), they started to polarize, followed by directional extension of lamellipodia. In the EGF-stimulated cells, Girdin localized not only on the actin stress fibers but also on the lamellipodia at the leading edge, which was illustrated upon staining for the Arp2 / 3-binding protein Cortactin in (b) of FIG. 3a.
[0194]The localization of Girdin raises the possibility that Girdin is an F-actin (filamentous actin)-binding protein. To identify the actin-binding domain of Girdin, green fluorescence protein (GFP)-fused truncated versions encoding the NT (GFP-NT), N-terminal half (GFP-M1) and C-terminal half (GFP-M2) of the coiled...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com