Differentiated secondary index maintenance in log structured nosql data stores
a technology of structured nosql and secondary indexes, applied in the field of data storage, can solve the problems of secondary indexes, lack of basic database functionality, and has become a stumbling factor, and achieve the effect of accelerating point queries, avoiding broadcast queries, and being more robus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018]Astonishing growth and diversity in data have profoundly affected a way that data have been stored and served. Monolithic relational databases that are good at processing structured data and excel in ACID (atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) cannot handle high-traffic Internet applications in an elastic manner. This is because relational databases put restrictions on data normalization and consistency, and also the relational databases are not able to perform data sharing in an automatic way so that the relational databases are difficult to scale out. To address challenges in flexible schema and elasticity, data stores dealing with columns, key / value pairs, documents and graphs have emerged and collectively identified as NoSQL data stores. A NoSQL data store, e.g., HBase, that supports a convergence of transactional and analytics workloads is able to offer balanced “read” and “write” performance.
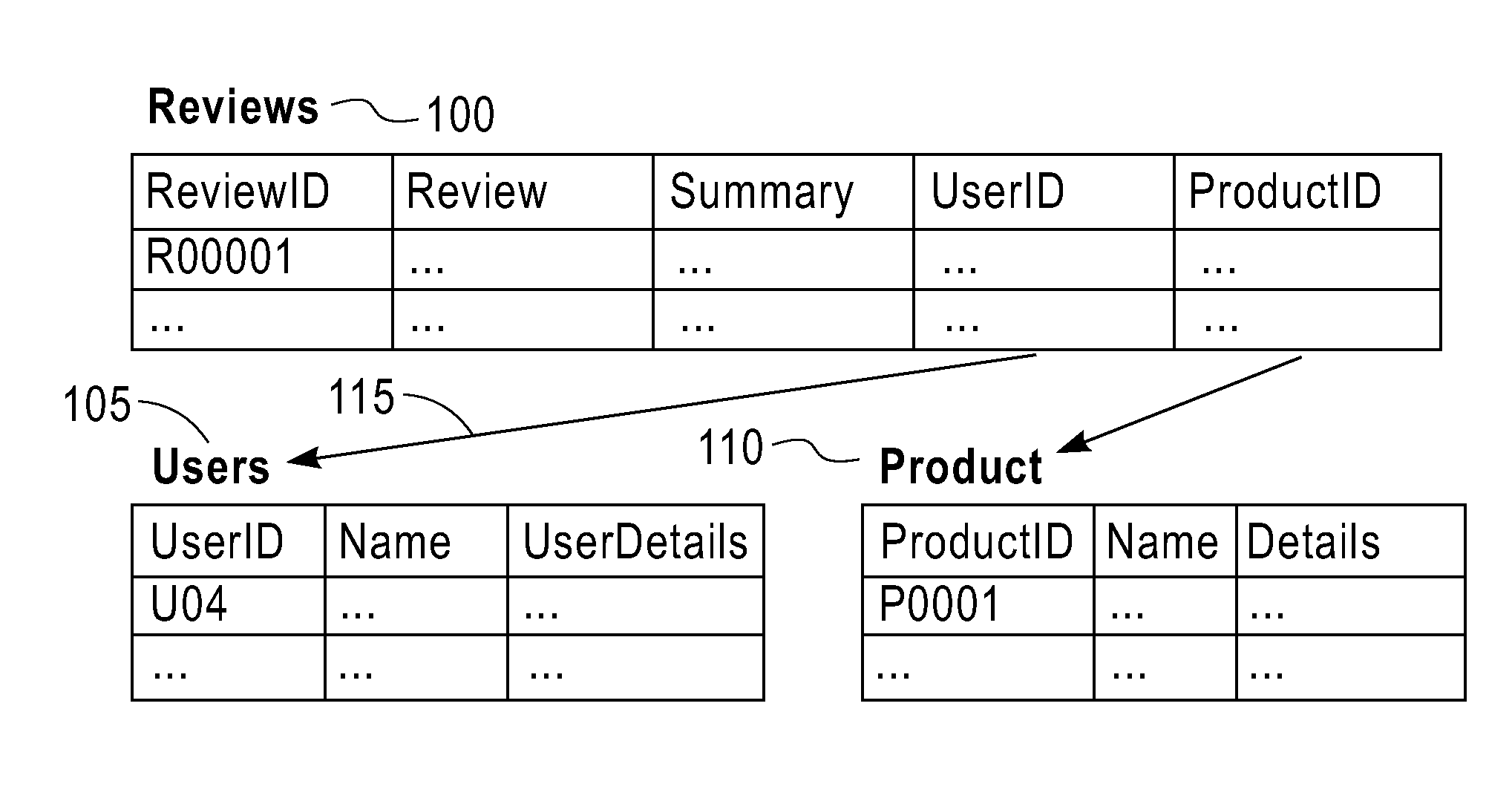
[0019]Consider a web application that manages social reviews (e.g., yel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com