Multiple panel column and methods
a multi-panel, support column technology, applied in the direction of paper/cardboard containers, structural elements, containers, etc., can solve the problems of low construction cost, low quality, scarce natural resources and raw materials, etc., to achieve the effect of less weight, less handling and transportation of composite sandwich panels, and greater strength-to-weight ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
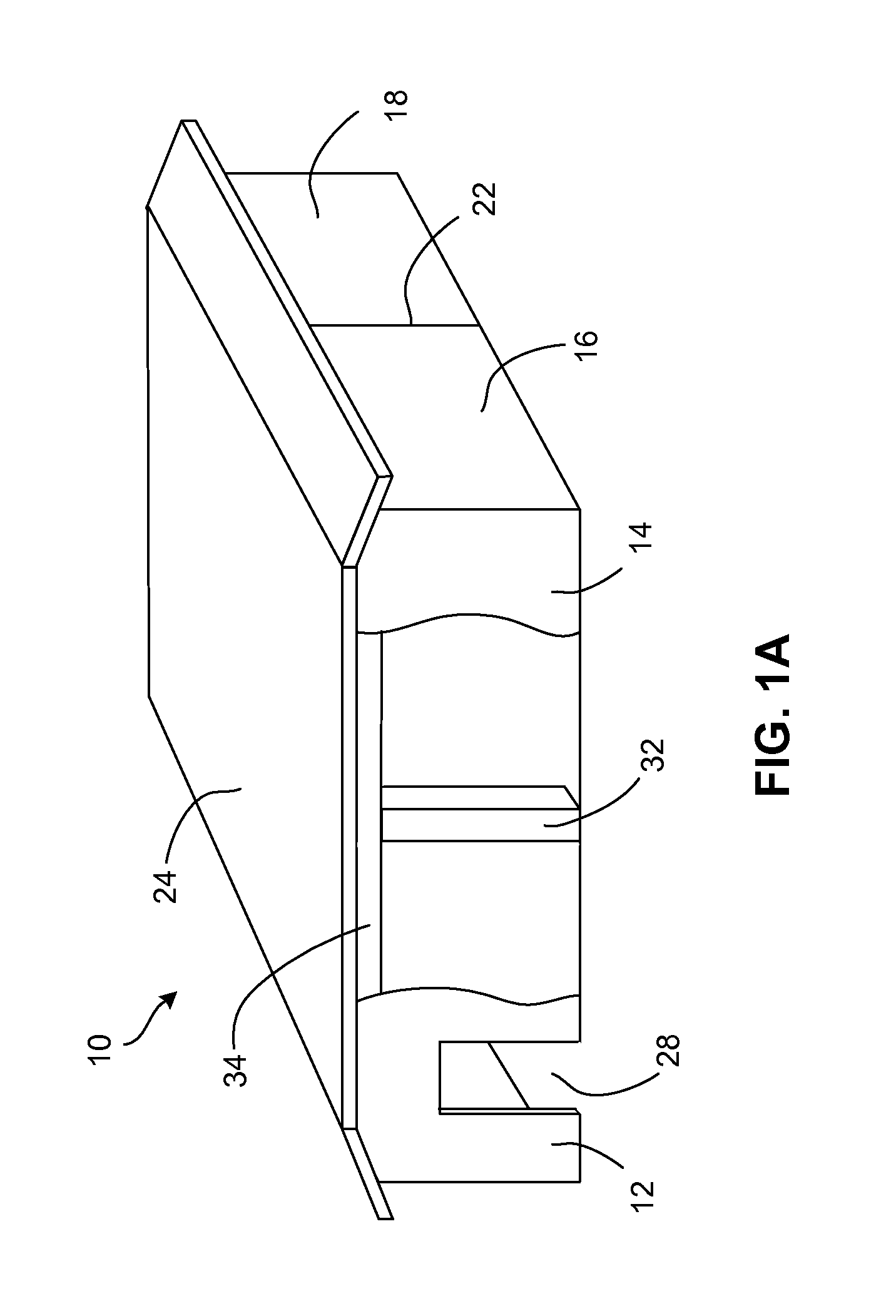
[0027]Referring to FIG. 1A, an exemplary monolithic structure 10, such as a house, is built from panels. The house 10 includes of a front wall formed from two panels 12, 14 connected by a straight joint (not shown), a side wall formed from two panels 16, 18 connected by a straight joint 22, and a roof 24. As shown in FIG. 1A, the straight joint joins two panels in a substantially common plane, e.g. a 180-degree joint. Also illustrated is a doorway 28. Although not shown in FIG. 1A, it will be appreciated that the house 10 also includes another side wall and a rear wall, which also may be formed by adjacent panels connected by straight joints.
[0028]Exemplary panels and methods for forming a monolithic structure, such as the monolithic structure 10, are disclosed in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 12 / 101,620, filed Apr. 11, 2008, the entirety of which is incorporated by reference herein.
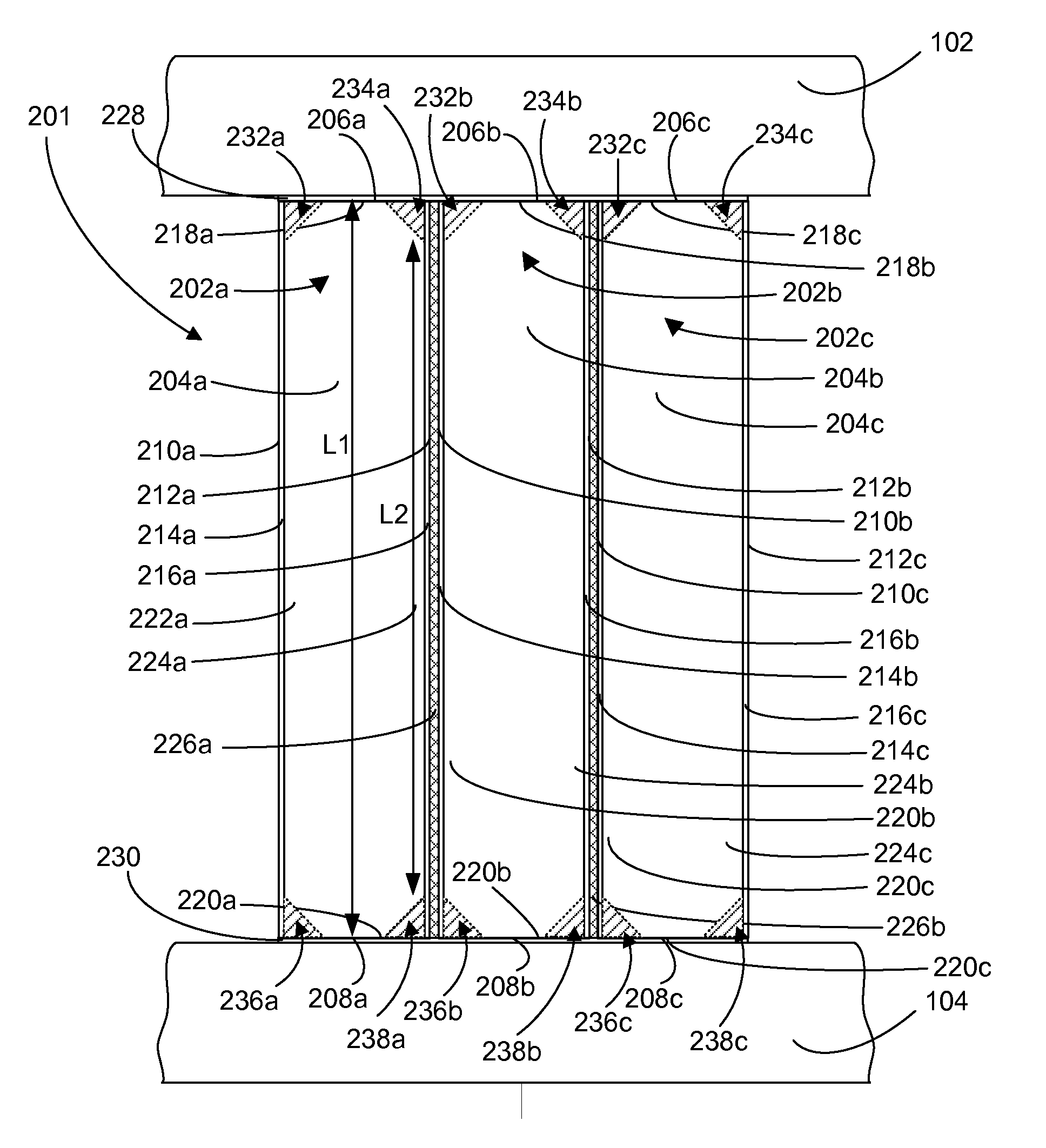
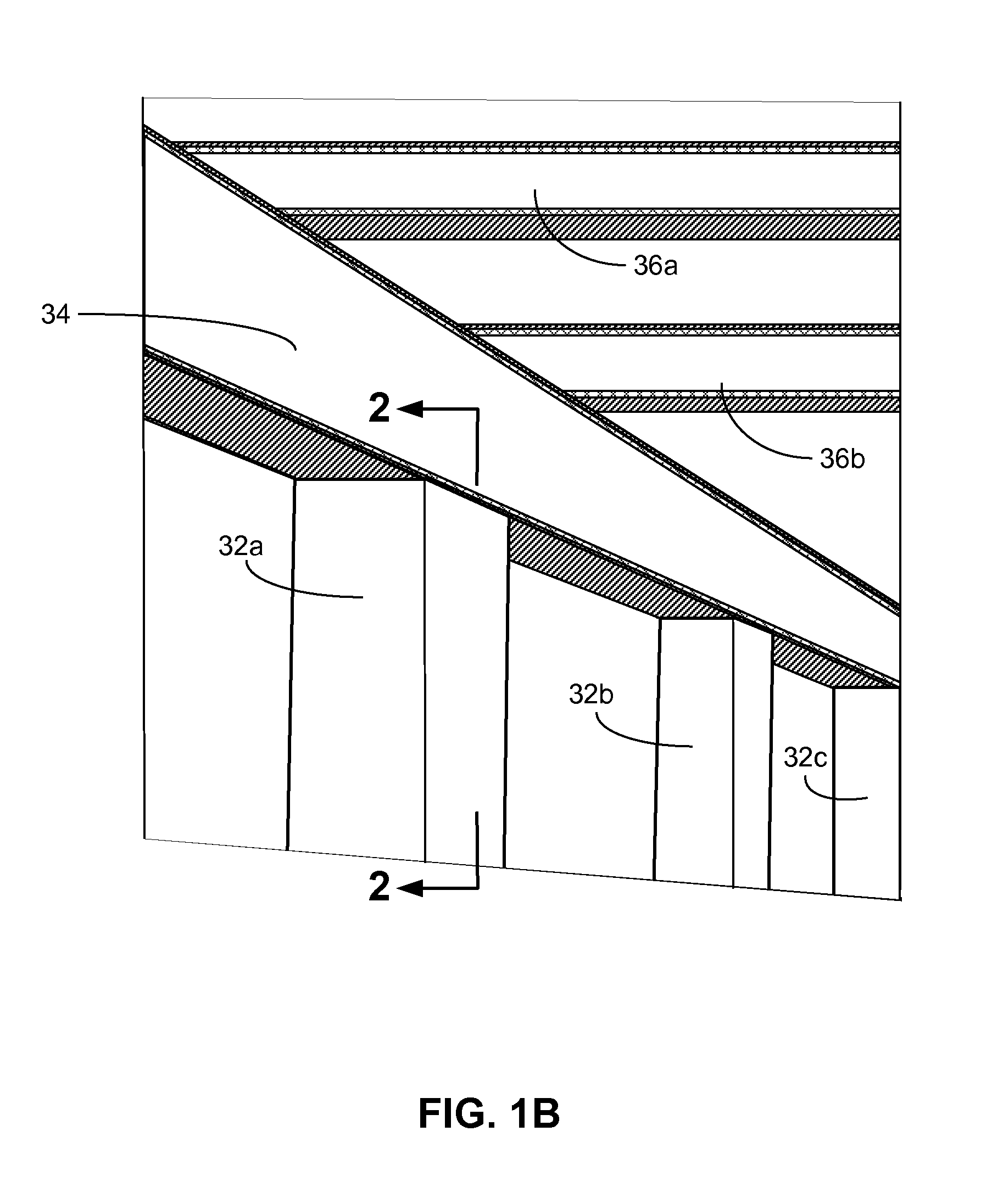
[0029]Like with any standard building material, columns, such as column 32, and beams, such as bea...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thick | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com