Pneumatic tire tread comprising a plurality of incisions
a pneumatic tire and plurality of incisions technology, applied in the field of pneumatic tire treads, can solve the problems of energy loss, energy loss through hysteresis, energy loss, etc., and achieve the effect of ensuring the closure of said sipes and limiting the deformation of the blocks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0061]In the description that follows, elements that are identical or similar will be denoted by identical references.
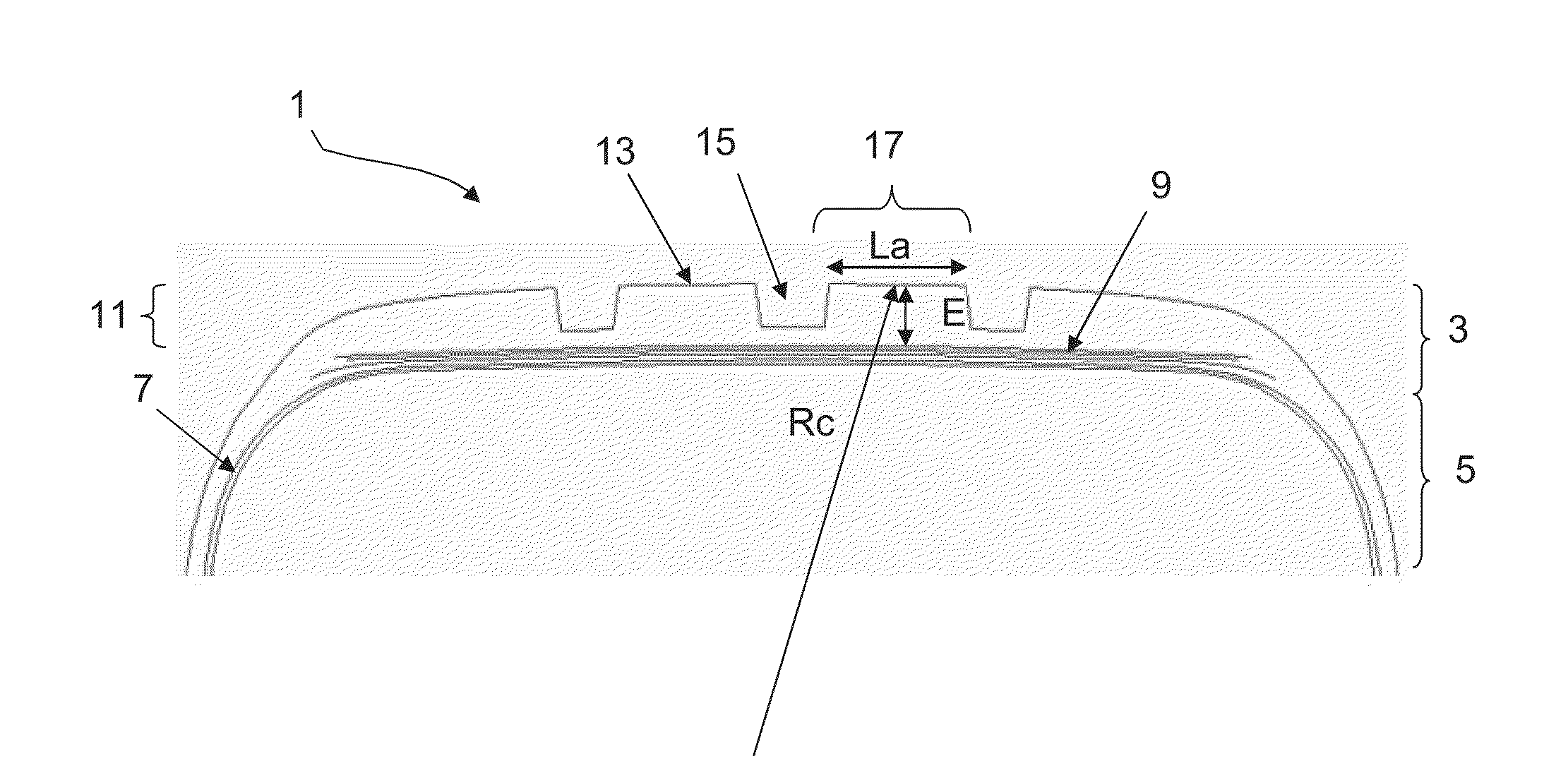
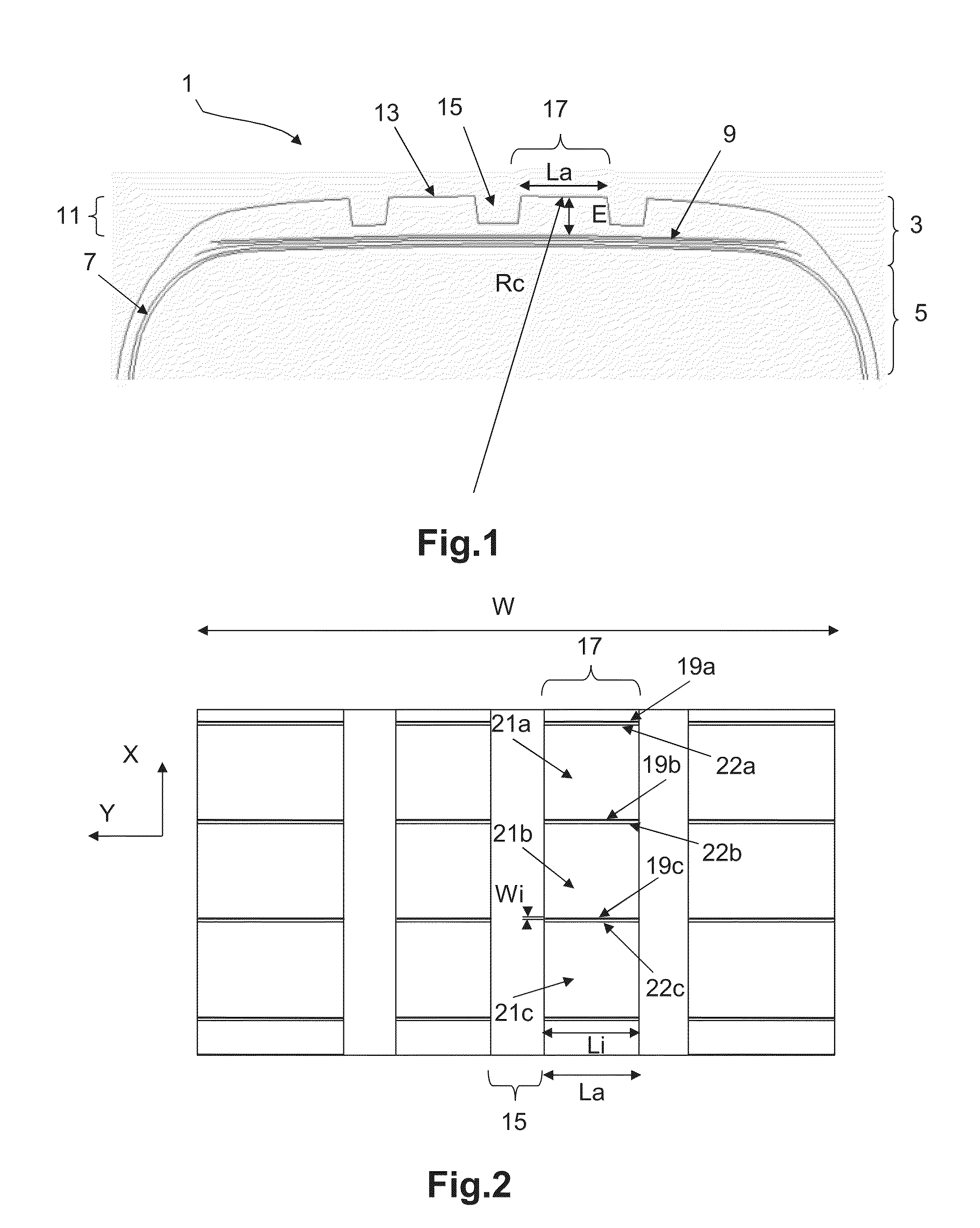
[0062]FIG. 1 schematically depicts a partial view in cross section of a tire 1.
[0063]The tire 1 comprises a crown comprising a crown region 3 extended laterally by sidewalls 5 connecting to beads (not depicted) intended to be in contact with a mounting rim.
[0064]The tire 1 comprises a carcass reinforcement 7 extending from one bead to the other bead via the sidewalls 5 and the crown region 3.
[0065]The crown region 3 comprises a reinforcement 9 surmounted radially on the outside by a tread 11.
[0066]The tread 11 comprises, radially on the outside, a tread surface 13 intended to come into contact with the ground when the vehicle is running.
[0067]The tread 11 comprises a plurality of grooves 15.
[0068]The grooves 15 delimit raised circumferential bands 17.
[0069]Each circumferential band 17 has a contact surface intended to come into contact with the ground when the tire i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com