Suture passing instrument and method
a technology of suturing instruments and needles, applied in the field of surgical stitching devices, can solve the problems of protruding needles being caught in tissue, limited maneuverability of most currently available suturing instruments,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0075] Described herein are various embodiments of suture passers for passing a suture through tissue, and components of suture passers that particularly enhance use. In general, the suture passers described herein are continuous suture passers that are configured to pass a suture back and forth through a tissue without having to reload the device. Thus, these devices may be used for continuous stitching of tissue.
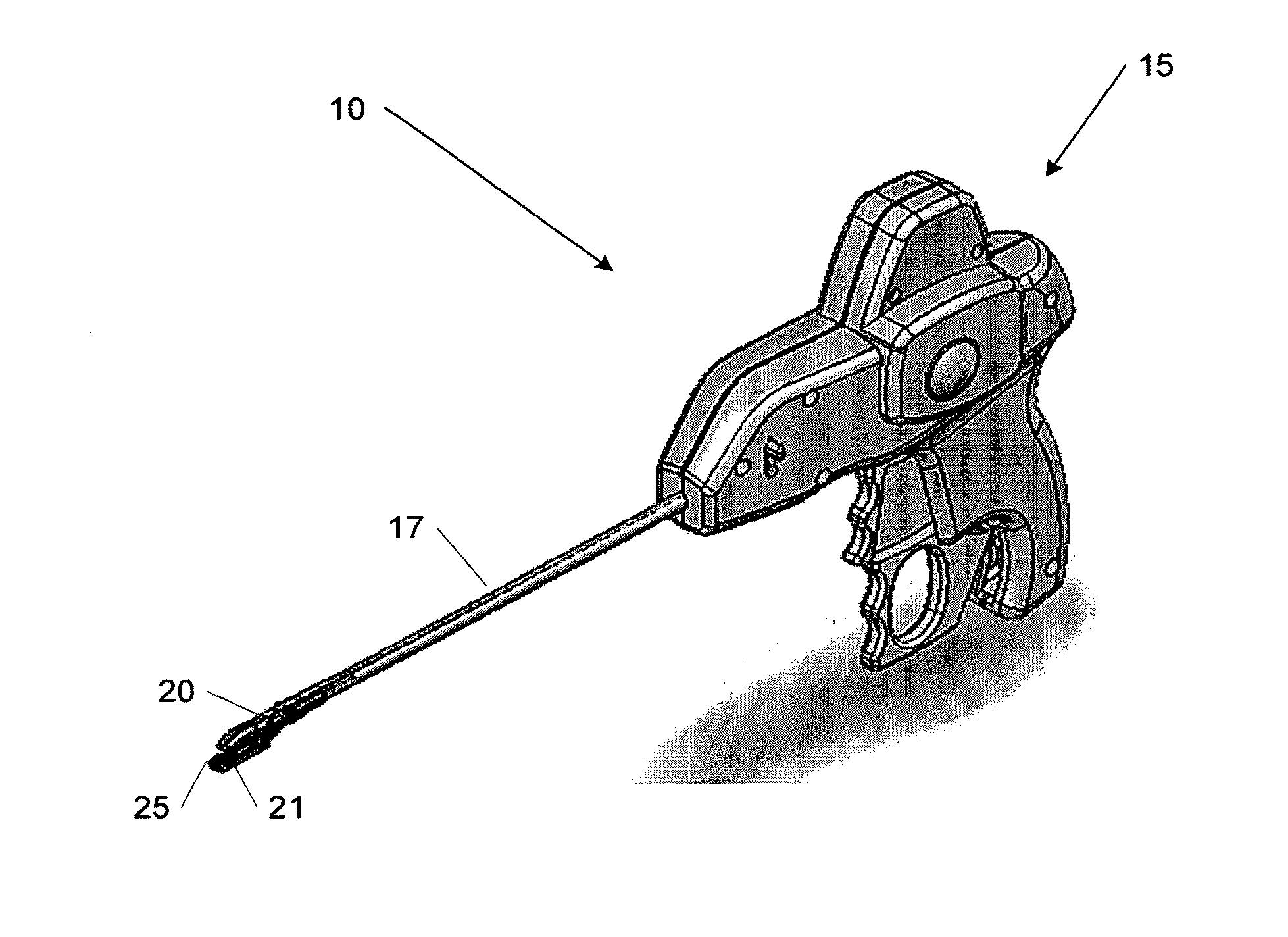
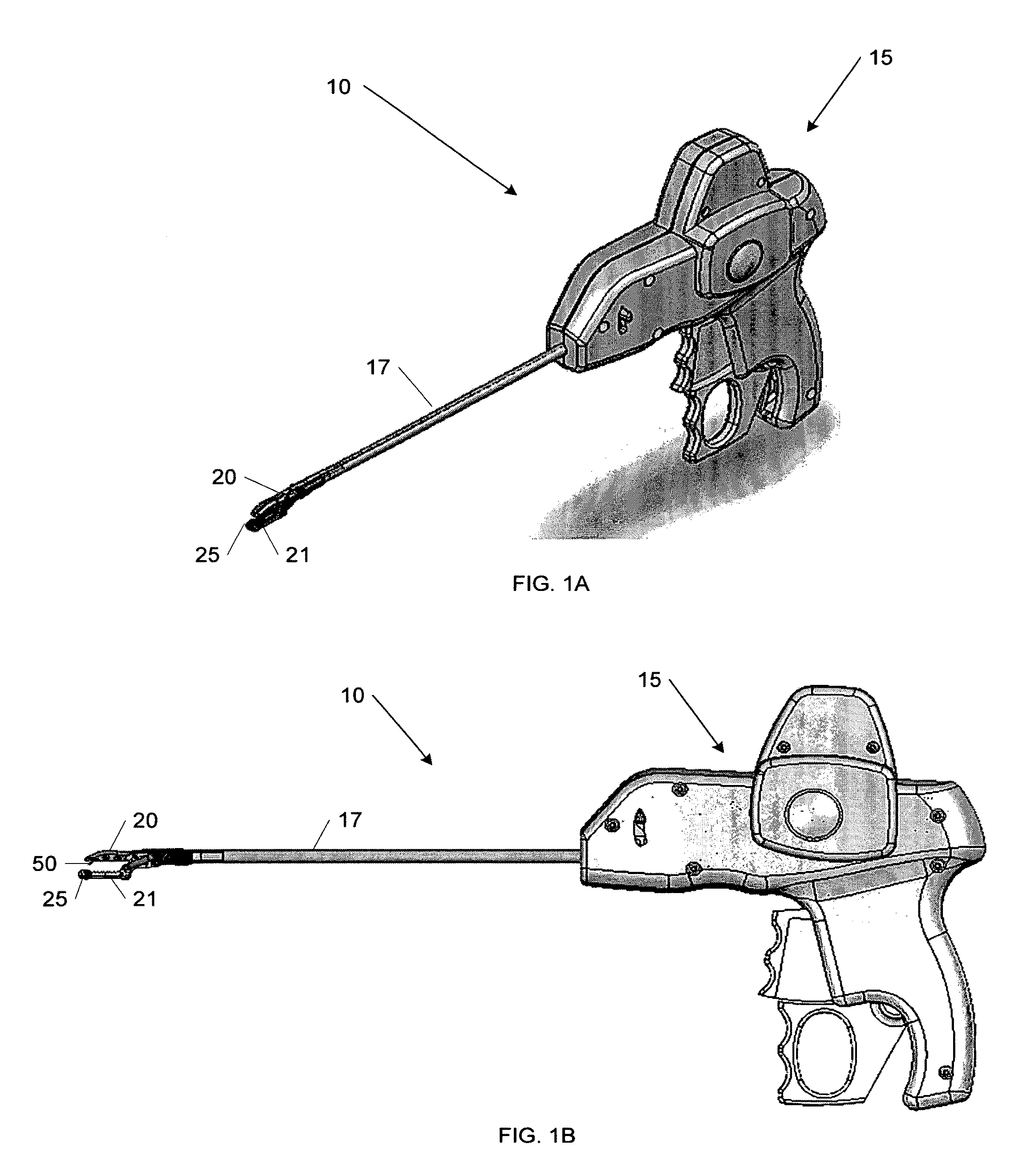
[0076]FIG. 1A illustrates a first embodiment of a continuous suture passer 10, including some of the enhanced features described herein, which may include, but is in no way limited to, a tissue penetrator (not shown), shuttle (not shown), reciprocating parallel-opening first and second jaws 20 and 21, jaw lock (not shown), and lower-jaw shuttle retainer seat 25. FIG. 1B shows a planar view of the device 10, including the parallel-opening jaws 20 and 21, tissue penetrator 50, and lower-jaw shuttle retainer seat 25.
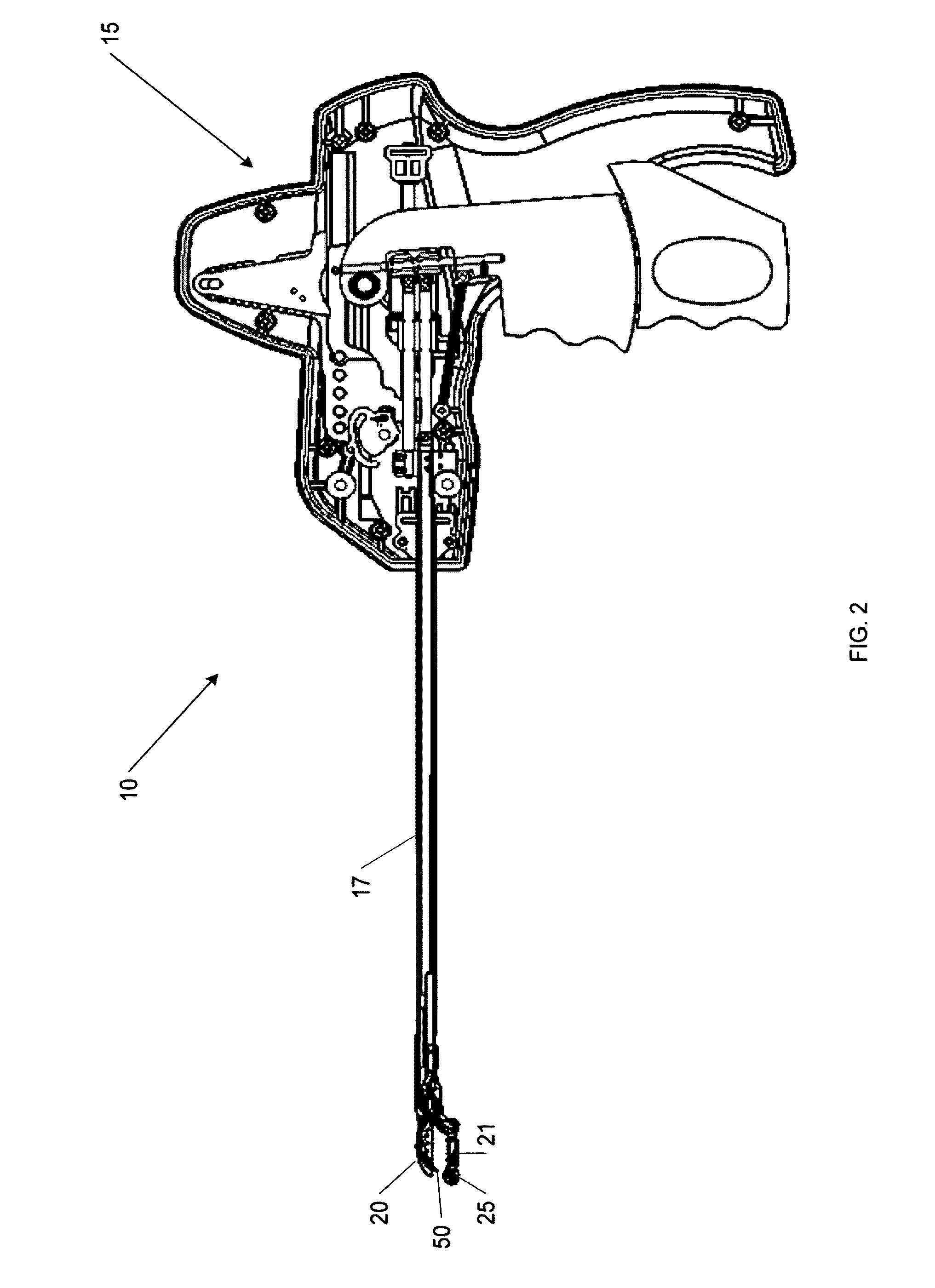
[0077]FIG. 2 illustrates a cross-sectional view of a first...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com