Locating Method
a technology of locating method and locating device, which is applied in the direction of instruments, measurement devices, electrical devices, etc., can solve the problems of high (technical) cost, high power consumption of the terminal, and strain on the limited air interfa
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028]The invention is described below using exemplary and non-limiting embodiments with reference to the drawings.
Efficient Control of Accurate Locating Methods for Detecting Update Zones
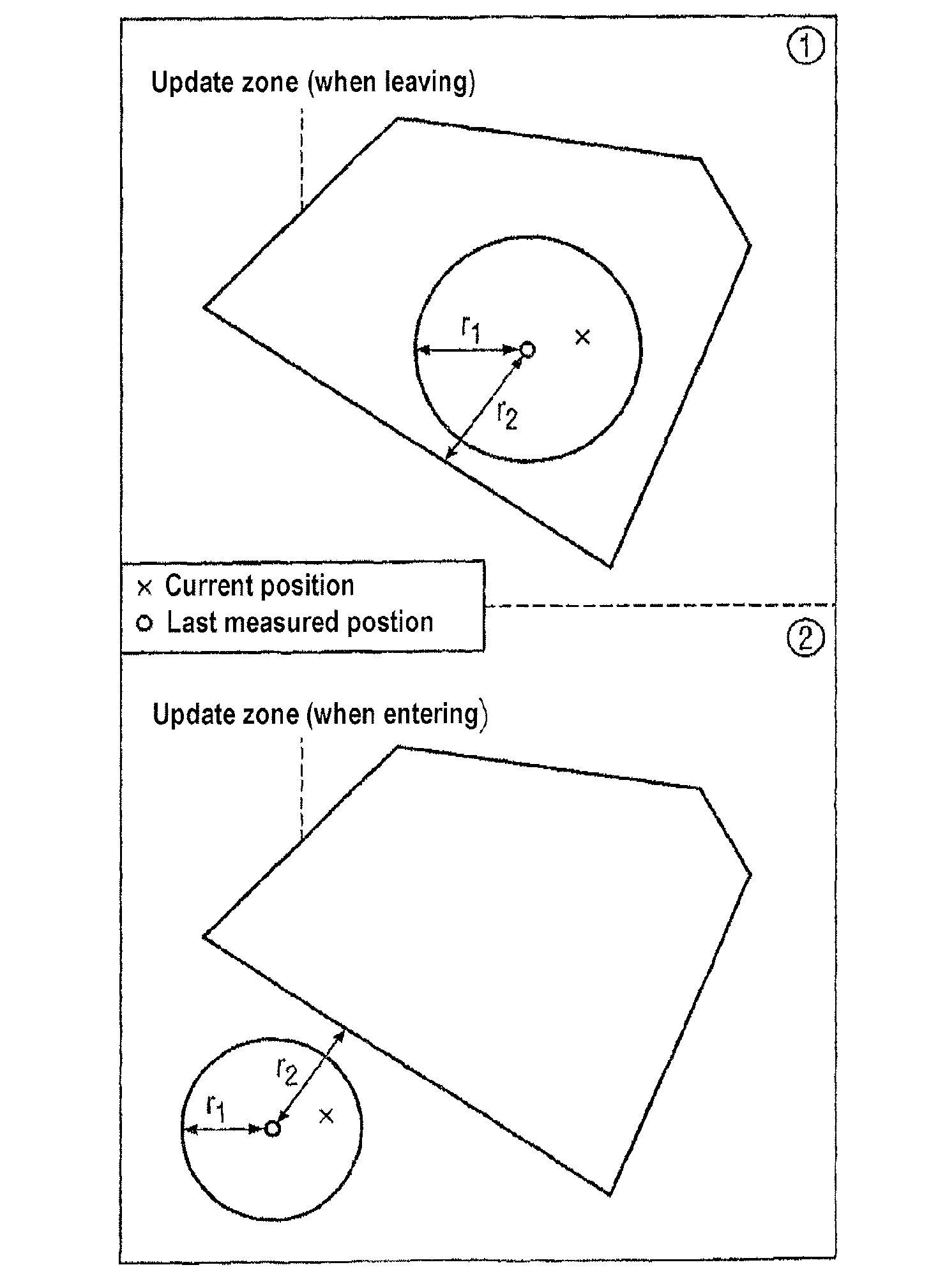
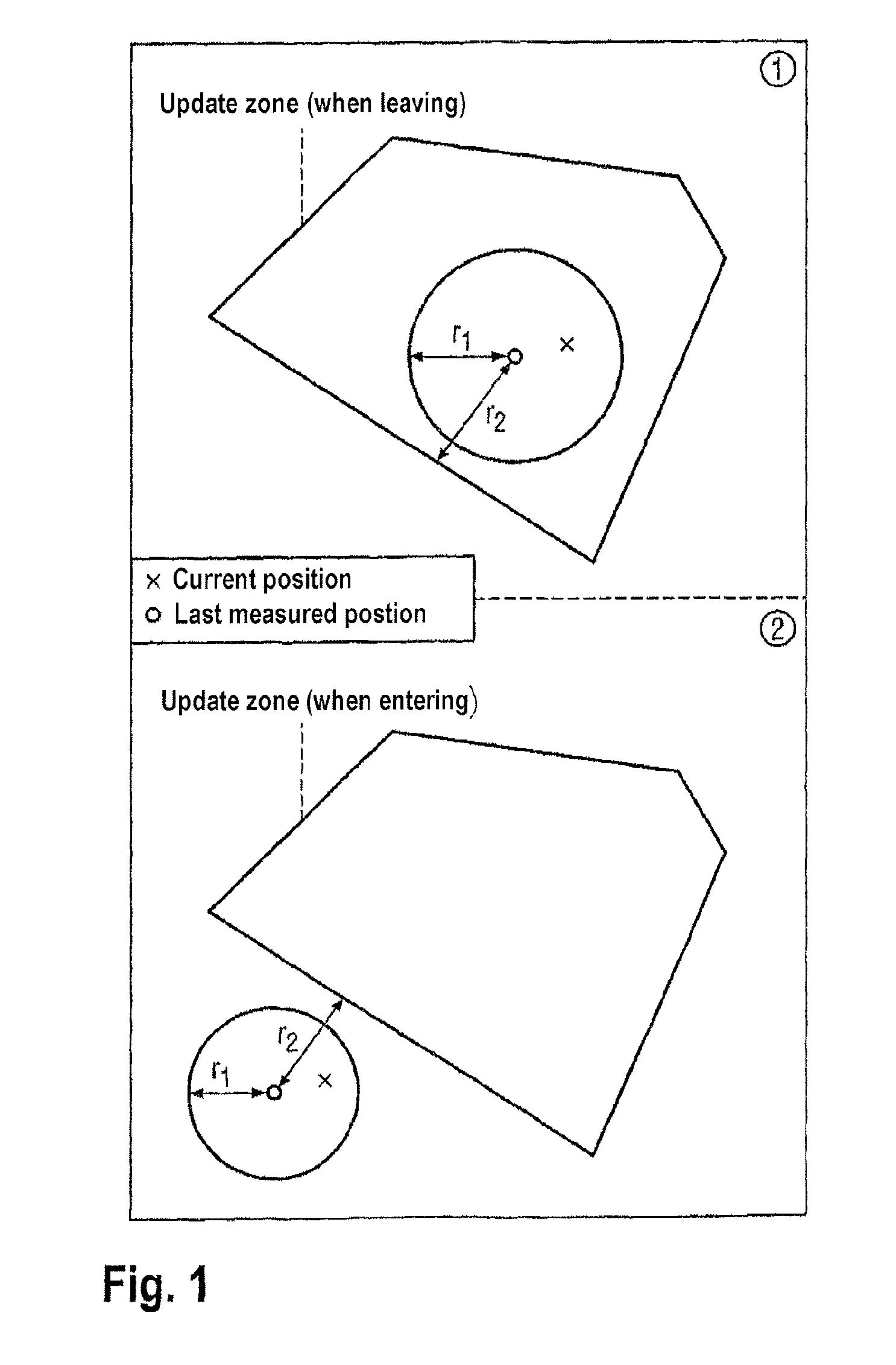
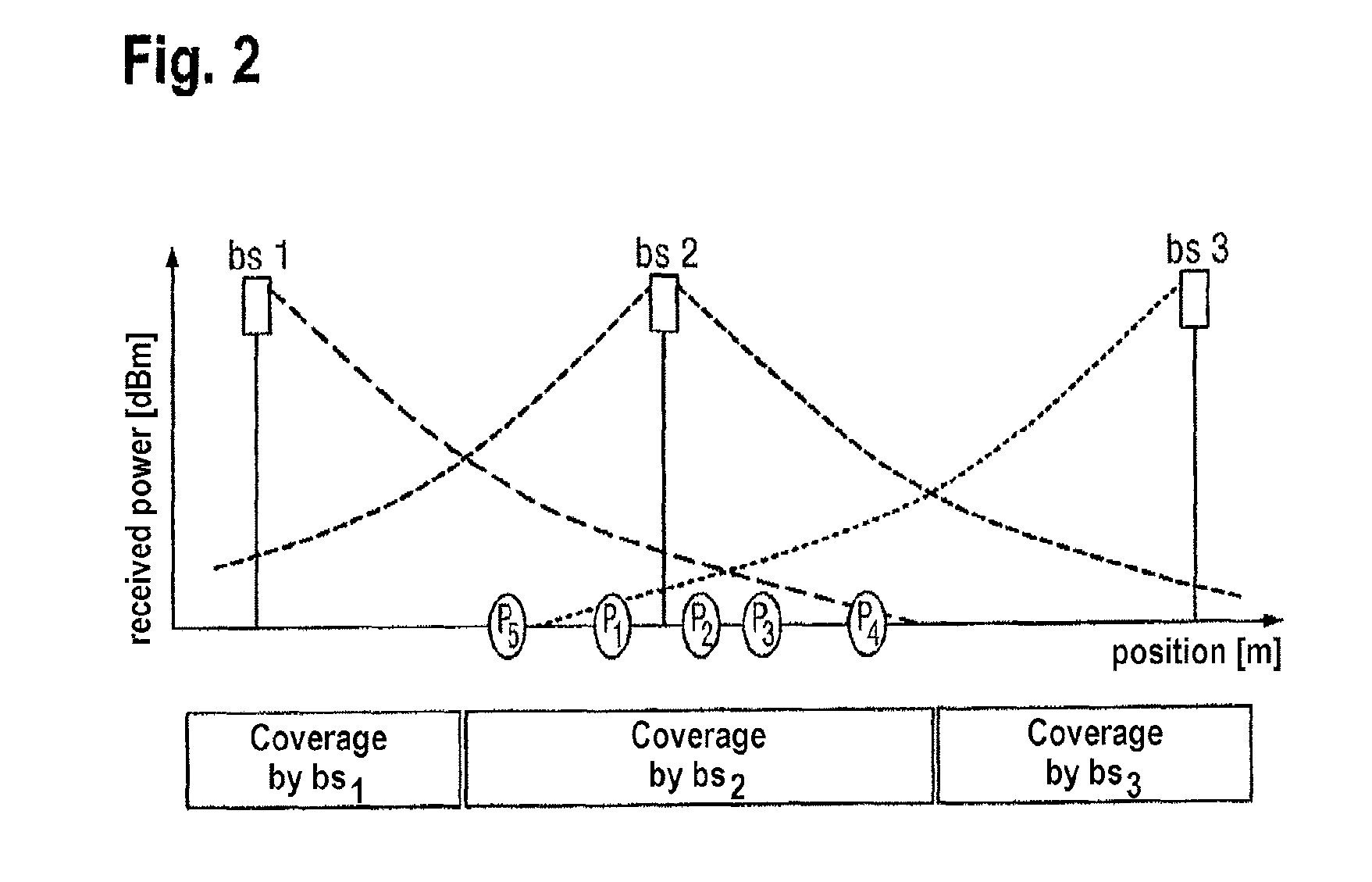
[0029]Described below is a series of processes according to exemplary embodiments of the invention, with the help of which it is possible to identify when update zones are entered and left with sufficiently high temporal and spatial resolution. This involves selective use of the locating processes described above, so that energy and other resources are conserved.
[0030]In other words, the processes described below are based on dynamic control of the locating processes.
[0031]The basic mechanism according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention is described with the aid of FIG. 1. This shows an update zone U, which is set by a service, the user of a terminal or by the network. The update zone U is assigned to a service, for which it is relevant whether the user leaves or enters the update ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com