Method and apparatus for total disc replacements with oblique keels
a total disc and oblique technology, applied in the field of artificial disc replacements, can solve the problems of reduced efficiency of disc degeneration surgery treatment, reduced treatment effect of disc degeneration surgery, and reduced ability to control vertebral motion, so as to reduce the risk of injuring the great vessels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
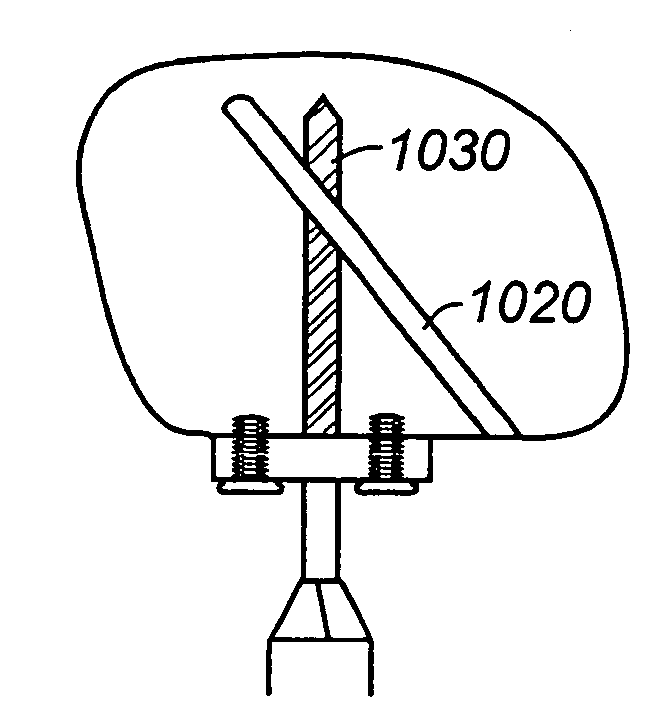
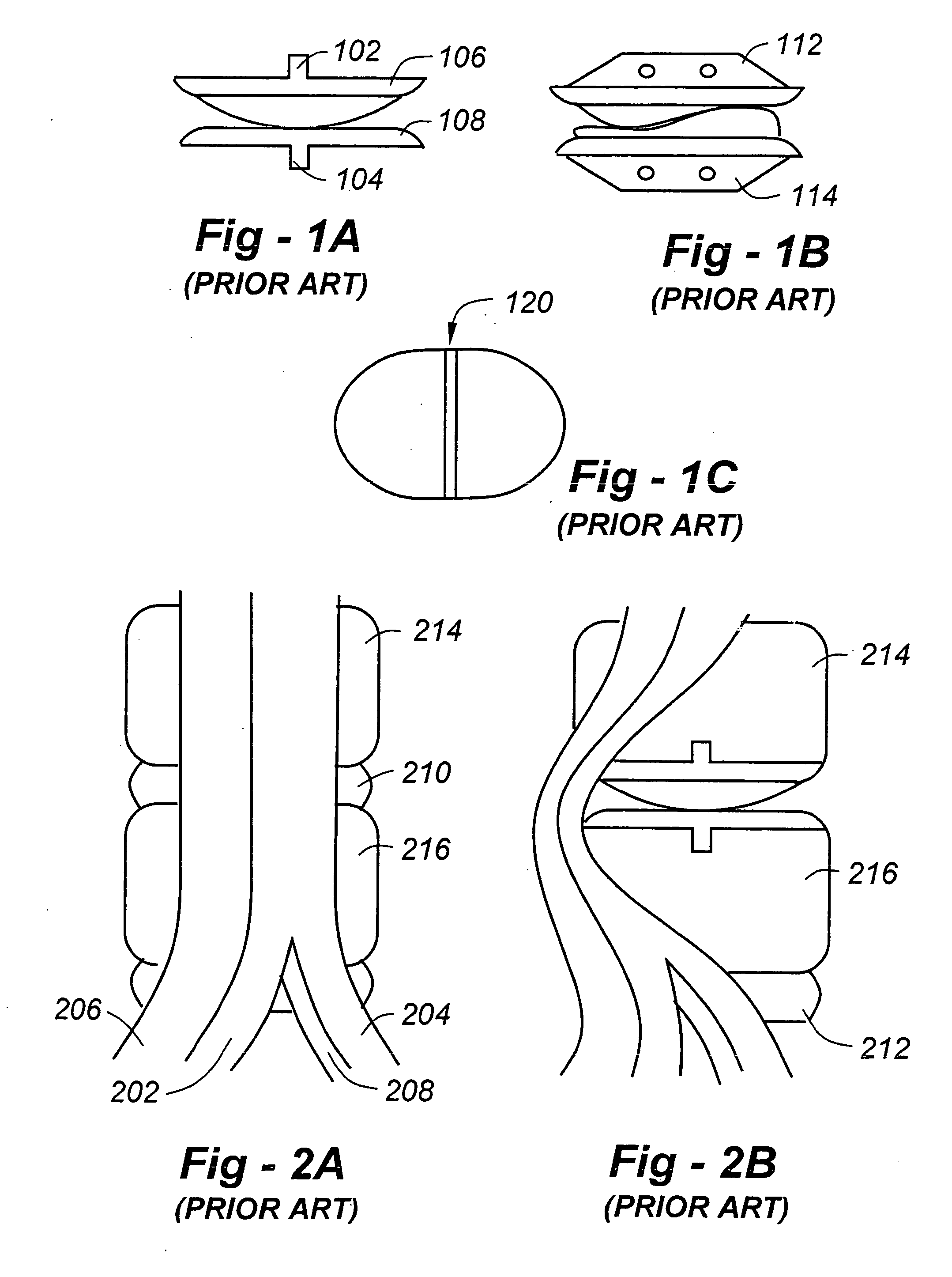
[0078]FIG. 1A is a view of the anterior aspect of a prior-art ADR. The anterior-to-posterior (A-P) oriented keels 102, 104 are represented by the projections from the top and bottom ADR endplates 106, 108. FIG. 1B is a view of the side of a prior-art ADR with anterior to posterior oriented keels 112, 114. The keels are represented by the trapezoidal shaped projections from the top and bottom ADR endplates. FIG. 1C is a view of the vertebral side of a prior-art ADR endplate. The keel is represented by area 120 of the drawing that courses from the top (posterior aspect of the ADR) to the bottom (anterior aspect of the ADR) of the drawing.
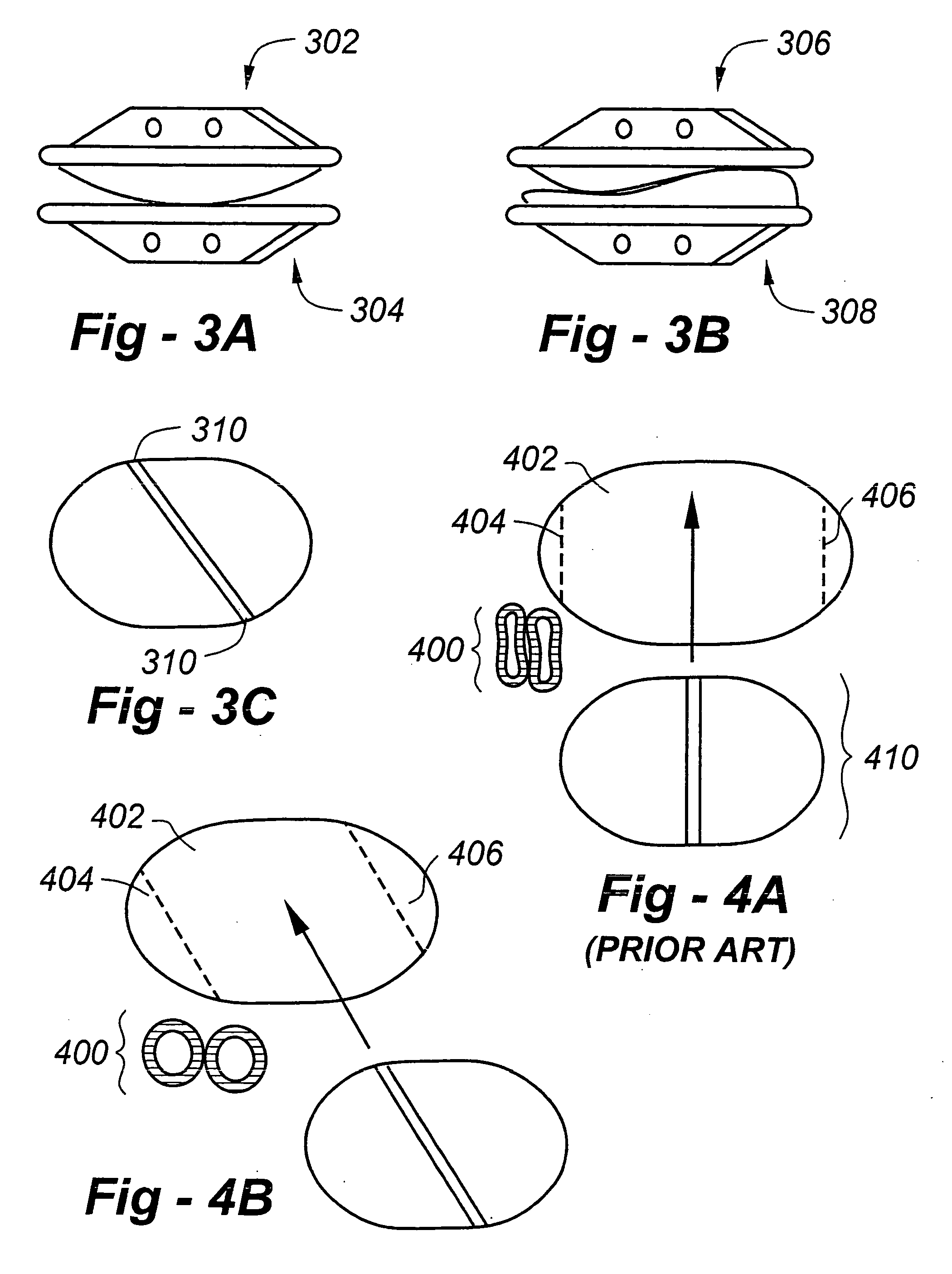
[0079]FIG. 2A is a view of the anterior aspect of the lumbar spine and the great vessels overlying the spine. The aorta and iliac arteries are indicated at 202, 204, and the vena cava and iliac veins are indicated at 206, 208. Intervertebral discs are shown at 210, 212, and vertebrae are shown at 214, 216. FIG. 2B is a view of the anterior aspect of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com