Inspection and assurance system
a technology of inspection and assurance system, applied in the direction of conveyors, electric digital data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the load of inspection work, shortening the number of conveyors and sorting at the downstream side, and complicated working in order to cope with different requirements of different clients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0038] (Sorting Method and Apparatus)(FIGS. 1, 4)
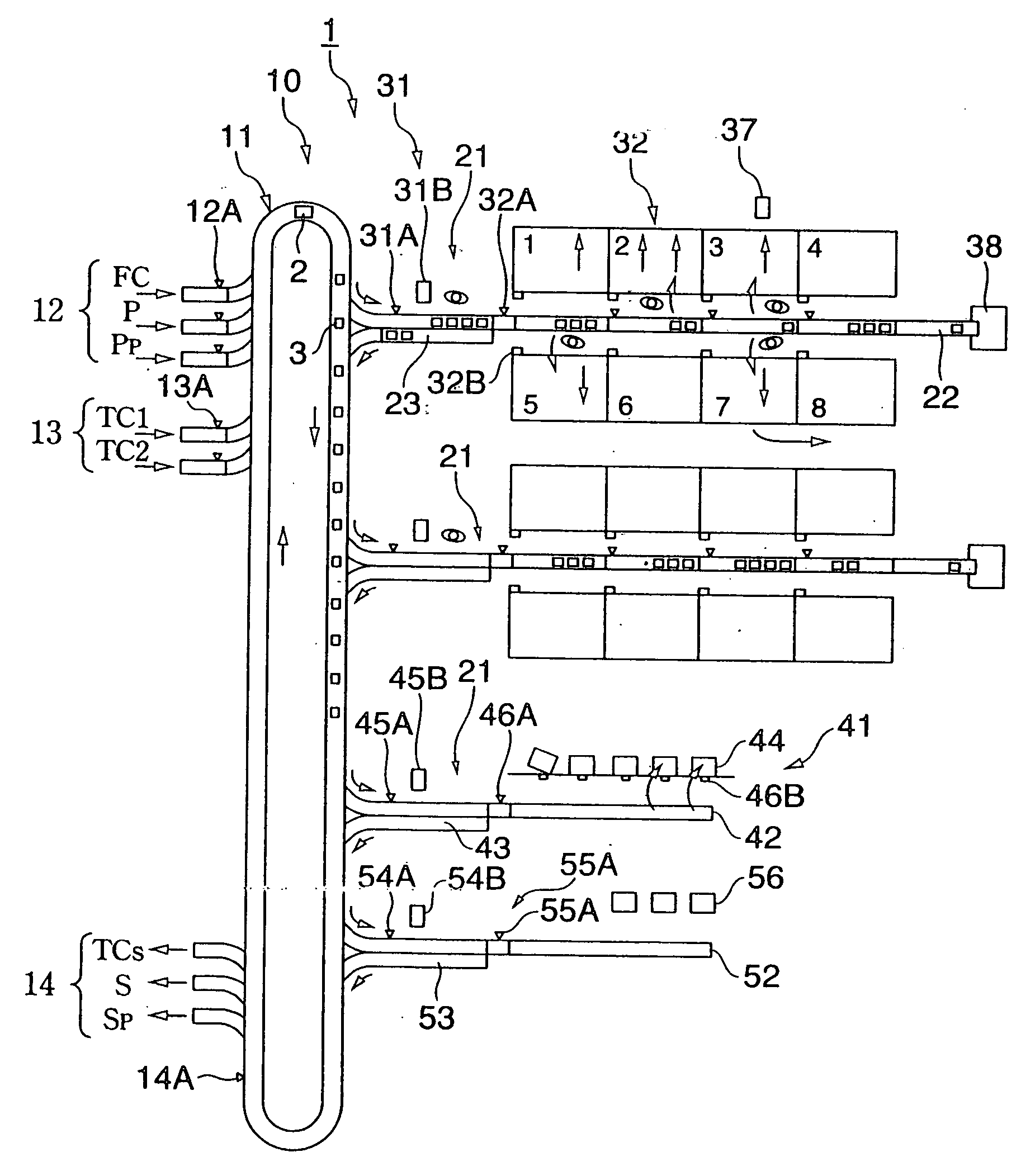
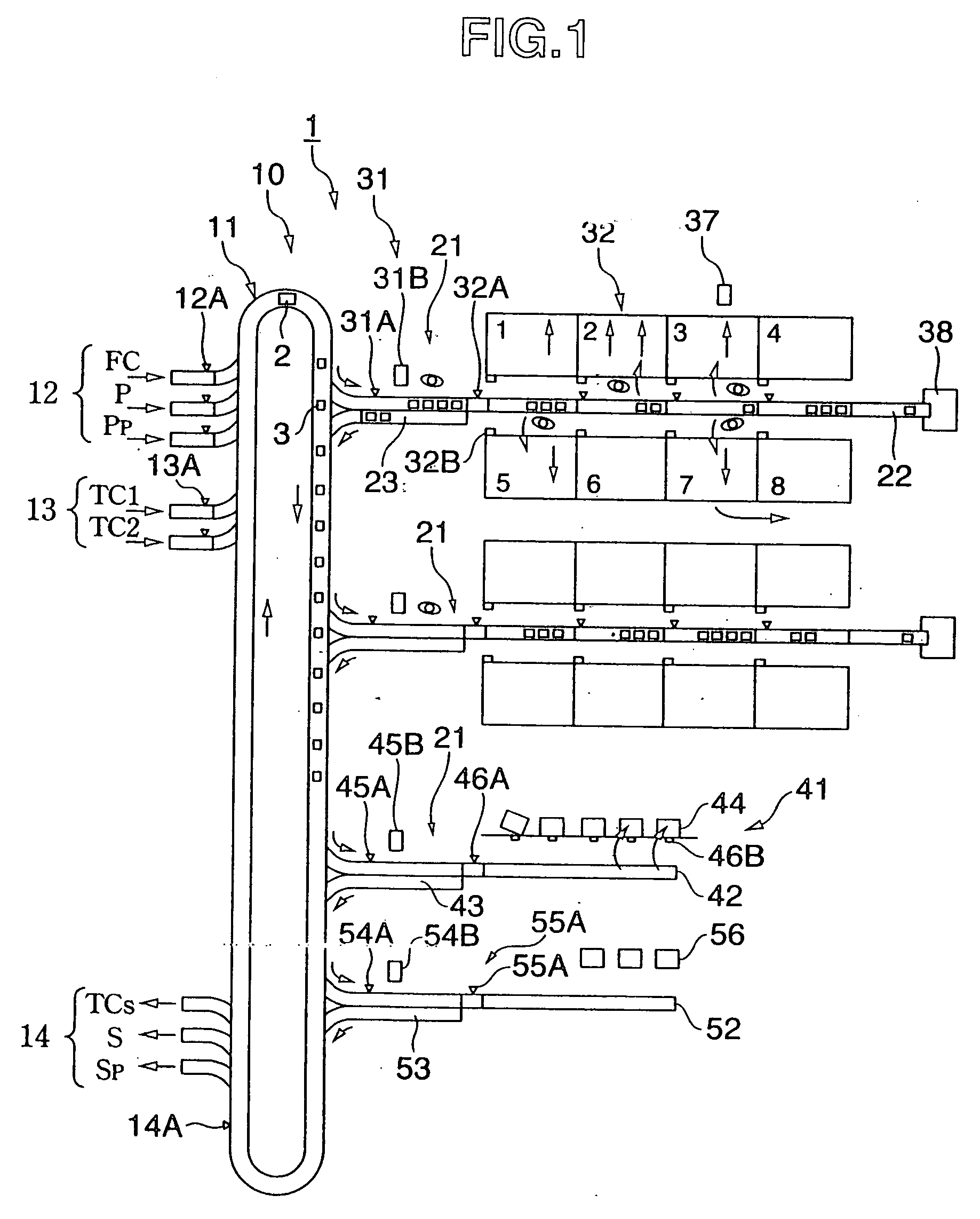
[0039] A delivery inspection center 1 of FIG. 1 is provided between a plurality of suppliers and a plurality of retailers and has a sorting apparatus 10.
[0040] The sorting apparatus 10 has a first sorting / conveying line 11 and a second sorting / conveying line 21. The second sorting / conveying line 21 has a fractionating zone 31 and a segmenting zone 32, or has a large case article sorting line 41.
[0041] (First Sorting / Conveying Line 11)
[0042] The first sorting / conveying line 11 has a stock article (DC article) supplying section 12 as a place for stock and a loop shaped sorting conveyer circulating commodities supplied from another supplier's article (TC article) supplying section 13. These commodities are sorted into a plurality of the second sorting / conveying lines 21 (branching destinations). Further, the first sorting / conveying line 11 has a surplus article branching section 14 for returning the surplus articles which is not nece...
second embodiment
THE SECOND EMBODIMENT
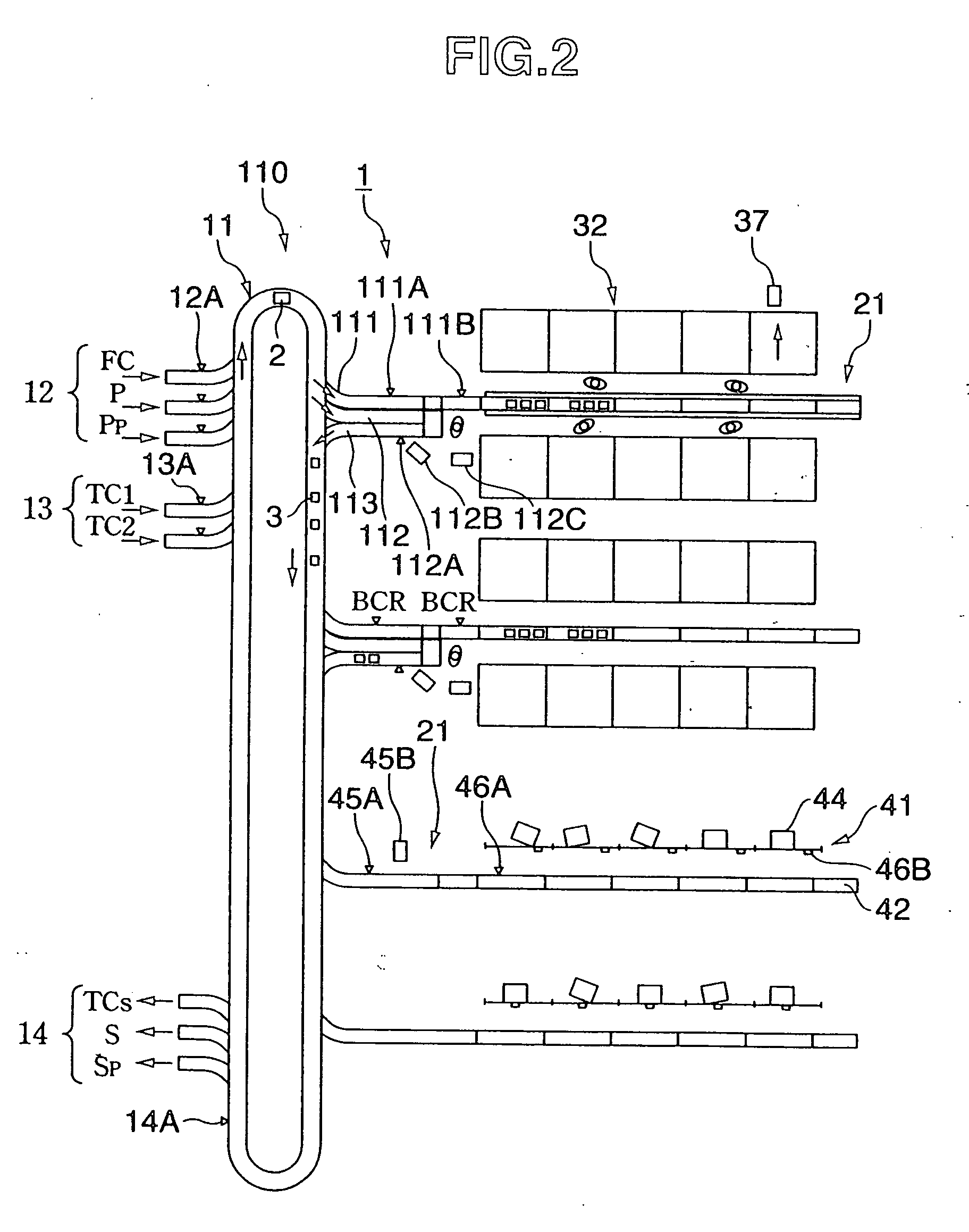
[0190] (FIG. 2)
[0191] The sorting apparatus 110 shown in FIG. 2 differs from the sorting apparatus shown in FIG. 1 such that the second sorting / conveying line 21 is provided with the case unit passing article branch line 111, surplus article segregation branch line 112, and surplus article returning line 113. The sorting apparatus 110 is effective when the case unit branch amount from the first sorting / conveying line 11 to the second sorting / conveying line 21 is large.
[0192] The case article branched to the case unit passing article branch line 111 is read out by bar code reader BCR 111A. Further, the case article is read out by bar code reader BCR 111B provided at the entrance of each zone of the segmenting zone 32. The case article is sent to a corresponding zone based on the read out data.
[0193] The commodity branched to the surplus article segregation branch line 112 is read out by a bar code reader 112A. The fetching indicator 112B performs the fetching ...
third embodiment
THE THIRD EMBODIMENT
[0194] (FIG. 3)
[0195] The sorting apparatus 120 shown in FIG. 3 differs from the sorting apparatus 10 shown in FIG. 1 such that there are provided a subsection line 121 and a pass line 122 as a commodity provision system for the first sorting / conveying line 11. A plurality of second sorting / conveying lines 21 are constituted by the branch lines 123 which are not necessary to be returned and are taken to be dedicated lines in every area A, B, and C. The sorting apparatus 120 separates the commodity of single article case 2, or singleness container 3, introduced to the subsection line 121 into necessary article and surplus article of each area A, area B or area C based on instruction of subsection indicator 124A of subsection working area 124. The necessary articles are subjected to subsection into tray 5 in each area A, area B, area C. A label issued by the label issuing machine 124B is attached to this tray 5. Bar code reader BCR 121A of the exit of the subsecti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com