Receiver architecture with digitally generated intermediate frequency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
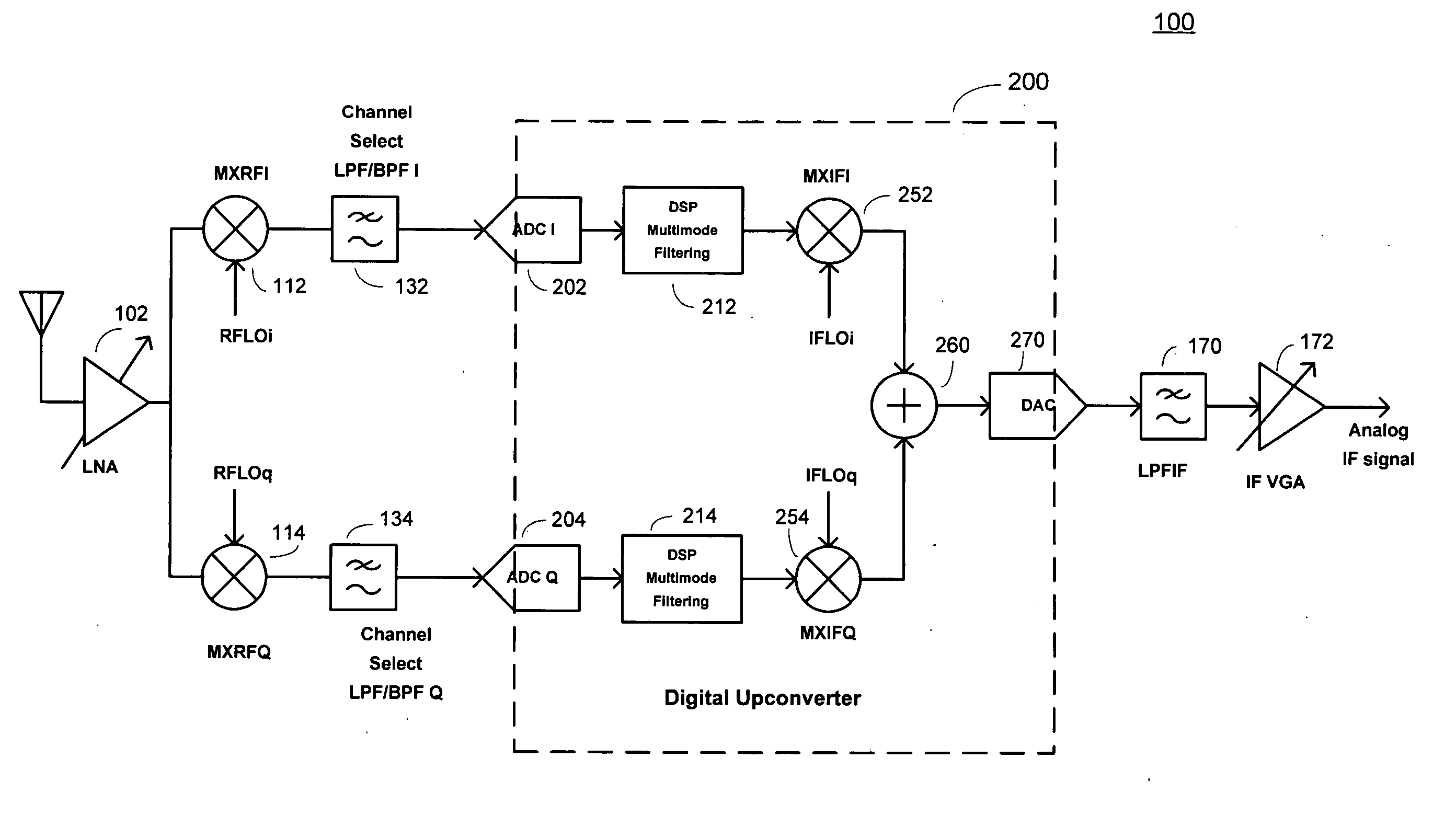
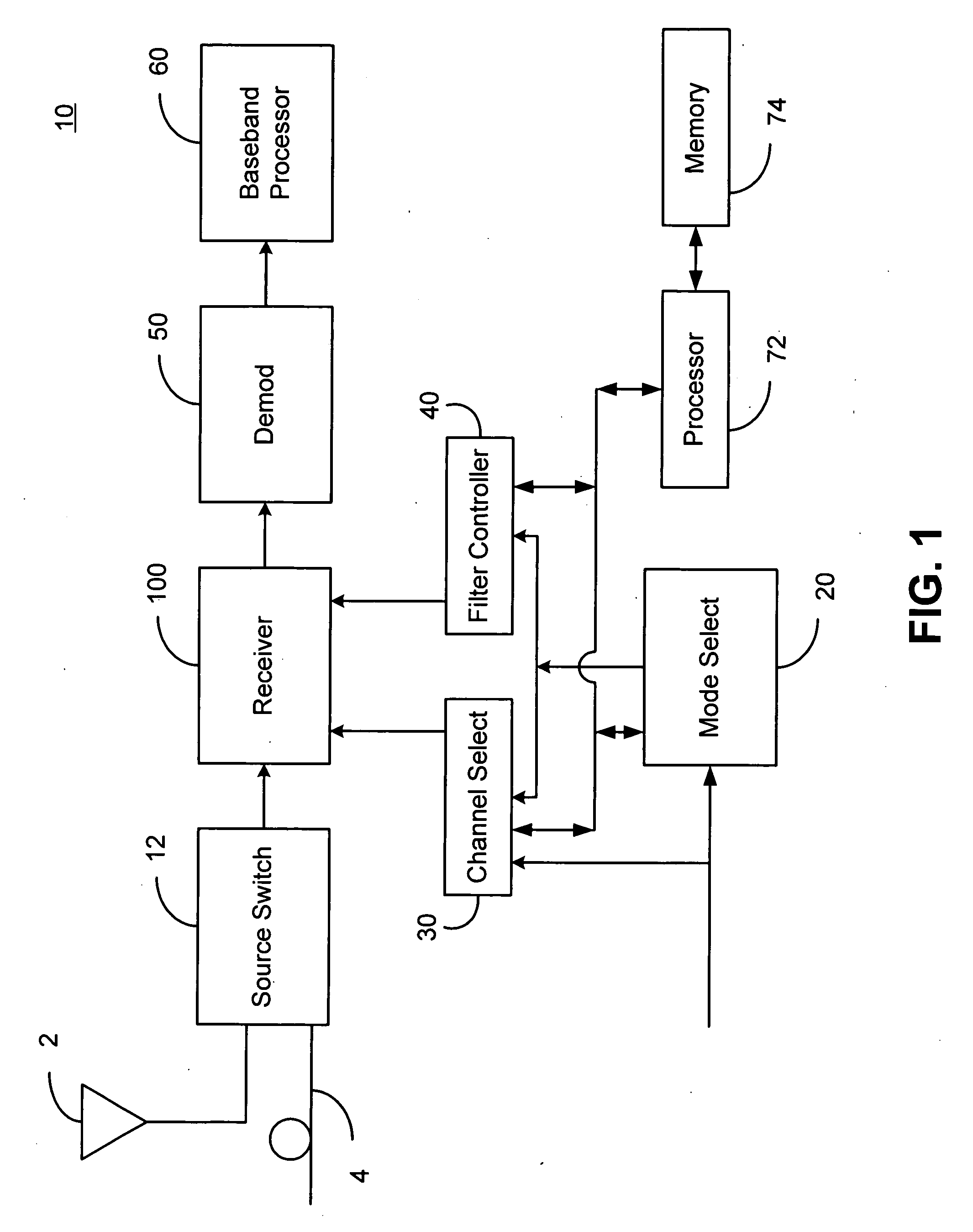
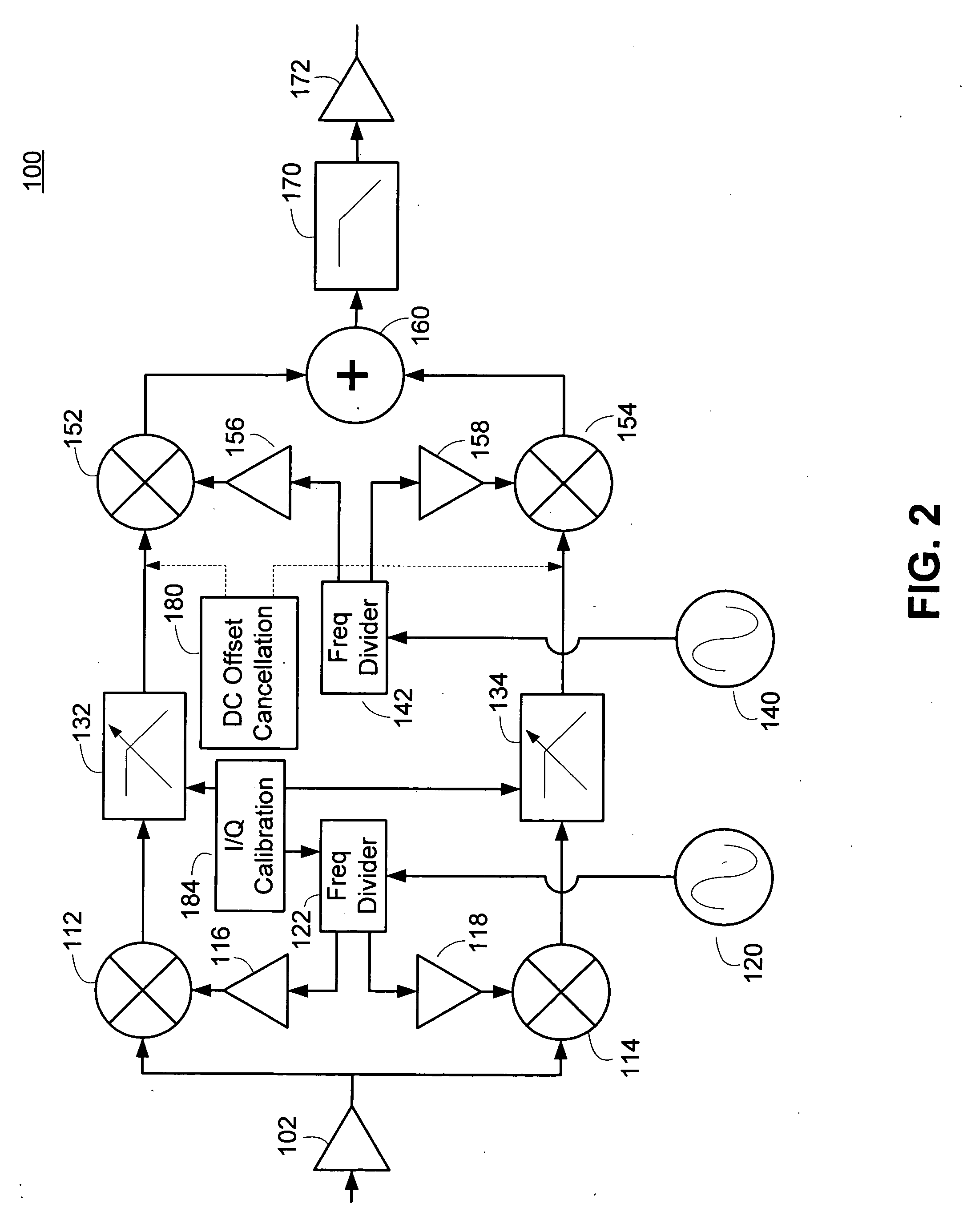
[0022] A receiver architecture is disclosed where the receiver performs conversion to zero Intermediate Frequency (IF) or low IF, performs anti-aliasing and partial channel selection filtering, converts the zero- or low-IF signal to the digital domain, performs frequency conversion by digital processing (for example mixing) to an arbitrary intermediate frequency, then converts the signal back to the analog domain with a digital-to-analog converter.
[0023] This approach provides the receiver with the following key advantages: an architecture suitable for single-chip implementation; flexible channel selection and IF filtering compatible with analog and digital standards; hybrid operation allowing a choice of either a low-IF or direct conversion; flexible choice of IF; substantially perfect conversion of In-phase and Quadrature signal paths to the IF as a result of the digital implementation; the option to perform digital baseband / low-IF processing; and an analog output that can be use...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com