Methods for treating and preventing insulin resistance and related disorders
a technology for applied in the field of methods for treating and preventing insulin resistance and related disorders, can solve the problems of untimely death, untimely death, and significant personal and financial costs of patients and their families, and achieve the effects of preventing or treating the disease or condition in the individual, reducing lipolysis, and increasing the level of ffa and/or glycerol
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
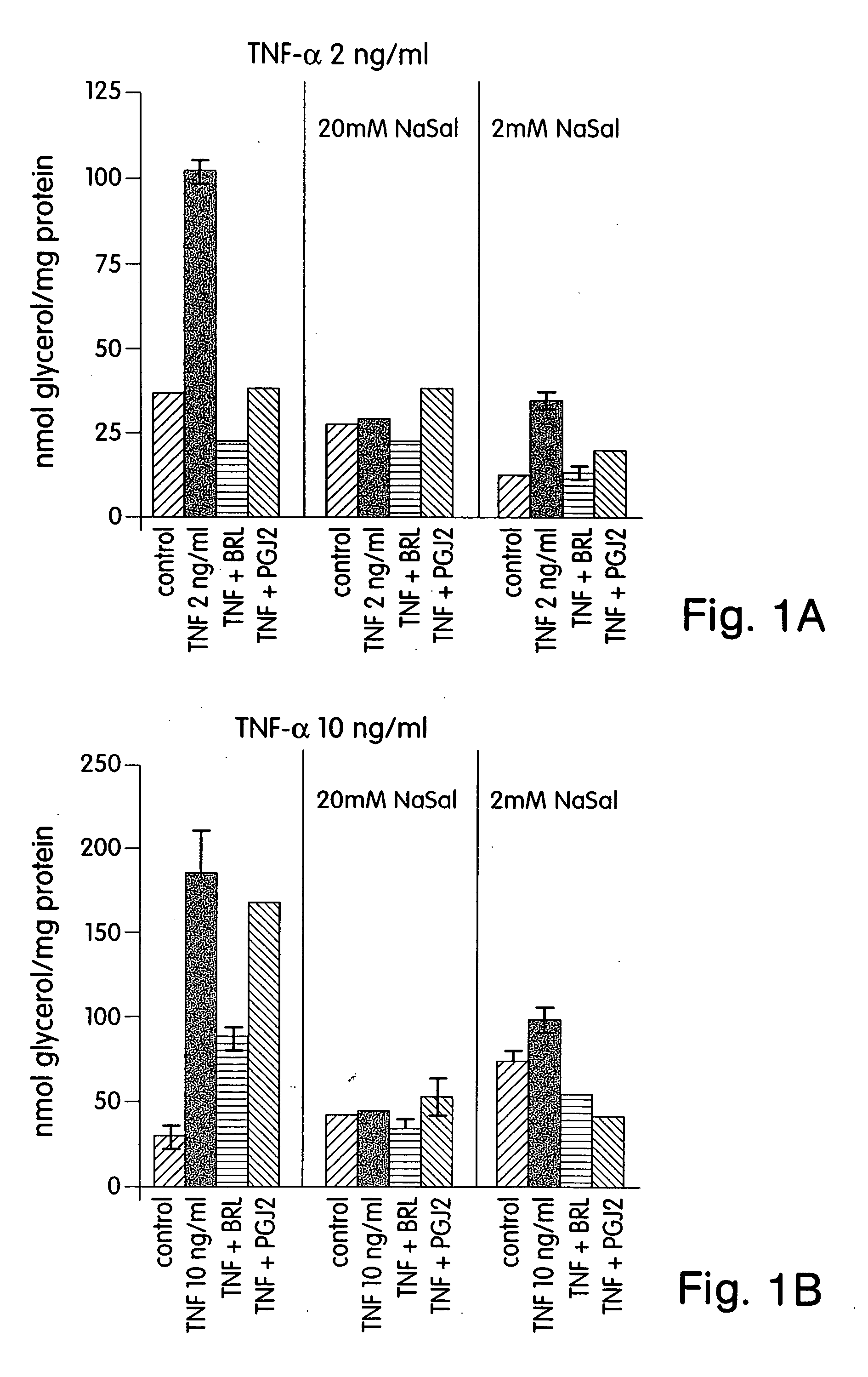
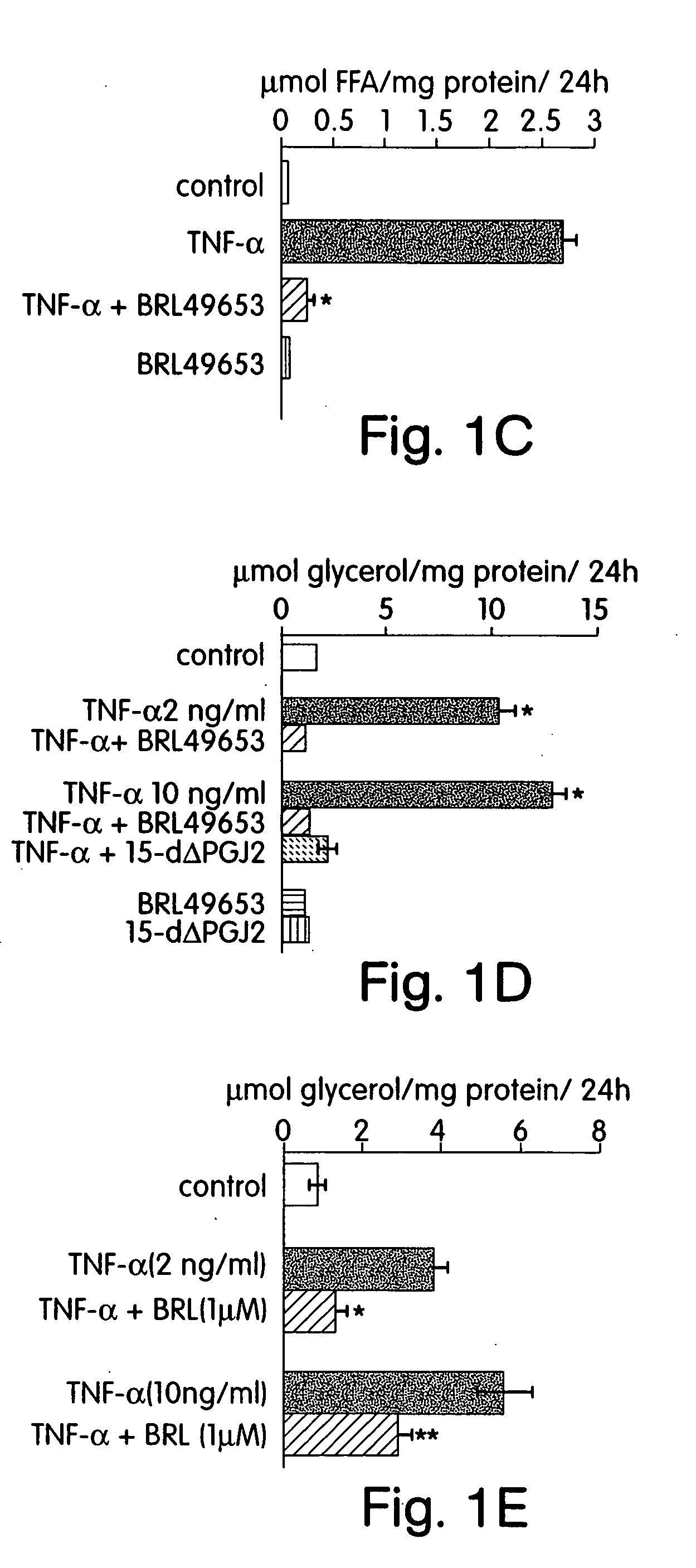
Sodium Salicylate and the PPAR-γ Agonists BRL and PGJ2 Each Block TNF-α Induced Lipolysis
[0207] This example demonstrates that salicylic acid, as well as the PPAR-γ agonists BRL and PGJ2 are capable of blocking TNF-α induced lipolysis.
[0208] 3T3-L1 adipocytes used in this example were obtained from 3T3-L1 fibroblasts as follows. 3T3-L1 fibroblasts (ATCC Deposit NO. CL-173, described in U.S. Pat. No. 4,003,789) were cultured in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM) containing 10% bovine calf serum, and induced to differentiate into adipocytes using standard protocols, as described, e.g., in Kohanski et al. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 261:12272. Adipocytes were used 10-15 days after the differentiation protocol was initiated.
[0209] Differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes cultured in 12 well plates were incubated overnight in DMEM+0.5% BSA in the absence of serum. The following morning, the cells were incubated in the presence or absence of 2 mM or 20 mM sodium salicylate (NaSal) and treated...
example 2
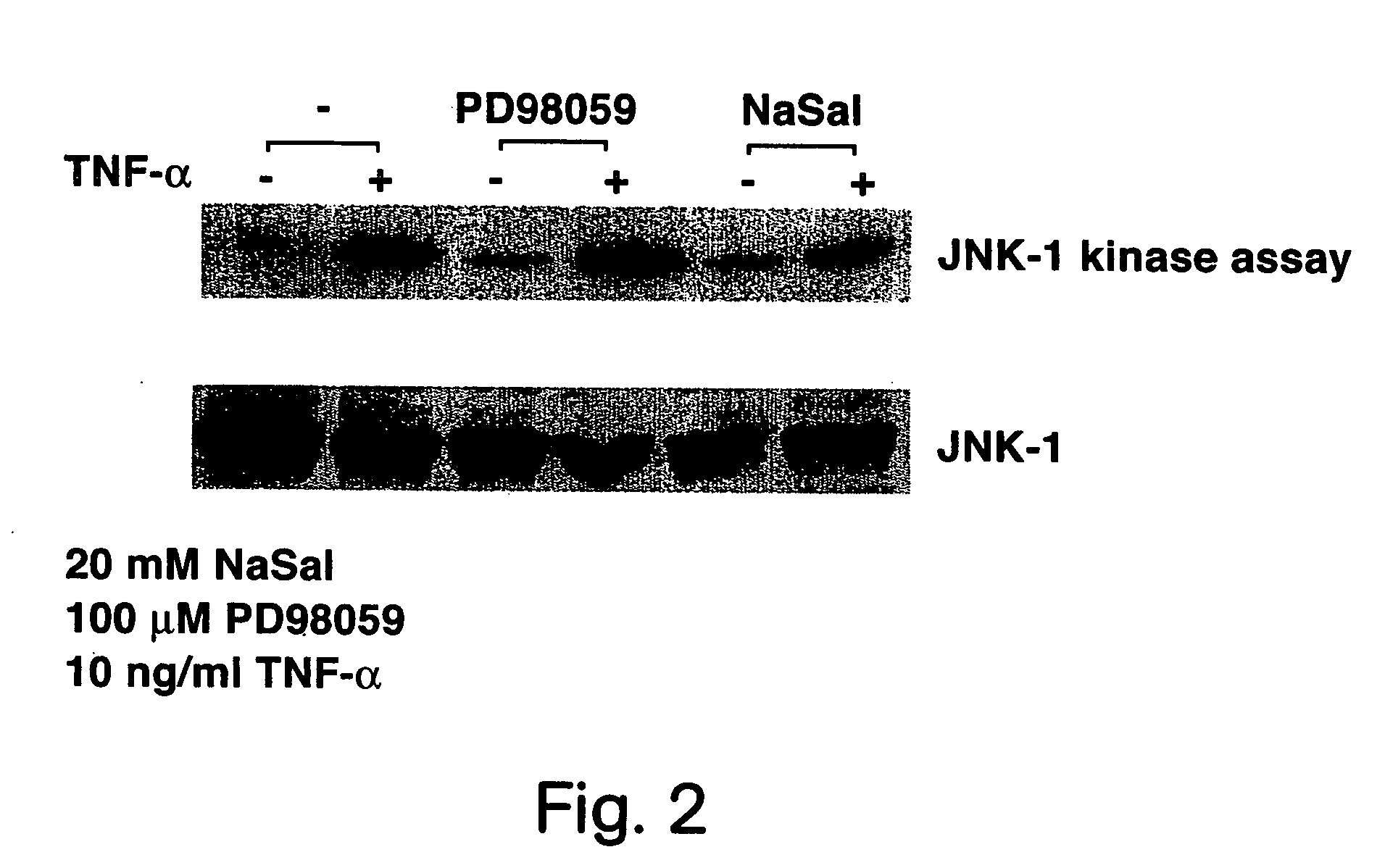
NaSal Inhibits TNF-α Induced JNK-1 Activation in Adipocytes
[0218] This example shows that NaSal inhibits JNK-1 activation by TNF-α in adipocytes.
[0219] 3T3-L1 adipocytes were pretreated for 3 hours with or without 20 mM NaSal, with or without 100 μM MAP kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitor PD98059 (Biomol; Cat. No. EI-360) and then for 15 minutes with 10 ng / ml mTNF-α. JNK-1 kinase assays were then performed with extracts of each of these cell cultures on an N-terminal portion of c-jun, as described in Derjarde et al. (1994) Cell 76: 1025.
[0220] The results are shown in FIG. 2. The results indicate that TNF-α induces activation of JNK-1 and this activation is significantly reduced by NaSal, but not by the MAK kinase inhibitor PD98059.
[0221] Thus, since NaSal inhibits TNF-α induced lipolysis and NaSal significantly reduces JNK-1 activation, JNK-1 activation is likely to play a significant role in blocking lipolysis induced by TNF-α.
example 3
NaSal Partially Inhibits TNF-α Induced MAP Kinase Activation
[0222] This example shows that, similarly to JNK-1 activation by TNF-α, activation of MAP kinases by TNF-α is also inihibited by NaSal.
[0223] In this example, 3T3-L1 cells were treated as described in Example 2, and cell extracts were used in an ERK 1 / 2 kinase assay, using MBP (myelin basic protein) as a substrate. The assay used is described in Boulton et al. (1991) Cell Reg. 2: 357.
[0224] The results, which are shown in FIG. 3, show that TNF-α significantly increases ERK112 activation, as shown by the seven fold increase in phosphorylation of the MBP substrate used in the assay. As expected, the MAP kinase inhibitor inhibited ERK1 / 2 activation, as shown by the fact that MBP phosphorylation was increased only by a factor of less than two in the presence of TNF-α and PD98059. ERK1 / 2 activation was also inhibited by about two fold by NaSal.
[0225] Thus, ERK1 / 2 activation by TNF-α is also inhibited by NaSal, as is JNK-1, i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com