Echogenic needle for transvaginal ultrasound directed reduction of uterine fibroids and an associated method
a technology of uterine fibroids and ultrasound, which is applied in the direction of ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnostics, applications, tomography, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the patient's recovery, and carries the usual risk of surgery, so as to achieve heightened visibility and facilitate the manipulation of the needle. , the effect of enhancing the visibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
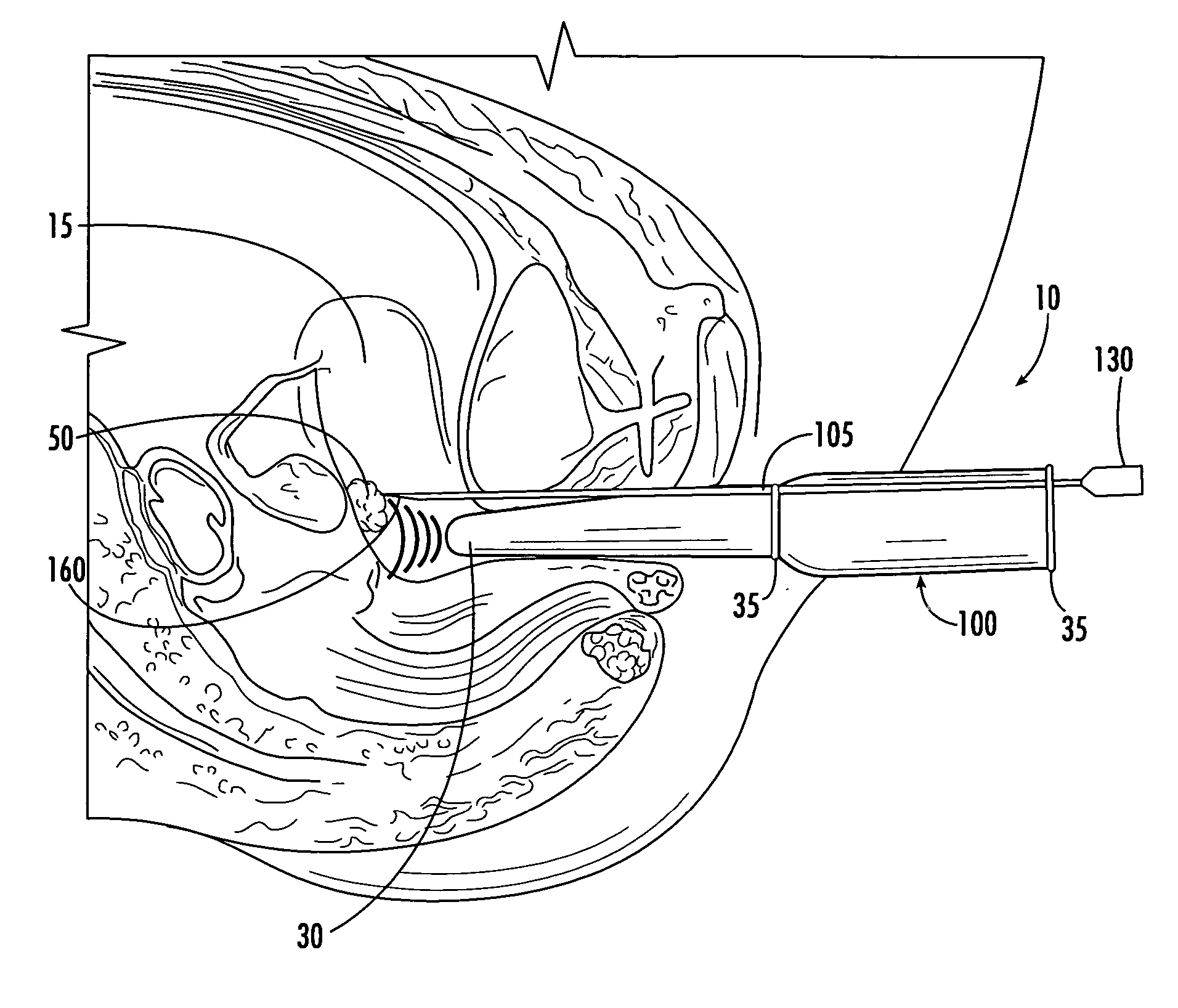
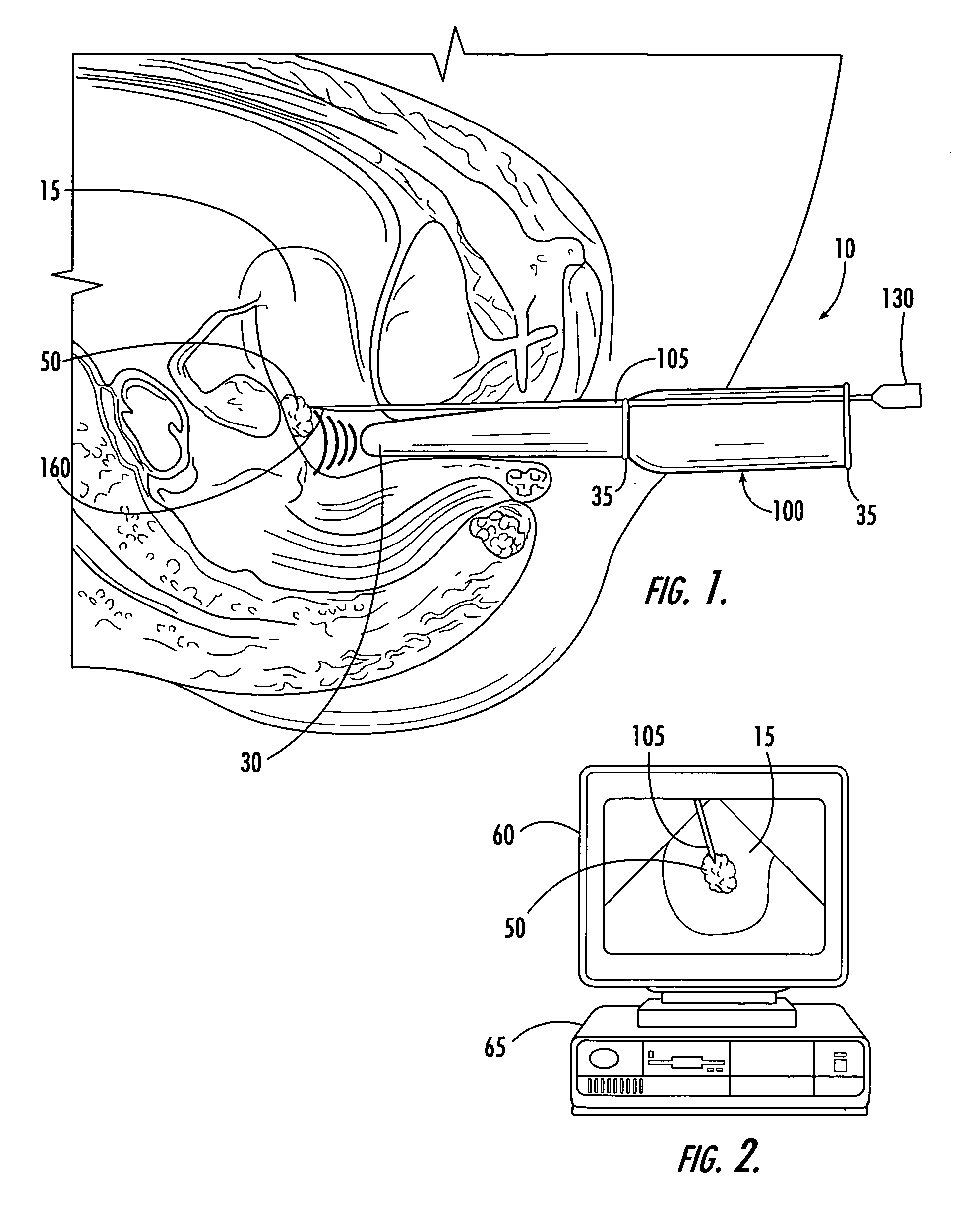
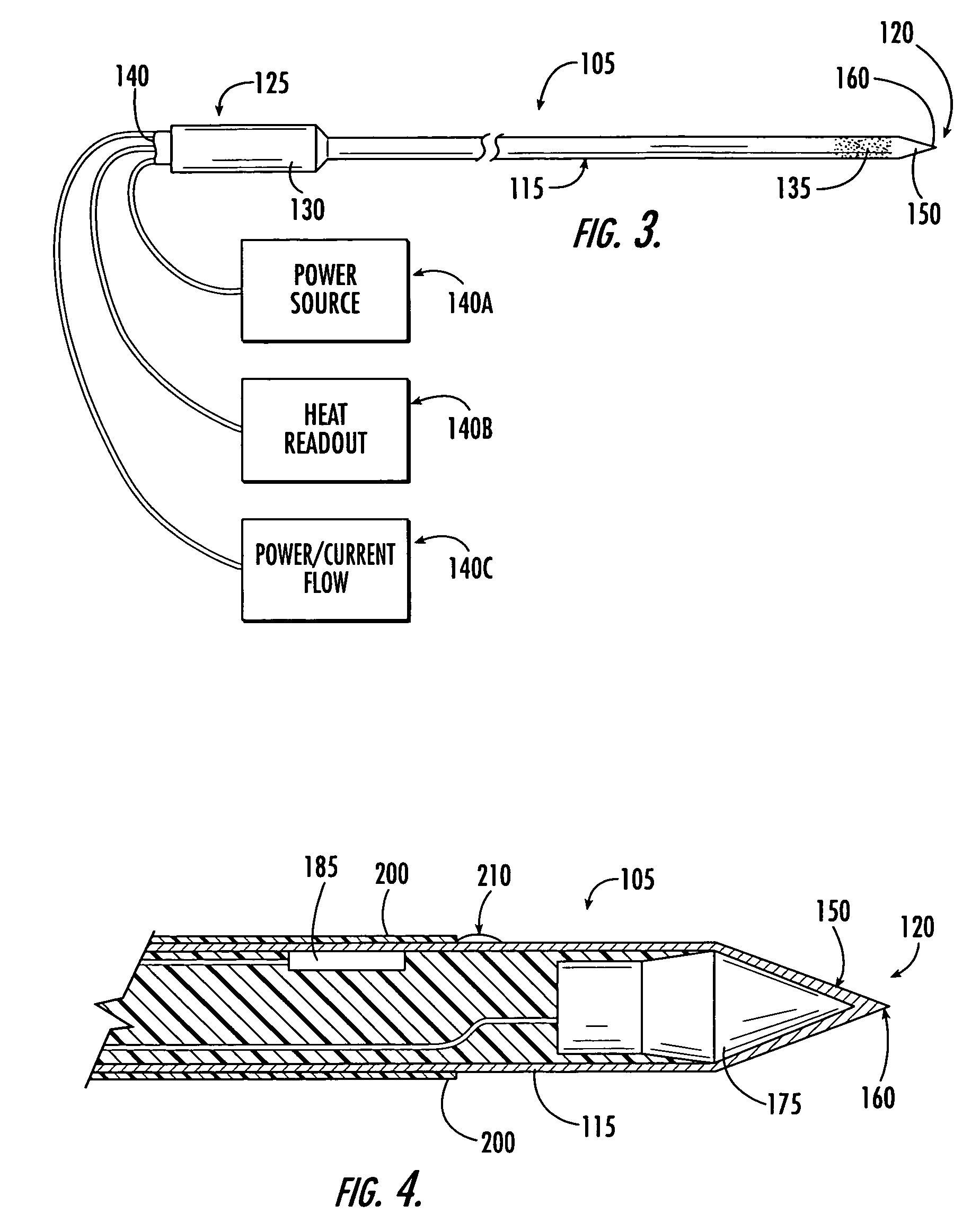
[0040] In FIG. 4, the active electrode 175 is depicted at the distal end 120 within the needle. In this first embodiment, the distal end's noninsulated outer surface 150 is electrically conductive so that RF energy passes from the active electrode 175 into fibroid tissue. The distal end 120 has a sharpened tip 160 that can penetrate fibroid tissue to deliver RF energy within the fibroid. As shown in FIG. 4, the RF needle optionally has a temperature sensor 185 disposed near the distal end 120. Typically, the temperature sensor will be disposed near the tip of the needle or within the insulation sheath. Normally, the temperature sensor is a thermocouple or thermistor. The sensor provides information that enables the physician to monitor tissue temperature and to adjust the power accordingly.
[0041] With reference to FIGS. 5 through 9, reference number 400 broadly designates a RF needle having a RF energy “shut-off” mechanism. The shut-off mechanism turns off RF energy to the active el...
second embodiment
[0046] In a needle having a safety mechanism 400, the active electrode is located at the blunt rear end. As shown in FIG. 8, the active electrode 175 is located at the blunt rear end 425 and an electrical connector 425a extends longitudinally from the conductive surface 410 to the active electrode 175. The outer member 115 has a second conductive surface 420 that is in communication with RF power supply, but rather than having a third surface in communication with the active electrode, the conductive surface 410 on the inner member 405 is in communication with the active electrode 175. When pressure is applied to the blunt rear end 425, the spring 430 compresses and the inner member retracts into the outer member. As a result, the conductive surfaces 410, 415 contact one another and RF current is applied to the active electrode 175. Typically, the electrical connector 425a is disposed within the inner member 405.
[0047] However, the electrical connector 425a may be disposed between t...
third embodiment
[0048] In a RF needle with a safety mechanism 400, the inner member is connected to a switch. With reference to FIG. 9, a needle is shown having an inner member 405 attached to a switch 450. The switch 450 is in communication with a RF power source via line 455. As pressure is applied to the blunt rear end 425 the inner member 405 retracts into the outer member 115 and closes the switch 450. When in the closed position, the switch 450 sends an electrical signal through line 455 to the RF power supply 140a and RF energy is delivered to the active electrode. The active electrode is located at the distal end and is in communication with the switch, or alternatively, the noninsulated distal end 120a is the active electrode.
[0049] In all the embodiments of a needle having a safety mechanism 400 the inner member 405 is typically made from a material that is non-conductive, such as a plastic. Normally, a non-conductive member will have a conductive material, such as stainless steel, insert...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com