Liquid crystal display device
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
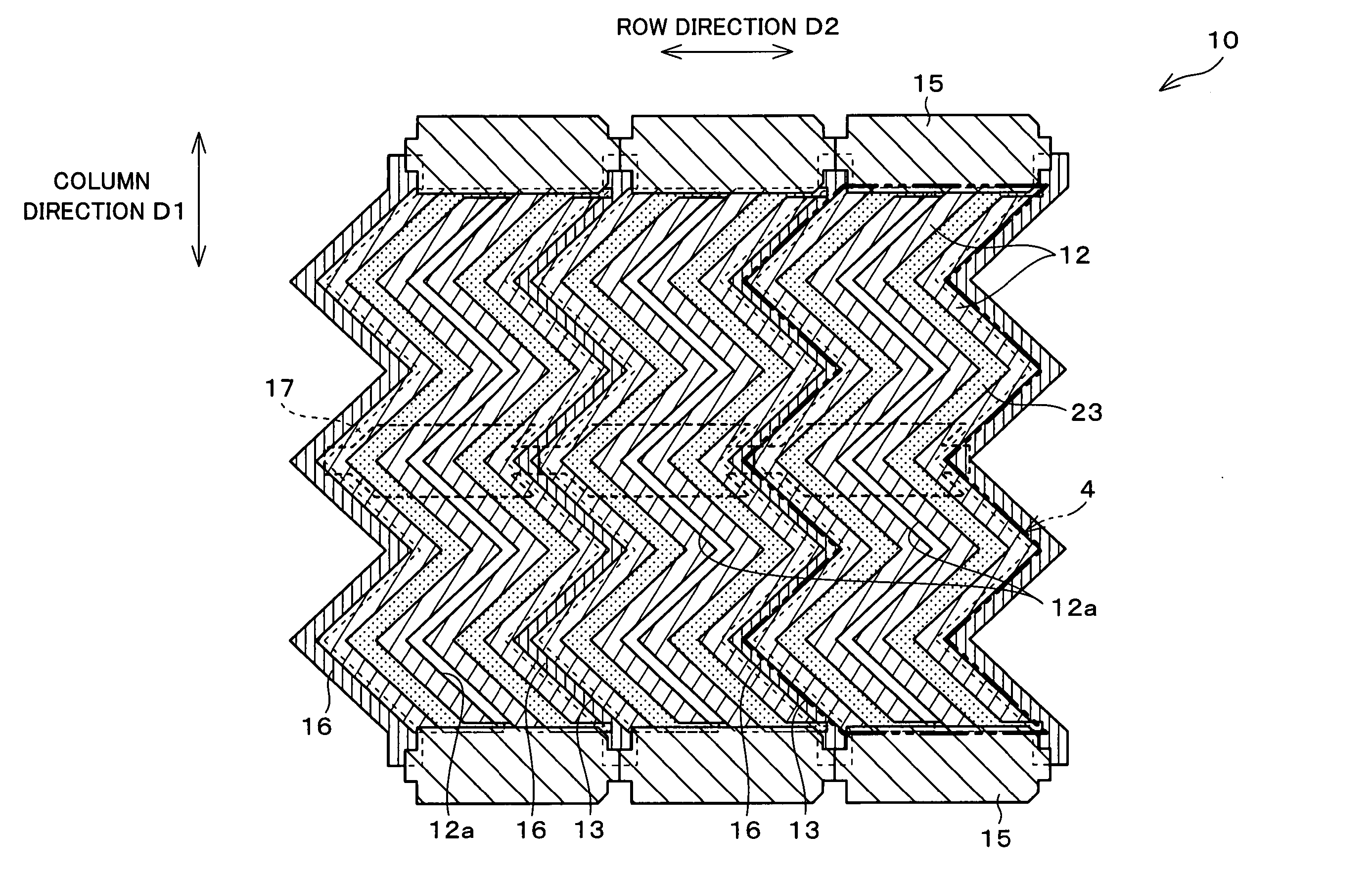
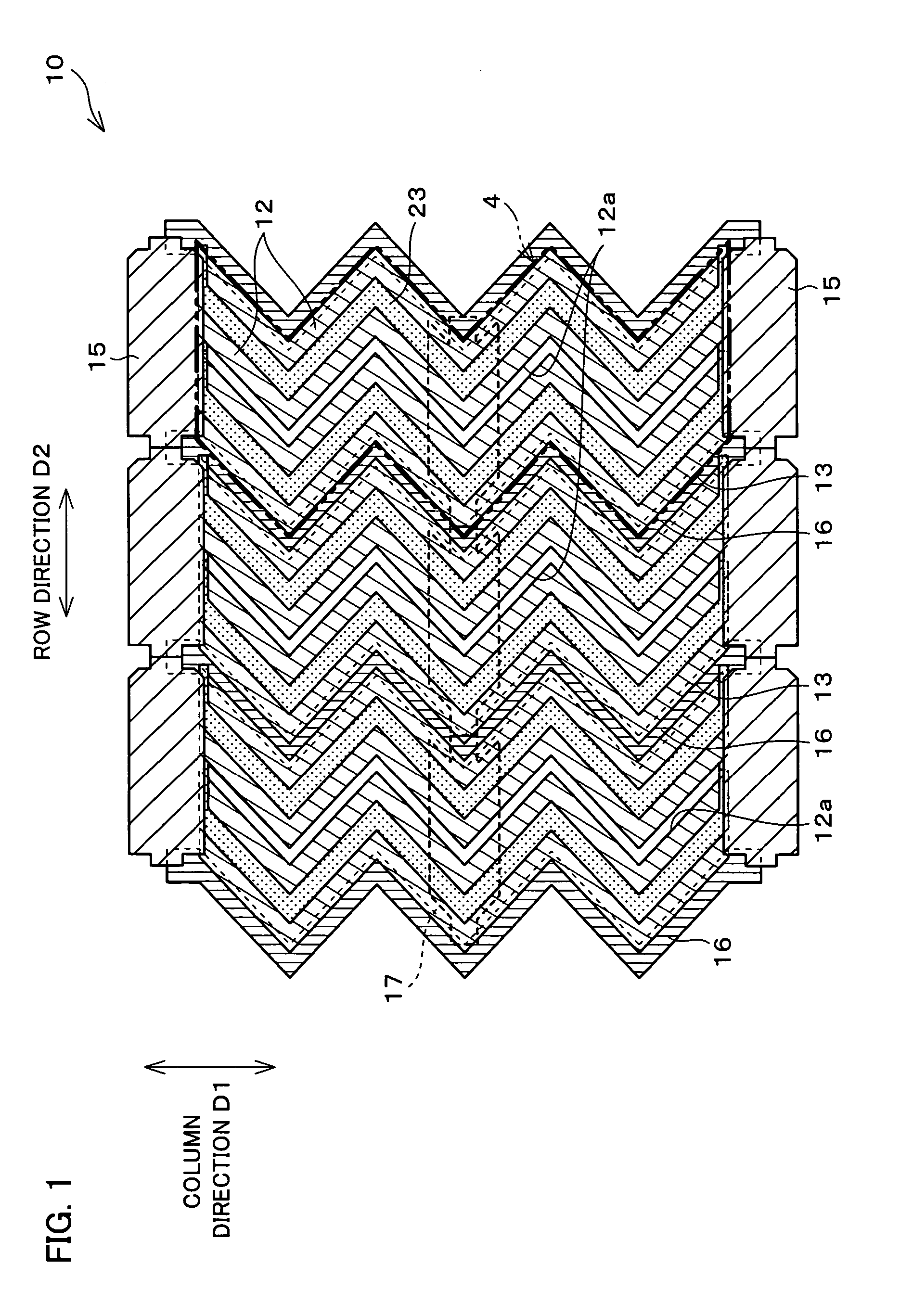
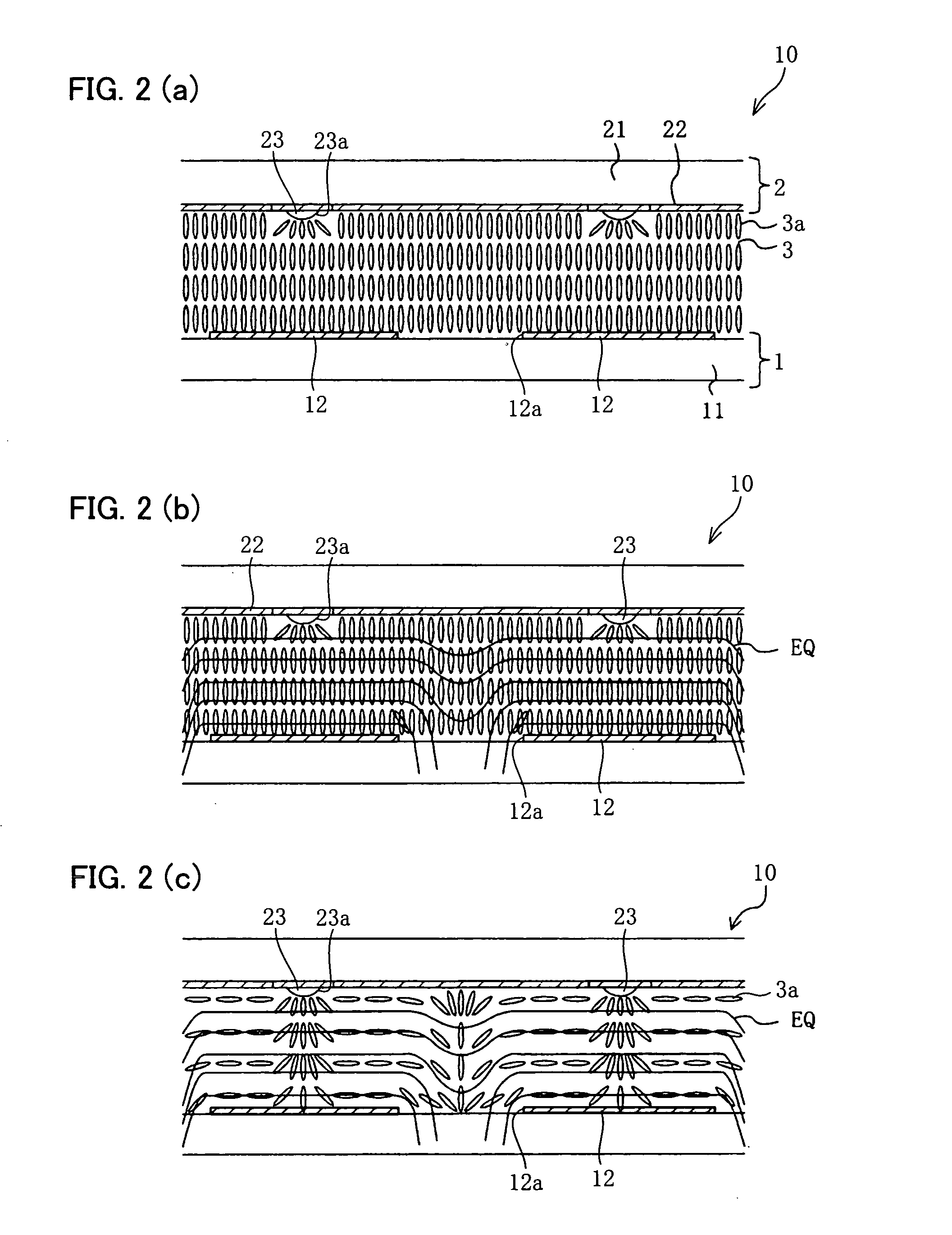
[0055] The following description deals with one embodiment of the present invention with reference to FIGS. 1 through 9. Note that, an active matrix type liquid crystal display device using a thin film transistor (TFT) is explained in the present embodiment. Moreover, a transmissive liquid crystal display device is explained as an example; however, the present invention is not limited to this and is also applicable to a reflective liquid crystal display device and a transflective liquid crystal display device. Furthermore, the present invention is applicable to a liquid crystal display device employing either a normally black mode or normally white mode.
[0056] Moreover, as used herein, the term “picture element region” is used to mean a region of the liquid crystal display device which corresponds to a “picture element,” which is a minimum unit of display. In a color liquid crystal display device, “picture elements” of R, G, and B correspond to a single “pixel.” In the active matri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com