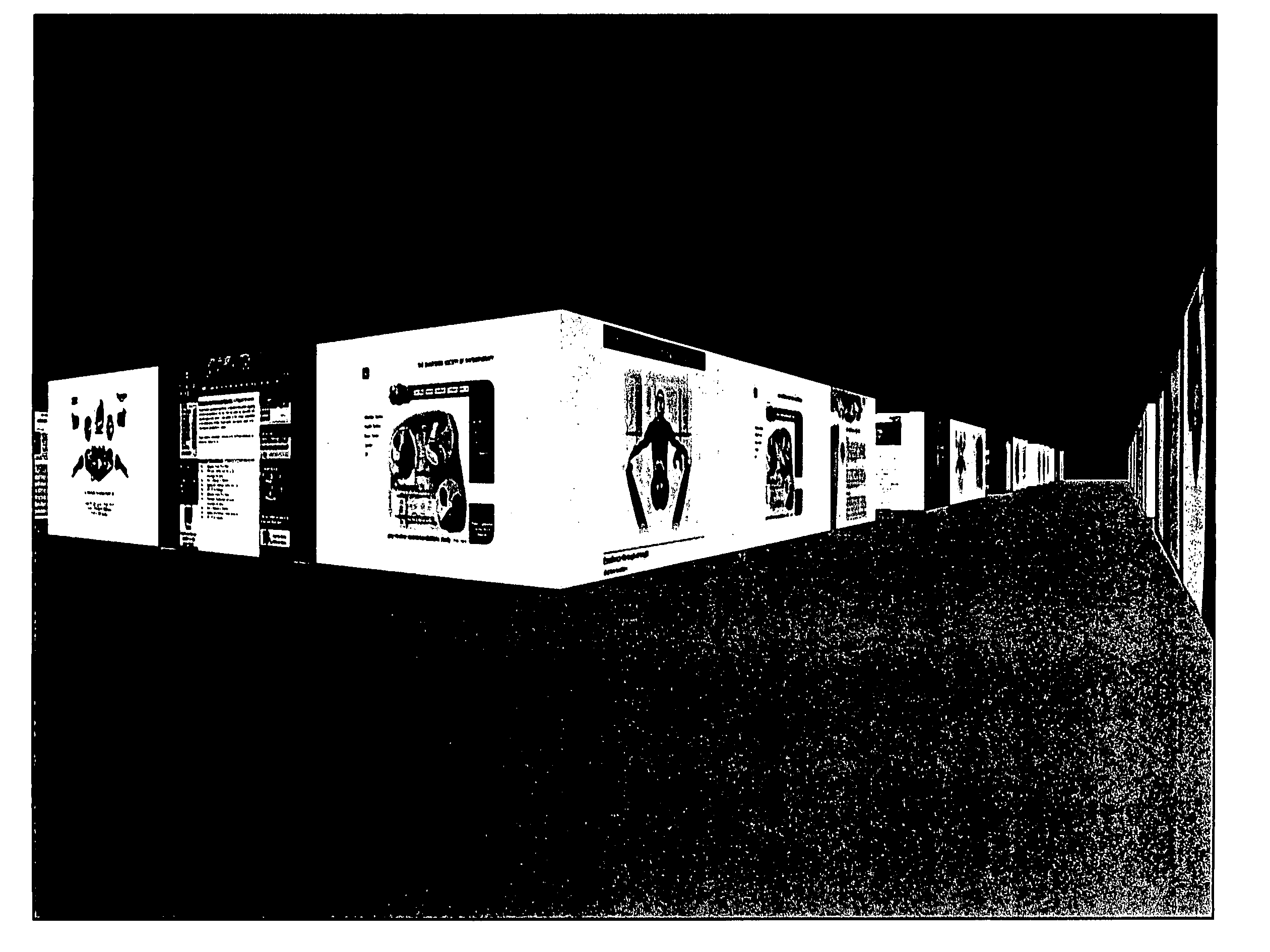
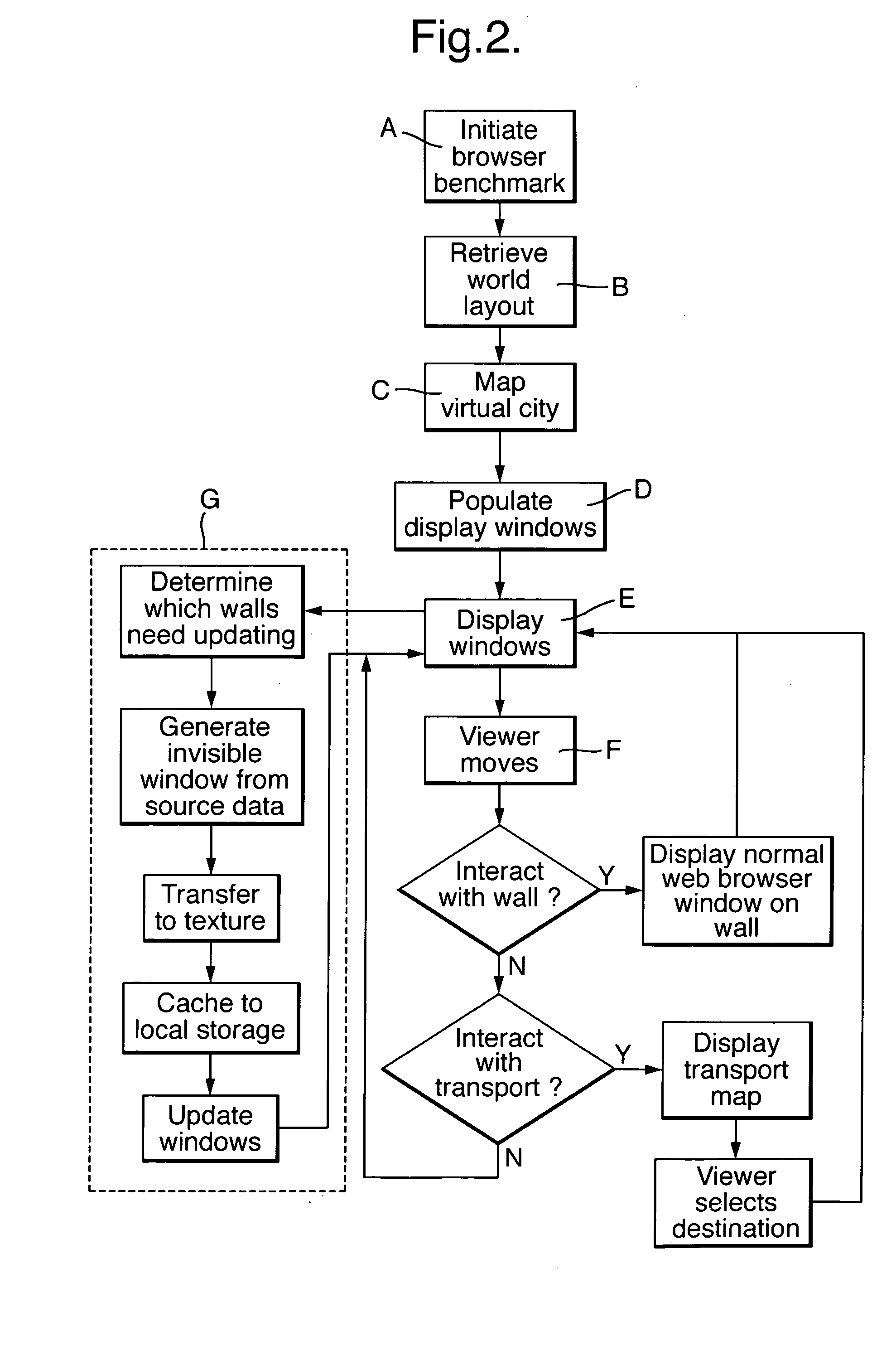
[0023] The present invention has advantages because it does not rely upon language and logic in browsing and navigating large volumes of content. Instead of relying upon language and logic, the invention makes it possible to indicate the relevance of content to a viewer by applying a rule of spatial proximity. Specifically, if content A is relevant to the viewer, and content B is similarly relevant, then A and B can be positioned near to one another, so that the viewer of content A is likely also to see content B with a minimum of navigation.
[0025] (1) The creation of a three-dimensional virtual space containing many display windows in fixed, specified positions,
[0027] (3) The operation of a self-organising allocation process in which content providers compete for the most beneficial display window positions for their content.
[0016] According to a second aspect of the present invention there is provided apparatus for organizing and presenting material content on a display to a viewer, the apparatus comprising: a display, means for mapping a plurality of display windows within a three-dimensional virtual space so that each display window is allocated a specific and predetermined position, means for rendering each display in three-dimensional perspective according to its position and angle relative to the viewer's position in the virtual space, means for cross referencing the position of each display window to the
network address or storage location of the material content that is designated to be rendered in that particular display window at a particular
time based on at least one predetermined condition, means for selecting, retrieving and preparing material content for possible subsequent display according to a predetermined
algorithm, means for selecting and rendering
prepared material content within its cross-referenced display window according to a predetermined algorithm, and means for navigation controlled by the viewer that changes the viewer's position in such a manner as to simulate movement through a plurality of predefined channels in the virtual space.
[0006] There is a desire amongst viewers accessing a large volume of material content to be able to browse and navigate the full set of content in order to find a subset or single unit of content which is relevant or interesting to the viewer. Currently such browsing and navigation is typically conducted by means of descriptive text typed into
search engine software and thereby matched to text contained in the material content itself or to text which a content provider has used to
label the content. Browsing and navigation is also sometimes aided by third-party content categorisers who provide directories and sub-directories of content labels and descriptions.
[0006] There is a desire amongst viewers accessing a large volume of material content to be able to browse and navigate the full set of content in order to find a subset or single unit of content which is relevant or interesting to the viewer. Currently such browsing and navigation is typically conducted by means of descriptive text typed into
search engine software and thereby matched to text contained in the material content itself or to text which a content provider has used to
label the content. Browsing and navigation is also sometimes aided by third-party content categorisers who provide directories and sub-directories of content labels and descriptions.
[0023] The present invention has advantages because it does not rely upon language and logic in browsing and navigating large volumes of content. Instead of relying upon language and logic, the invention makes it possible to indicate the relevance of content to a viewer by applying a rule of spatial proximity. Specifically, if content A is relevant to the viewer, and content B is similarly relevant, then A and B can be positioned near to one another, so that the viewer of content A is likely also to see content B with a minimum of navigation.
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More