Post-delubrication peening for forged powder metal components
a powder metal and peening technology, applied in the field of powder metal peening, can solve the problems of weakened components decarburization and oxide penetration, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing decarburization, oxide penetration and surface porosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
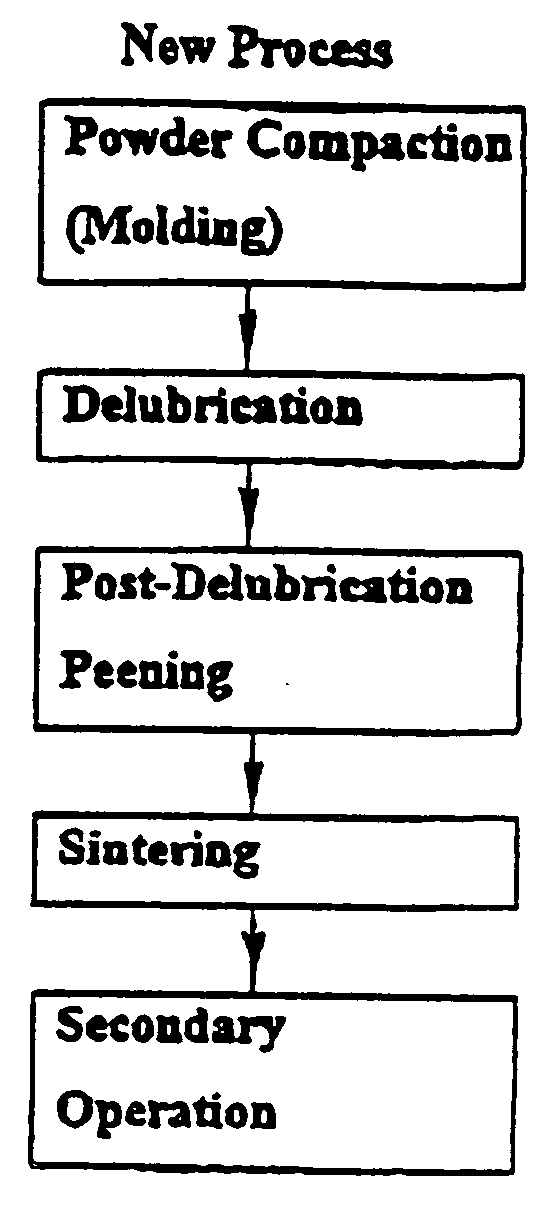
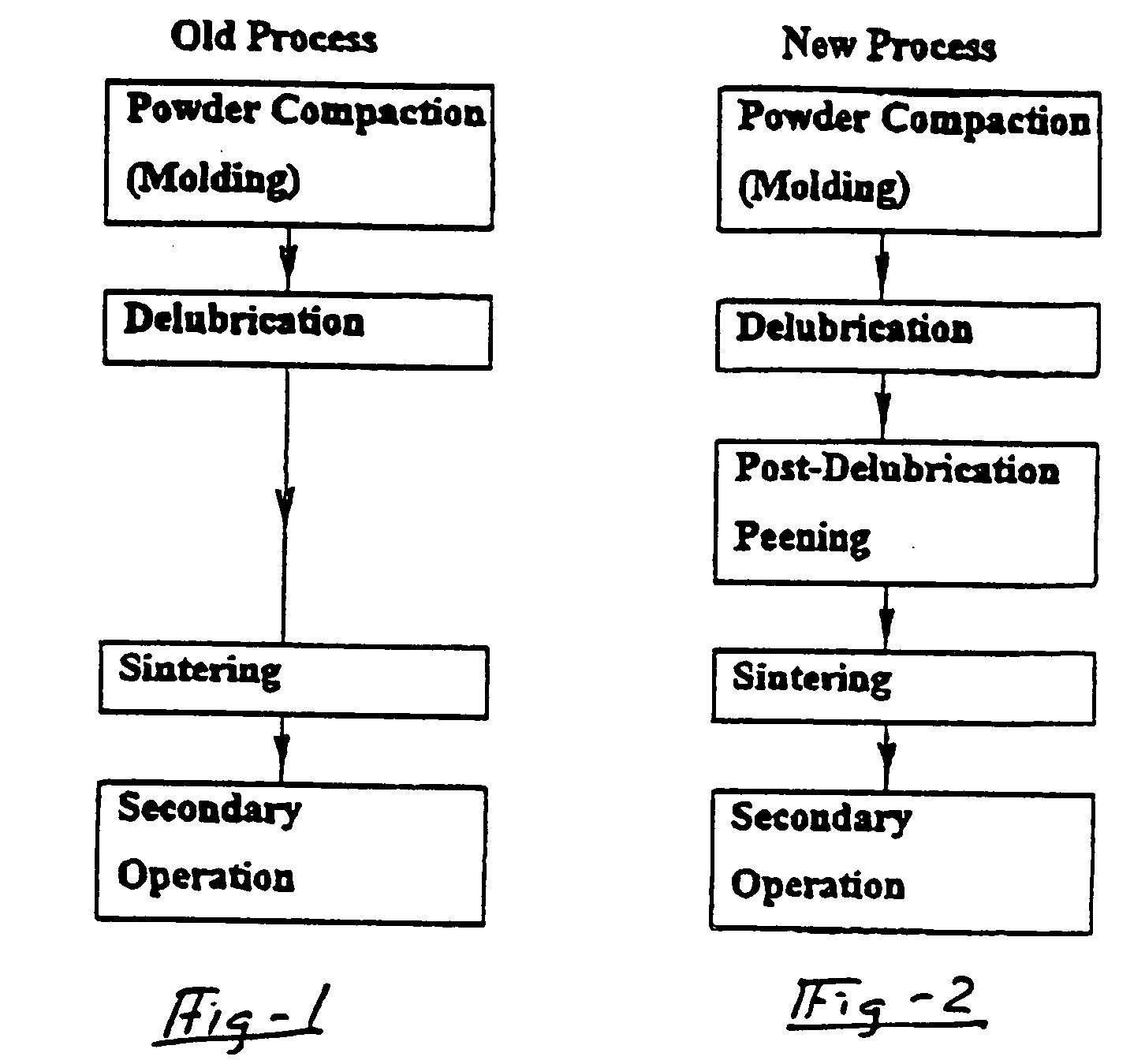
[0014] Referring first to FIGS. 1 and 2, there are shown flow charts for the prior known process 100 of forming a powder metal component and the new process 10 of the present invention. The process 10 can be used in the manufacture of a variety of powder metal components particularly where the strength and reliability of the component is critical. The present process was developed in connection with the manufacture of connecting rods for vehicle engines. The prior known process of sintering and forging powder metal components resulted in oxides trapped in the channels and pores of the preformed powder metal component which can cause fatigue and stress cracks in the component.
[0015] The process of the present invention begins with compaction or molding 12 of powder metal material into a preform configuration. The molding process 12 utilizes a lubricant to facilitate the molding process. The next step involves delubrication 14 of the perform. In a preferred embodiment of the process, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| shot speed | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com