Face description, recognition method and device
A descriptor and facial image technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, computer components, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of AFR descriptor extraction complexity, achieve the effect of improving recognition or identification performance and reducing extraction complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
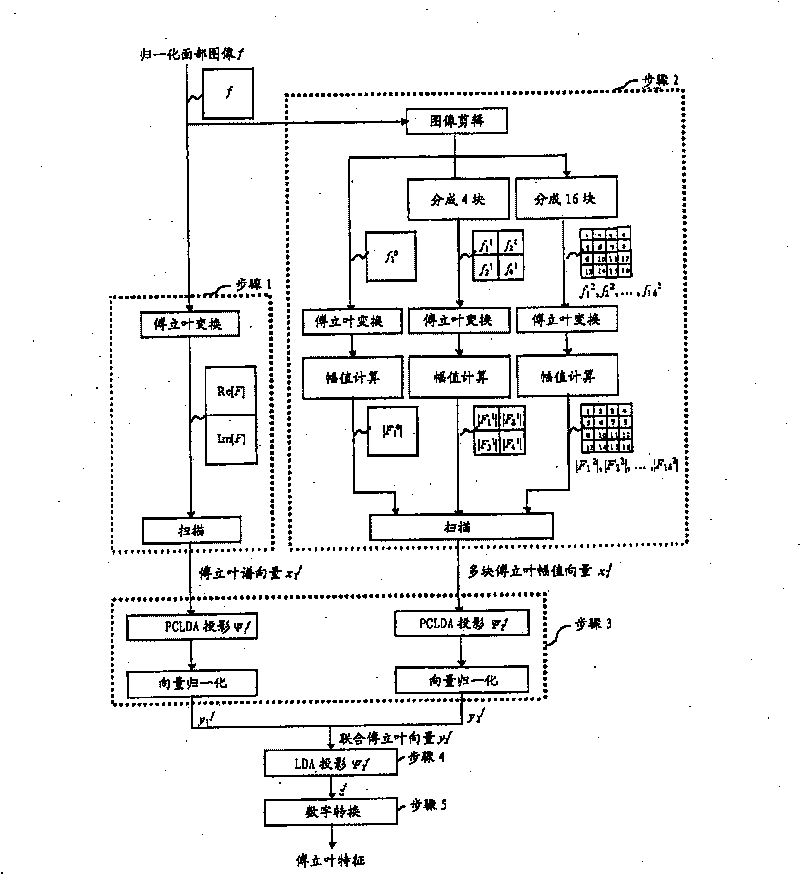
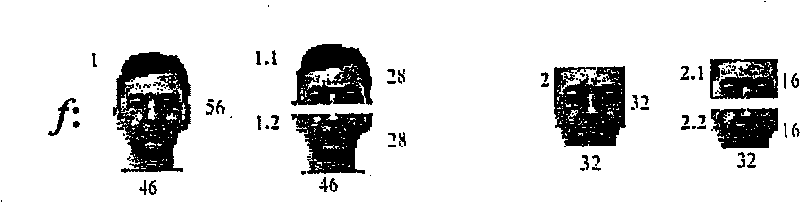
[0052] Table 1 explains the block symbols in the figure. The basic components are: Fourier transform (T, F); eigenvector transform (discriminant transform) (D) in the form of a linear map (specifically Dual-LDA); normalization (N) and digital transformation (Q). As seen in the block diagram of the structure, there are only 6 input images compared to the 42 images used for feature extraction in the Fourier domain part of AFR: f 1 , f 1,1 , f 1,2 , f 2 , f 2,1 , f 2,2 . figure 2 These images used in the preferred embodiment are shown in and described below. Note that the proposed scheme uses a 3-level discriminative structure, and Fourier facial features are extracted from the overall and central image regions combined in the final level DLDA map.
[0053] Although only at the initial discriminative level ( Figure 9 ) shows normalization, but normalization can also be performed in subsequent discriminative stages.
[0054] Table 1 - Block Symbols
[0055]
[0056]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com