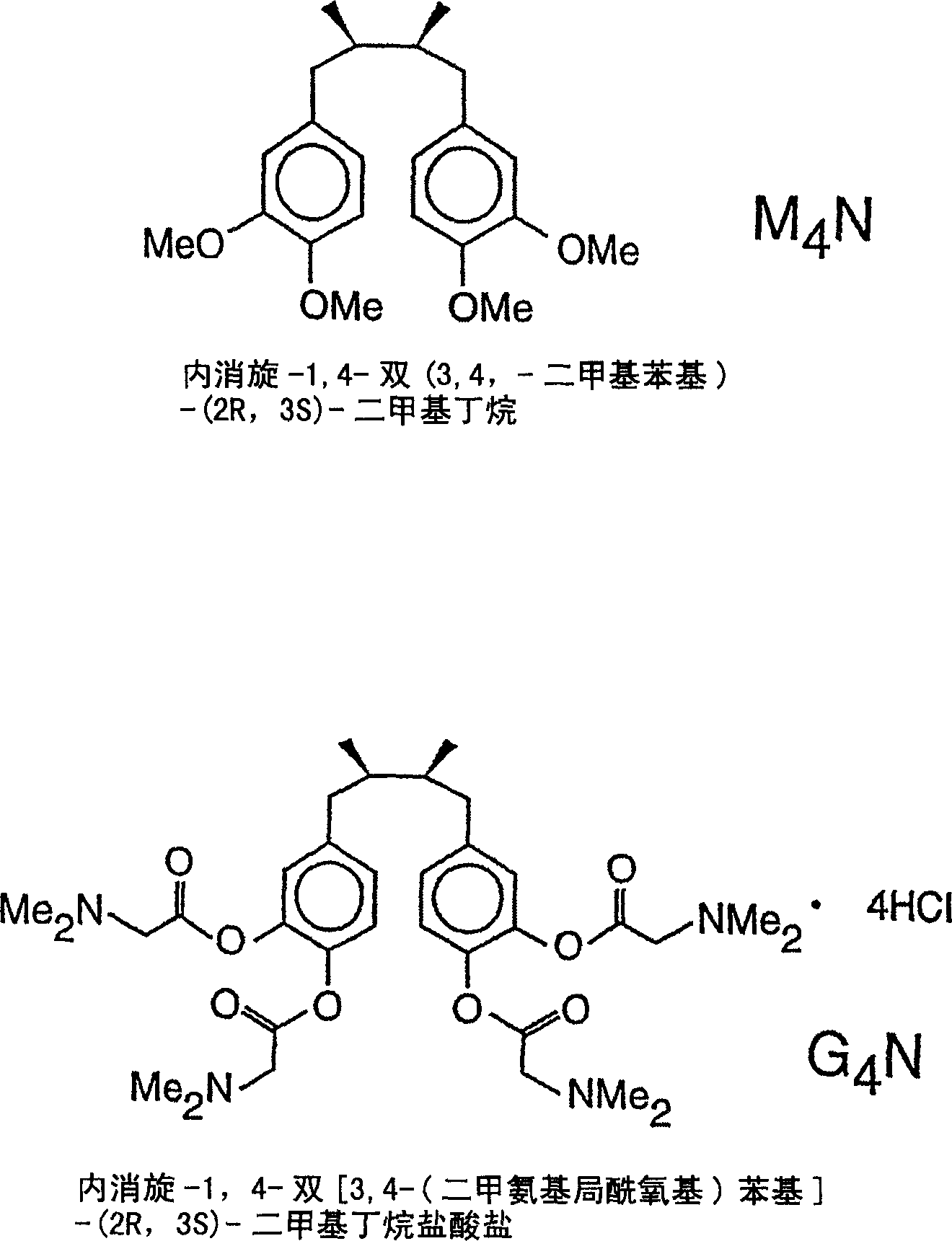
Method for regulation of gene expression in eukaryotic cells using nordihydroguaiaretic acid derivatives
一种肿瘤、氨基酸的技术,应用在抗肿瘤药、药物组合、医药配方等方向,能够解决加快细胞凋亡和死亡的速度等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
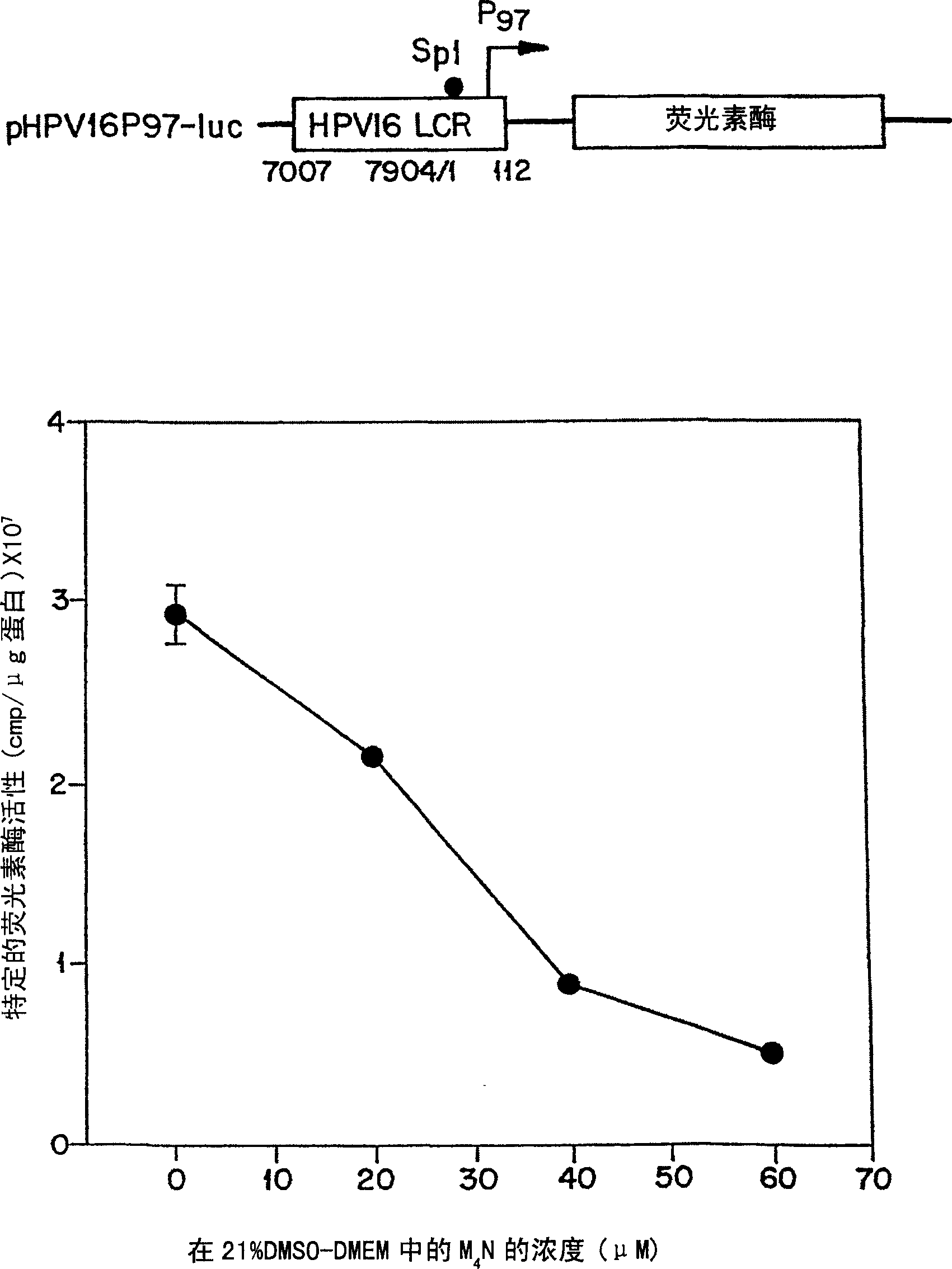
[0067] m 4 N and several other NDGA derivatives contribute to SP1-regulated E 6 / E 7 effect on promoter activity.
[0068] m 4 N and several other NDGA derivatives contribute to SP1-regulated E 6 / E 7 The effect on promoter activity was detected using luciferase as a reporter. In this test method, the HPV16LCR (P 97 ) DNA was transfected into C33A cells. C33A is a cervical tumor cell line (ATCC accession number HTB-31 ) that does not contain any integrated HPV DNA, but possesses transcription factors necessary for strong expression of HPV early gene promoters. On the second day of DNA transfection, drugs of different concentrations formulated in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) were added to the cells. Thirty hours after drug treatment (to allow testing to be completed within 48 hours of the standard transient transfection assay), cells were lysed and specific luciferase activity was determined (Luciferase AssaySystems, Promega, U.S. Pat. No. 5283, 179 ). With M 4 Specific...
Embodiment 2
[0071] use M 4 E after N treatment 6 / E 7 Inhibition of mRNA synthesis
[0072] use M 4 E after N treatment 6 / E 7 Inhibition of mRNA synthesis was achieved by the cervical cell line C 3 RT-PCR in the test. Correlative RT-PCR was performed based on total cellular RNA amounts normalized to cell counts. The RT-PCR product was analyzed on 2% agarose gel, and the results are shown in FIG. 3 . RT-PCR results showed that amplified cDNAs with the expected size of E7 (321 bp) and E6 (204 bp) were detected at cycle 22 in DMSO-treated cells. Such products were barely detectable in drug-treated RNA extracts amplified for 30 cycles. No amplified product was detected in the total RNA extracts for the no-template PCR control or the HPV16-negative C33a cell line.
Embodiment 3
[0074] by M 4 N treatment inhibited the growth of cervical C3 cells
[0075] Immortal mouse epidermal cells (C3 cells) transfected with HPV16 were placed in vials so that each bottle contained 10 5 cells. After 24 hours, half of the vials were given growth matrix containing 40 μM M in 1% DMSO 4 N, while the other half was given a growth substrate containing only 1% DMSO. see results Figure 4A . Within 24 hours, the cell morphology of drug-treated C3 cells and control C3 cells showed differences. Drug-treated cells grew and divided significantly less than non-drug-treated control cells, while the ratio fraction of viable cells to total counted cells remained unchanged for drug-treated and DMSO-only control cells. This shows that M 4 N can significantly reduce cell differentiation.
[0076] Will M 4 The effect of N on the growth of C3 cells after removal from the matrix was also examined. C3 cells were placed in vials so that each vial contained 10 4 cells. At time ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com