Method for vreeding transgenic antifungal rape with specificities of dual genes being expresses
An anti-fungal and transgenic technology, applied in genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, botanical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of low efficiency of transgenic technology, weak disease resistance of single-gene transformation of rapeseed, and large energy consumption, etc. To achieve the effect of reducing physiological disturbance, reducing energy consumption and improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: Construction of organ and development-specific expression double-gene vector ApSCO
[0029] 1.1 with SAG 12 The construction of the intermediate vector pSPCHiN of promoter, chitinase gene and cell membrane guiding peptide gene:
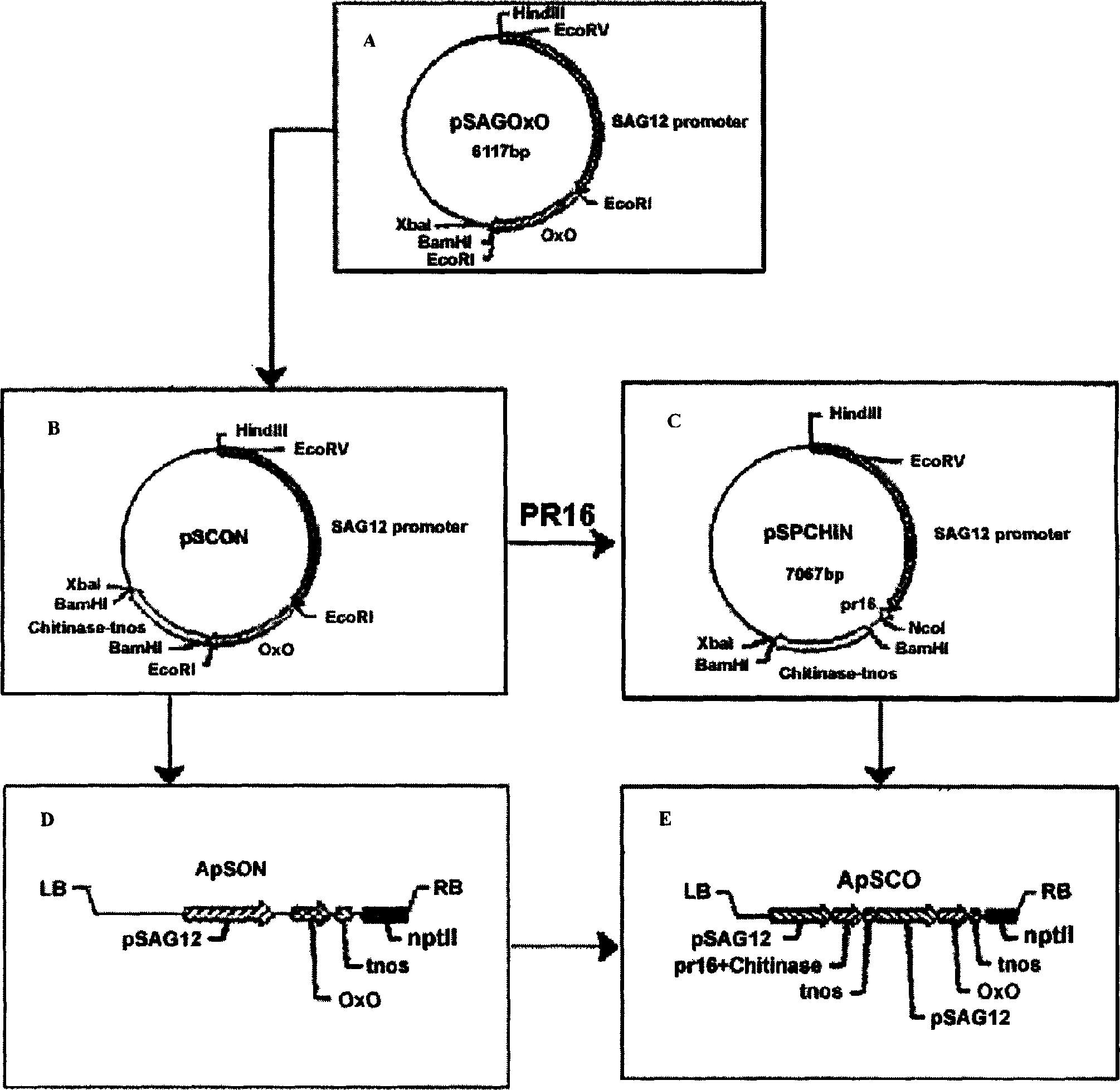
[0030] Double digestion of Arabidopsis leaf senescence promoter SAG with EcoRV and NcoI 12 After the plasmid vector pSG449, the 1.3kb fragment was recovered by electrophoresis, filled in with the Klenow fragment, and inserted into the EcoRV site of the barley oxalate oxidase gene vector pHvOxOa to obtain the recombinant plasmid pSAGOxO (see attached figure 1 A). The plasmid vector pHGC39 containing chitinase gene and glucanase gene was digested with BamHI, and the 1.4kb fragment containing chitinase gene and nos terminator was recovered and inserted into the BamHI site of pSAGOxO to obtain a recombinant plasmid pSOCN (see attached figure 1 B). The vector pSOCHiN containing the oxalate oxidase gene was digested with EcoRI, and th...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2: Transform Brassica napus with living transformation method (in planta)
[0036] Take 100 μl of Agrobacterium containing the carrier ApSCO cryopreserved in glycerol, inoculate it in 10 ml of fresh LB (1% peptone, 0.5% yeast extract, 1% NaCl, pH7.0) culture medium, shake at 150 rpm at 28°C overnight . Inoculate 10ml of the above culture into 1L containing 50mg·L -1 In the LB medium of kanamycin, shake culture at 150 rpm at 28°C for more than 24 hours until OD 660 = 1-1.5.
[0037] The cultured Agrobacterium suspension was centrifuged at 8000 g for 8 minutes, and the precipitated Agrobacterium was resuspended with 1 liter of fresh LB medium. In the experiment, the rapeseed inflorescences were directly dipped with the Agrobacterium suspension. Before dipping, make sure that there is no dew and soil on the flowers, and then select those branches whose flowers are about to open, and cut off the flowers that have already opened on the branches. When dipping, ...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3: Screening and Molecular Biological Identification of Transgenic Rapeseed Plants
[0041] 3.1 Kanamycin selection in vivo transformation method (in planta) to treat seeds
[0042] Select the plump ones from the seeds treated with in planta, soak them in 0.1% mercuric chloride for 12 to 15 minutes, wash them with sterile water three times, and sprinkle them evenly on seeds containing kanamycin 270 mg·L -1 MS solid medium (see Murashige T and Skoog F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco issue culture., 1962, Physiologia Plantarum 15: 473-497). Four to five days later, the germinated seedlings with the exogenous gene transferred had kanamycin resistance and could survive normally; the seedlings without the exogenous gene did not have kanamycin resistance, and the edges of the cotyledons were browned, White spots appear on the surface of the cotyledon and the first true leaf, the petiole turns purple and red, and eventually dies. The sur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com