Method of inactivating pathogens
A pathogen and inactivation technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, botanical equipment and methods, antiviral agents, etc., to achieve the effect of reliable preparation, less harmful reactions or by-products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Embodiment 1
[0088] Example Example 1. Synthesis, purification and analysis of iodoacetaldehyde (IAA) A. Synthesis of IAA
[0089] Iodoacetaldehyde (IAA) was synthesized using the method of Glinsky G, Z CHEM, 618 (1868), modified in several places. 2mmol of chloroacetaldehyde (45% in water, 6.9M) was diluted to 0.29M in 7ml of acetone. Sodium iodide (2 mmol) was added and mixed, and the mixture was incubated at room temperature for 18 hours. The reaction mixture was filtered to remove solid material, and 5.5 ml of the filtrate was diluted 5-fold with water. To remove unreacted iodide and iodine, the diluted sample was passed through an 8.5 ml DEAE-Sephadex column (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech AB, Uppsala, Sweden) swollen with 20% acetone at 5 ml / min. The first 7 ml of eluate was discarded and the remaining eluate was collected. The column was washed with 5 ml of 20% acetone and the eluate was added to the collected pool. B. Purification of Synthetic IAA
[0090]...
Embodiment 2
[0091] One-dimensional recording with Bruker DRX 500 spectrometer at 40°C 1 H-NMR spectrum. The TSP signal is used as an internal reference (δ H = 0.0 ppm). By adding 50 μl of reverse chromatography (RPC) purified solution to 650 μL D 2 O, and then transfer the diluted sample to a 5 mm NMR tube to prepare the sample. For quantitative detection, a sodium trimethylsilylpropionate (TSP, 0.991 mg / ml) solution was prepared; and 10 μl of this solution was added to the sample. By comparing the accumulation of methyl groups in TSP and CH2 groups in hydrated IAA, the concentration of IAA in the sample can be estimated. Iodoacetaldehyde is in equilibrium with its hydrated form in aqueous solution. Estimates based on NMR were that the hydrated form accounted for about 90% of the sample, while the acetaldehyde form accounted for about 10%. This balance should be considered when calculating IAA concentrations in aqueous media. Example 2 Viruses of Iodoacetaldehyde (IAA) in the Prese...
Embodiment 3
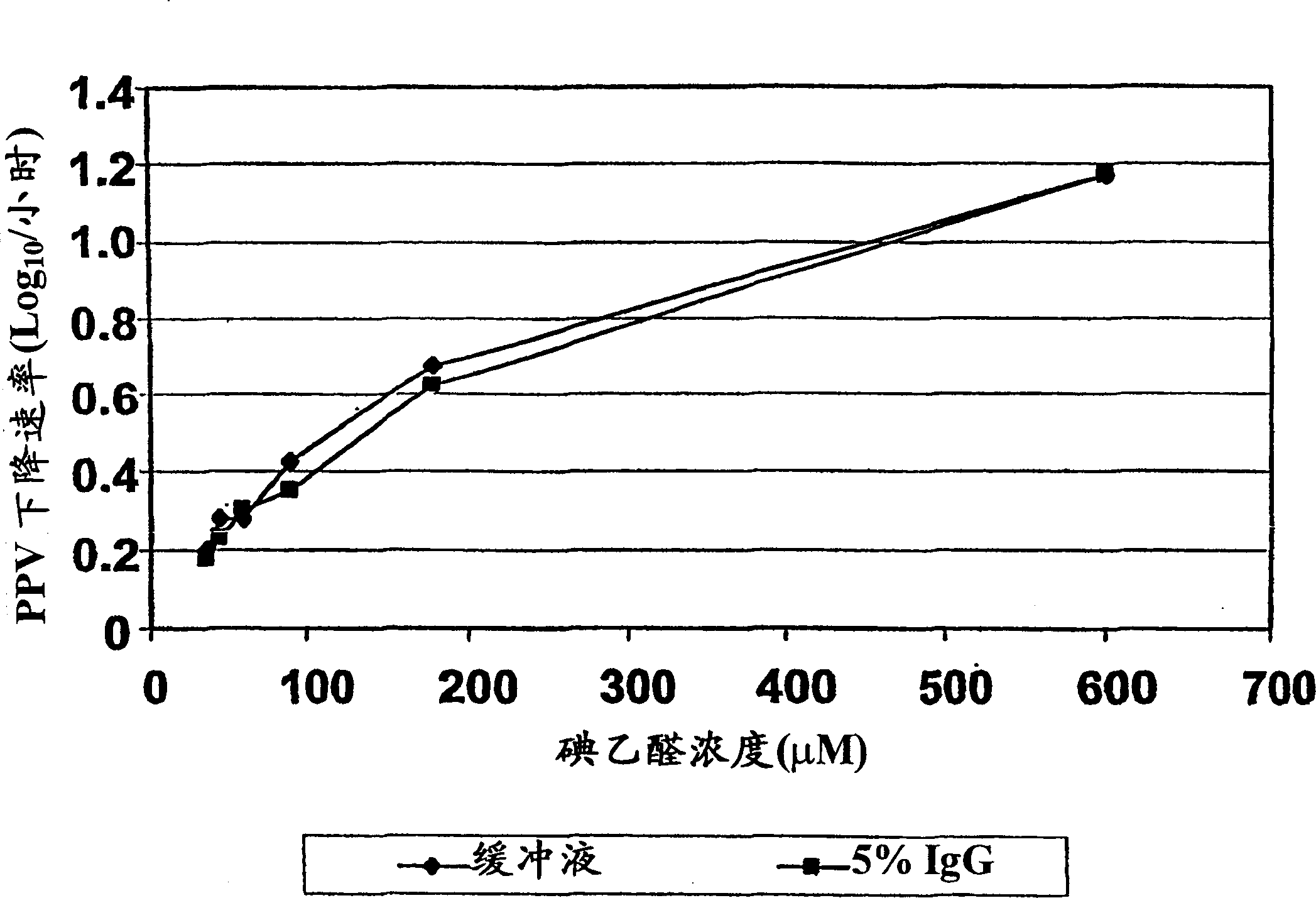
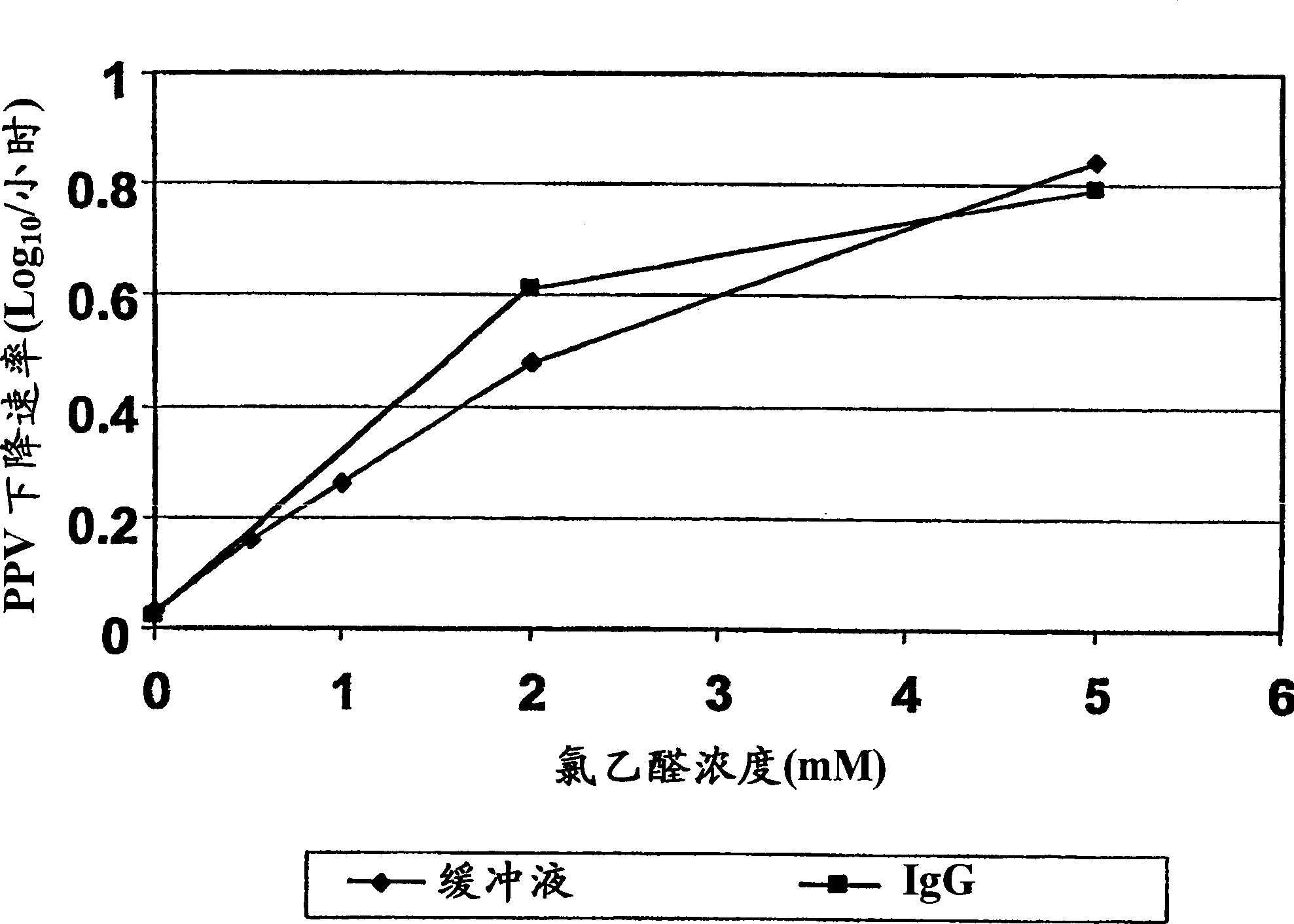
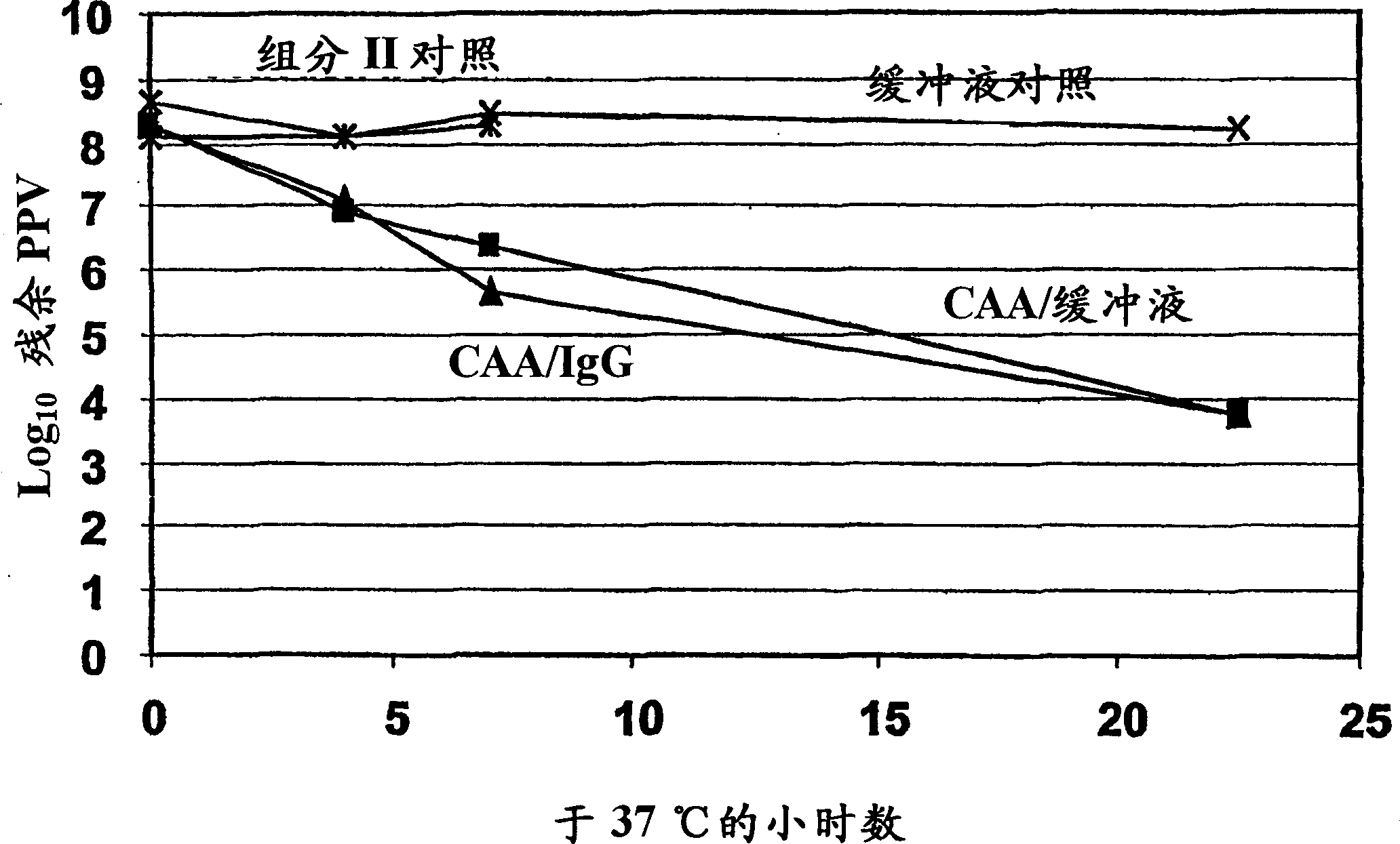
[0106] This experiment demonstrates the potential virus inactivating ability of iodoacetaldehyde. At concentrations of 180-600 [mu]M, IAA rapidly inactivates porcine parvovirus, one of the most potent viruses of the non-enveloped virus class. IAA is expected to inactivate poorly adapted viruses equivalent to or exceed inactivation of PPV. Importantly, the rate of PPV inactivation was found to be equal in the presence and absence of IgG. At 5% protein, the IgG molarity is approximately 320 [mu]M. The highest concentration of IAA (600 μM) was less than 2-fold the molar concentration of the protein, while the second highest concentration of IAA (180 μM) was only about half of the molar concentration of the protein. Any reaction of IAA with even a small fraction of the protein molecule Both should consume most of the IAA, making it ineffective against inactivated virus. This is strong evidence that IAA is not consumed by the protein and does not react with the protein. It also s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com