Power distribution network single-phase earth fault positioning method and device based on zero-sequence current continuous adjustment, and readable storage medium
A zero-sequence current, distribution network technology, applied in the field of distribution network, to achieve the effect of amplifying fault characteristics, accurate positioning, and wide application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
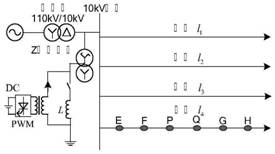
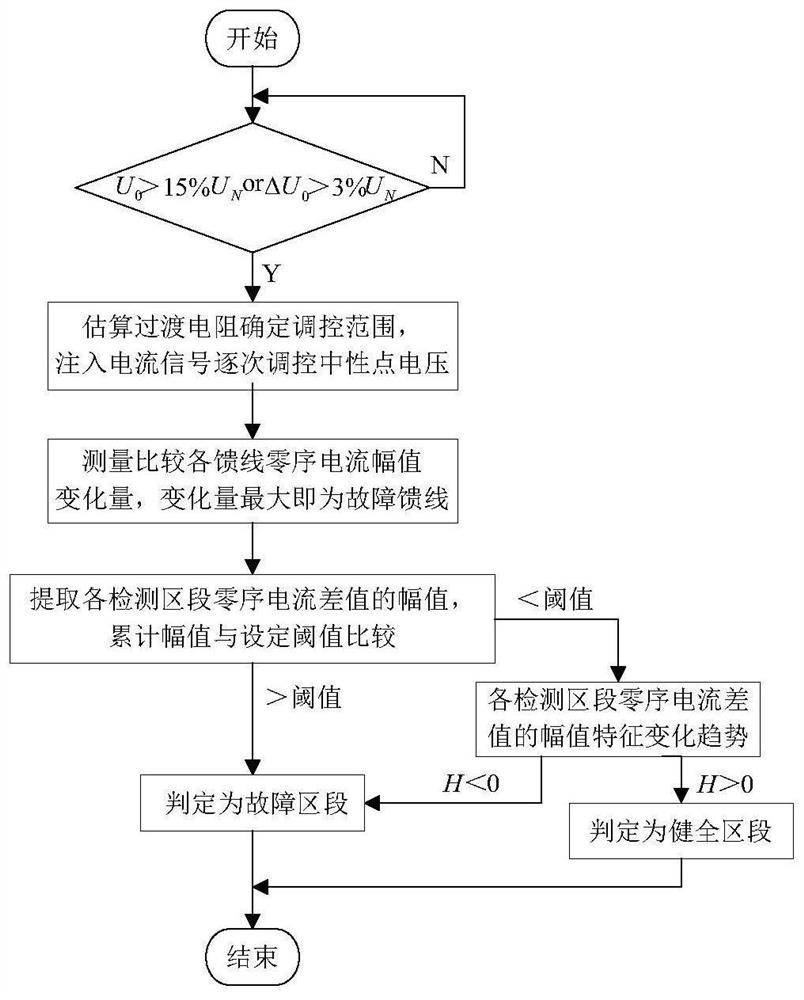
[0127] The method for locating a single-phase-to-ground fault in a distribution network based on the continuous adjustment of zero-sequence current provided by this embodiment is based on the theoretical elaboration of the above third part. When applied to fault feeder location, the method includes the following steps:
[0128] The injected current signal regulates the neutral point voltage successively, and collects the zero-sequence current on each feeder after each regulation;
[0129] Calculate the variation of the zero-sequence current amplitude of each feeder;
[0130] Among them, the feeder with the largest variation is the faulty feeder.
[0131] It should be noted that, when adjusting the neutral point voltage successively, it is preferable to adjust according to the aforementioned adjustment range determined by the transition resistance. Furthermore, the present invention can realize the identification of the faulty feeder and the faulty section under the adjustment,...
Embodiment 2
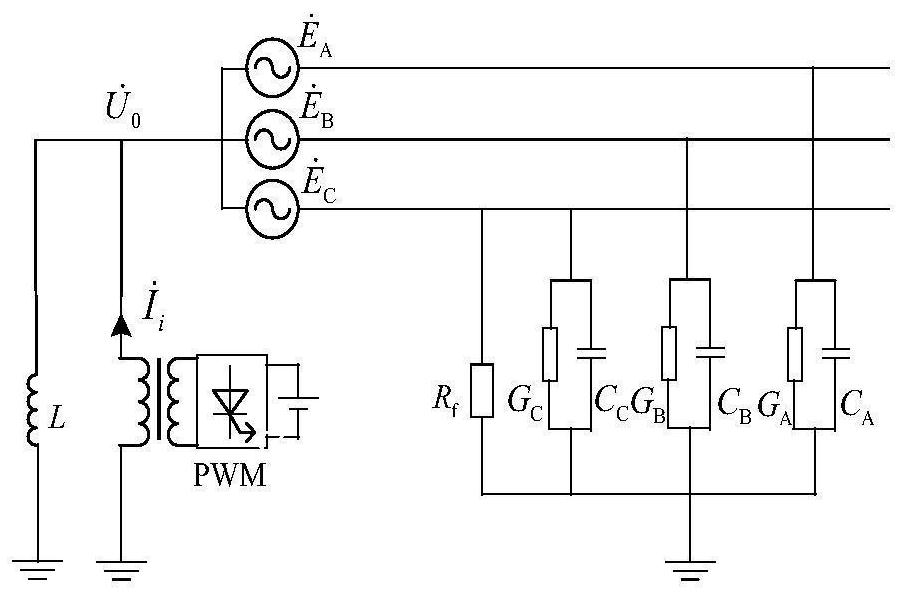
[0141] The present invention provides a method for locating a single-phase grounding fault in a distribution network based on continuous adjustment of zero-sequence current, in which the faulty feeder is known (the faulty feeder can be determined in the manner of Embodiment 1 or the faulty feeder can be determined in other ways), and the known faulty feeder Identify the faulted section on the faulted feeder and apply it to the faulted section location of the faulted feeder, and when it is a non-high-resistance grounding fault, the following steps are also included:
[0142] The injected current regulates the neutral point voltage successively, and collects the zero-sequence currents at both ends of each section on the faulty feeder after each regulation and calculates the magnitude of the difference between the zero-sequence currents at both ends of each section;
[0143] Then calculate the cumulative amplitude of each section based on the amplitude of the zero-sequence current...
Embodiment 3
[0146] The present invention provides a method for locating a single-phase grounding fault in a distribution network based on continuous adjustment of zero-sequence current. The faulted feeder is known, and the faulted section is identified on the known faulted feeder, which is applied to the faulted section location of the faulted feeder. , and is applicable to non-high-resistance ground faults and high-resistance ground faults, and also includes the following steps:
[0147] The injected current regulates the neutral point voltage successively, and collects the zero-sequence currents at both ends of each section on the faulty feeder after each regulation and calculates the magnitude of the difference between the zero-sequence currents at both ends of each section;
[0148] Based on the amplitude of the zero-sequence current difference obtained by each section in each regulation, calculate the cumulative amplitude of each section and identify the amplitude variation trend of e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com